
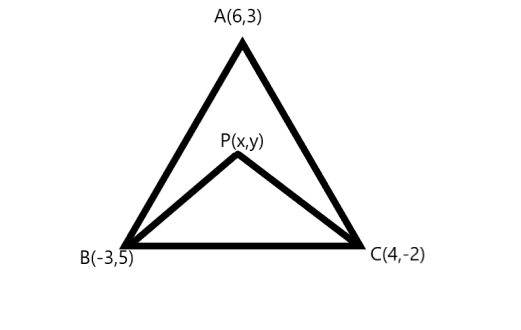
The coordinates of A, B, C are \[(6,3),( - 3,5),(4, - 2)\], respectively, and P is any point \[(x,y)\]. Show that the ratio of the area of \[\Delta PBC\]to that of\[\Delta ABC\] is \[\dfrac{{(x + y - 2)}}{7}\].
Answer
586.8k+ views
Hint: As all the three coordinates of triangle is known so to calculate the area of both the triangles, we use determinant method as \[\Delta = \left| {\dfrac{1}{2}\left| {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
{{x_1}}&{{y_1}}&1 \\
{{x_2}}&{{y_2}}&1 \\
{{x_3}}&{{y_3}}&1
\end{array}} \right|} \right|\]and hence, take the ratios of both the triangles it will be our required answer.
Complete step-by-step answer:
As the coordinates of \[\Delta ABC\]are \[A\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right) = \left( {6,3} \right)\],\[B\left( {{x_2},{y_2}} \right) = \left( { - 3,5} \right)\]and \[C\left( {{x_3},{y_3}} \right) = \left( {4, - 2} \right)\].
To, calculate the area of both the triangles we use determinant method as \[\Delta = \left| {\dfrac{1}{2}\left| {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
{{x_1}}&{{y_1}}&1 \\
{{x_2}}&{{y_2}}&1 \\
{{x_3}}&{{y_3}}&1
\end{array}} \right|} \right|\]
So calculating the area of \[\Delta ABC\], we substitute the values \[A\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right) = \left( {6,3} \right)\],\[B\left( {{x_2},{y_2}} \right) = \left( { - 3,5} \right)\]and \[C\left( {{x_3},{y_3}} \right) = \left( {4, - 2} \right)\]in the above formula, we get,
\[ \Rightarrow \]\[\Delta ABC = \left| {\dfrac{1}{2}\left| {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
6&3&1 \\
{ - 3}&5&1 \\
4&{ - 2}&1
\end{array}} \right|} \right|\]
On expanding the determinant, we get,
\[ \Rightarrow \]\[\Delta ABC = \left| {\dfrac{1}{2}\left( {6\left( {5 + 2} \right) - 3\left( { - 3 - 4} \right) + 1\left( {6 - 20} \right)} \right)} \right|\]
On simplifying further, we get,
\[ \Rightarrow \]\[\Delta ABC = \left| {\dfrac{1}{2}\left( {42 + 21 - 14} \right)} \right|\]
On solving the bracket, we get,
\[ \Rightarrow \]\[\Delta ABC = \left| {\dfrac{1}{2}\left( {49} \right)} \right|\]
Hence, the area of \[\Delta ABC = \dfrac{{49}}{2}\].
Now, calculating the area of \[\Delta PBC\]using the determinant method as,
\[\Delta = \left| {\dfrac{1}{2}\left| {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
{{x_1}}&{{y_1}}&1 \\
{{x_2}}&{{y_2}}&1 \\
{{x_3}}&{{y_3}}&1
\end{array}} \right|} \right|\]
On substituting the values of P\[(x,y)\],\[B\left( {{x_2},{y_2}} \right) = \left( { - 3,5} \right)\]and \[C\left( {{x_3},{y_3}} \right) = \left( {4, - 2} \right)\], we get,
\[ \Rightarrow \]\[\Delta PBC = \left| {\dfrac{1}{2}\left| {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
x&y&1 \\
{ - 3}&5&1 \\
4&{ - 2}&1
\end{array}} \right|} \right|\]
On expanding the above determinant, we get,
\[ \Rightarrow \]\[\Delta PBC = \left| {\dfrac{1}{2}\left( {x\left( {5 + 2} \right) - y\left( { - 3 - 4} \right) + 1\left( {6 - 20} \right)} \right)} \right|\]
On simplifying further, we get,
\[ \Rightarrow \]\[\Delta PBC = \left| {\dfrac{1}{2}\left( {7x + 7y - 14} \right)} \right|\]
\[ \Rightarrow \]\[\Delta PBC = \dfrac{{7x + 7y - 14}}{2}\]
Hence, as we have to find the ratio of area of \[\dfrac{{\Delta PBC}}{{\Delta ABC}}\]
Hence, on putting the above calculated value we can simplify as,
\[\dfrac{{\Delta PBC}}{{\Delta ABC}} = \dfrac{{\dfrac{{7x + 7y - 14}}{2}}}{{\dfrac{1}{2}\left( {49} \right)}}\]
Hence, on cancelling the common terms out, we get,
\[ = \dfrac{{7x + 7y - 14}}{{\left( {49} \right)}}\]
Now, take 7 common from numerator,
\[ = \dfrac{{7(x + y - 2)}}{{\left( {49} \right)}}\]
Cancel \[7\]from both numerator and denominator,
\[\dfrac{{\Delta PBC}}{{\Delta ABC}} = \dfrac{{(x + y - 2)}}{7}\]
Hence proved.
