
The conversion of acetophenone into benzoic acid can be achieved by its reaction with:
A. sodium hydroxide followed by acidification
B. iodine and sodium hydroxide, followed by acidification
C. hydroxylamine followed by reaction with \[{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}\]
D. m-chloroperoxybenzoic acid
Answer
602.4k+ views
Hint: The above conversion can be achieved by performing iodoform test. The iodoform test is commonly used as a test for the \[-C{{H}_{3}}CO\] group. The group to which the \[-C{{H}_{3}}CO\] group is attached can be aryl, alkyl and hydrogen.
Complete step by step solution:
When methyl ketones are treated with the halogen in basic solution, polyhalogenation followed by cleavage of the methyl group occurs.
The products are the carboxylate and trihalomethane, otherwise known as haloform.
The reaction proceeds via successively faster halogenations at the α-position until the 3 H have been replaced.
The halogenations get faster since the halogen stabilizes the enolate negative charge and makes it easier to form.
Then a nucleophilic acyl substitution by hydroxide displaces the anion \[C{{X}_{3}}\] as a leaving group that rapidly protonates.
The mechanism for the reaction can be given as:
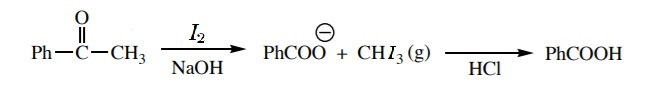
The \[-C{{H}_{3}}CO\] group is present in acetophenone, when it reacts with iodine in presence of an alkaline medium, the group gets converted to carboxylate ion. On acid hydrolysis, this carboxylate ion gives benzoic acid as the product.
So, the correct option is (b).
Note: This reaction is often performed using iodine and as a chemical test for identifying methyl ketones. Iodoform is yellow and precipitates under the reaction conditions. Iodine in an alkaline medium such as sodium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide act as an oxidizing agent.
Complete step by step solution:
When methyl ketones are treated with the halogen in basic solution, polyhalogenation followed by cleavage of the methyl group occurs.
The products are the carboxylate and trihalomethane, otherwise known as haloform.
The reaction proceeds via successively faster halogenations at the α-position until the 3 H have been replaced.
The halogenations get faster since the halogen stabilizes the enolate negative charge and makes it easier to form.
Then a nucleophilic acyl substitution by hydroxide displaces the anion \[C{{X}_{3}}\] as a leaving group that rapidly protonates.
The mechanism for the reaction can be given as:
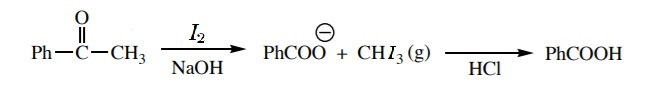
The \[-C{{H}_{3}}CO\] group is present in acetophenone, when it reacts with iodine in presence of an alkaline medium, the group gets converted to carboxylate ion. On acid hydrolysis, this carboxylate ion gives benzoic acid as the product.
So, the correct option is (b).
Note: This reaction is often performed using iodine and as a chemical test for identifying methyl ketones. Iodoform is yellow and precipitates under the reaction conditions. Iodine in an alkaline medium such as sodium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide act as an oxidizing agent.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




