
The compound shown below is called as-:
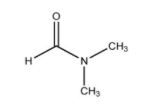
A.Acetamide
B.Formyl acetamide
C.Dimethyl acetate
D.N,N-dimethylformamide

Answer
587.4k+ views
Hint: For the nomenclature of primary amide, the name of the respective acid is changed by dropping the -ic or -oic acid ending and adding -amide. In it, carbonyl carbon gets the lowest numbering.
Complete step by step answer:
-Functional groups are specific substituents within a compound which are responsible for the characteristic chemical reactions of those compounds. Their names are also assigned on the basis of which functional group is attached.
-When a nitrogen atom is bonded to a carbonyl carbon atom, it gives us amide as a functional group. When amino hydrogens are replaced by methyl groups, it becomes formamide, the amide of formic acid.
-As we see in the structure, it belongs to the class of formamide. Since two methyl groups are bonded to nitrogen, we derive its nomenclature as N,N-dimethylformamide.
It is also known as DMF or N,N-dimethylmethanamide. It belongs to the tertiary carboxylic acid amides, a class of organic compounds.
-Whereas acetamide as the name suggests, has an amide group attached to methyl. In formyl acetamide, an additional aldehyde group is attached on the other side of the acetamide. Dimethyl acetate has a different functional group called ester and does not have an amide group. So, these three options can be marked as incorrect.
Hence, the correct option is (D).
Additional information:
DMF is used as a solvent in Sn2 reactions due to its polarity. In the reaction, it provides a good solution to the transition state. It does not decrease the nucleophilicity of the nucleophile by being an aprotic solvent.
Note:
The N- in the N,N-dimethylformamide signifies that the substituent groups(methyl) are bonded to the nitrogen atom, thereby removing ambiguity. It belongs to the class of tertiary carboxylic acid amides.
Complete step by step answer:
-Functional groups are specific substituents within a compound which are responsible for the characteristic chemical reactions of those compounds. Their names are also assigned on the basis of which functional group is attached.
-When a nitrogen atom is bonded to a carbonyl carbon atom, it gives us amide as a functional group. When amino hydrogens are replaced by methyl groups, it becomes formamide, the amide of formic acid.
-As we see in the structure, it belongs to the class of formamide. Since two methyl groups are bonded to nitrogen, we derive its nomenclature as N,N-dimethylformamide.
It is also known as DMF or N,N-dimethylmethanamide. It belongs to the tertiary carboxylic acid amides, a class of organic compounds.
-Whereas acetamide as the name suggests, has an amide group attached to methyl. In formyl acetamide, an additional aldehyde group is attached on the other side of the acetamide. Dimethyl acetate has a different functional group called ester and does not have an amide group. So, these three options can be marked as incorrect.
Hence, the correct option is (D).
Additional information:
DMF is used as a solvent in Sn2 reactions due to its polarity. In the reaction, it provides a good solution to the transition state. It does not decrease the nucleophilicity of the nucleophile by being an aprotic solvent.
Note:
The N- in the N,N-dimethylformamide signifies that the substituent groups(methyl) are bonded to the nitrogen atom, thereby removing ambiguity. It belongs to the class of tertiary carboxylic acid amides.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