Note: Remember the concept to calculate the area of triangle using determinant method as \[\Delta = \left| {\dfrac{1}{2}\left| {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
{{x_1}}&{{y_1}}&1 \\
{{x_2}}&{{y_2}}&1 \\
{{x_3}}&{{y_3}}&1
\end{array}} \right|} \right|\]. Hence, expand the determinant carefully and then finally take their ratios.
Area of Triangle Formula Using Determinants
Since the area is a positive quantity, we always take the absolute value of the determinant in (1).
If the area is given, use both positive and negative values of the determinant for calculation.
The area of the triangle formed by three collinear points is zero.
{{x_1}}&{{y_1}}&1 \\
{{x_2}}&{{y_2}}&1 \\
{{x_3}}&{{y_3}}&1
\end{array}} \right|} \right|\]and hence, take the ratios of both the triangles it will be our required answer.
Complete step-by-step answer:
As the coordinates of \[\Delta ABC\]are \[A\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right) = \left( {6,3} \right)\],\[B\left( {{x_2},{y_2}} \right) = \left( { - 3,5} \right)\]and \[C\left( {{x_3},{y_3}} \right) = \left( {4, - 2} \right)\].

To, calculate the area of both the triangles we use determinant method as \[\Delta = \left| {\dfrac{1}{2}\left| {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
{{x_1}}&{{y_1}}&1 \\
{{x_2}}&{{y_2}}&1 \\
{{x_3}}&{{y_3}}&1
\end{array}} \right|} \right|\]
So calculating the area of \[\Delta ABC\], we substitute the values \[A\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right) = \left( {6,3} \right)\],\[B\left( {{x_2},{y_2}} \right) = \left( { - 3,5} \right)\]and \[C\left( {{x_3},{y_3}} \right) = \left( {4, - 2} \right)\]in the above formula, we get,
\[ \Rightarrow \]\[\Delta ABC = \left| {\dfrac{1}{2}\left| {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
6&3&1 \\
{ - 3}&5&1 \\
4&{ - 2}&1
\end{array}} \right|} \right|\]
On expanding the determinant, we get,
\[ \Rightarrow \]\[\Delta ABC = \left| {\dfrac{1}{2}\left( {6\left( {5 + 2} \right) - 3\left( { - 3 - 4} \right) + 1\left( {6 - 20} \right)} \right)} \right|\]
On simplifying further, we get,
\[ \Rightarrow \]\[\Delta ABC = \left| {\dfrac{1}{2}\left( {42 + 21 - 14} \right)} \right|\]
On solving the bracket, we get,
\[ \Rightarrow \]\[\Delta ABC = \left| {\dfrac{1}{2}\left( {49} \right)} \right|\]
Hence, the area of \[\Delta ABC = \dfrac{{49}}{2}\].
Now, calculating the area of \[\Delta PBC\]using the determinant method as,
\[\Delta = \left| {\dfrac{1}{2}\left| {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
{{x_1}}&{{y_1}}&1 \\
{{x_2}}&{{y_2}}&1 \\
{{x_3}}&{{y_3}}&1
\end{array}} \right|} \right|\]
On substituting the values of P\[(x,y)\],\[B\left( {{x_2},{y_2}} \right) = \left( { - 3,5} \right)\]and \[C\left( {{x_3},{y_3}} \right) = \left( {4, - 2} \right)\], we get,
\[ \Rightarrow \]\[\Delta PBC = \left| {\dfrac{1}{2}\left| {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
x&y&1 \\
{ - 3}&5&1 \\
4&{ - 2}&1
\end{array}} \right|} \right|\]
On expanding the above determinant, we get,
\[ \Rightarrow \]\[\Delta PBC = \left| {\dfrac{1}{2}\left( {x\left( {5 + 2} \right) - y\left( { - 3 - 4} \right) + 1\left( {6 - 20} \right)} \right)} \right|\]
On simplifying further, we get,
\[ \Rightarrow \]\[\Delta PBC = \left| {\dfrac{1}{2}\left( {7x + 7y - 14} \right)} \right|\]
\[ \Rightarrow \]\[\Delta PBC = \dfrac{{7x + 7y - 14}}{2}\]
Hence, as we have to find the ratio of area of \[\dfrac{{\Delta PBC}}{{\Delta ABC}}\]
Hence, on putting the above calculated value we can simplify as,
\[\dfrac{{\Delta PBC}}{{\Delta ABC}} = \dfrac{{\dfrac{{7x + 7y - 14}}{2}}}{{\dfrac{1}{2}\left( {49} \right)}}\]
Hence, on cancelling the common terms out, we get,
\[ = \dfrac{{7x + 7y - 14}}{{\left( {49} \right)}}\]
Now, take 7 common from numerator,
\[ = \dfrac{{7(x + y - 2)}}{{\left( {49} \right)}}\]
Cancel \[7\]from both numerator and denominator,
\[\dfrac{{\Delta PBC}}{{\Delta ABC}} = \dfrac{{(x + y - 2)}}{7}\]
Hence proved.
Note: Remember the concept to calculate the area of triangle using determinant method as \[\Delta = \left| {\dfrac{1}{2}\left| {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
{{x_1}}&{{y_1}}&1 \\
{{x_2}}&{{y_2}}&1 \\
{{x_3}}&{{y_3}}&1
\end{array}} \right|} \right|\]. Hence, expand the determinant carefully and then finally take their ratios.
Area of Triangle Formula Using Determinants
Since the area is a positive quantity, we always take the absolute value of the determinant in (1).
If the area is given, use both positive and negative values of the determinant for calculation.
The area of the triangle formed by three collinear points is zero.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




