
What will be the compound C in the following reaction:
\[{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}} - {\text{C}} \equiv {\text{CH}}\xrightarrow[{{\text{One equib}}{\text{.}}}]{{{\text{Na/liq}}{\text{.N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}}}{\text{A}}\xrightarrow{{{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}} - {\text{I}}}}{\text{B}}\xrightarrow{{{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{/Pd}} - {\text{CaC}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}}}{\text{C}}\]
Compound ‘C’ is:
A) Trans-but-2-ene
B) Cis-but-2-ene
C) Mixture of cis and trans-but-2-ene
D) Butyne-2
Answer
563.4k+ views
Hint: Initially we are given a compound which is prop-1-yne. Prop-1-yne reacts with sodium metal in liquid ammonia and gets deprotonated. This deprotonated product then reacts with methyl iodide and results in formation of a symmetrical alkyne. The symmetrical alkyne undergoes hydrogenation and forms an alkene.
Complete solution:
We are given a reaction sequence as follows:
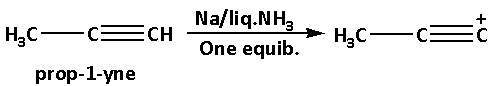
\[{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}} - {\text{C}} \equiv {\text{CH}}\xrightarrow[{{\text{One equib}}{\text{.}}}]{{{\text{Na/liq}}{\text{.N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}}}{\text{A}}\xrightarrow{{{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}} - {\text{I}}}}{\text{B}}\xrightarrow{{{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{/Pd}} - {\text{CaC}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}}}{\text{C}}\]
Initially we have prop-1-yne. Prop-1-yne reacts with sodium metal in liquid ammonia and gives product B.
Prop-1-yne reacts with sodium metal in liquid ammonia and produces a deprotonated product. In this reaction, a proton i.e. one hydrogen atom gets eliminated from prop-1-yne.
The reaction of prop-1-yne with sodium metal in liquid ammonia is as follows:
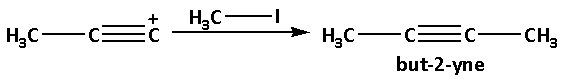
The deprotonated product reacts with methyl iodide and produces but-2-yne. In this reaction, the methyl group $\left( { - {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}} \right)$ gets attached to the positively charged carbon atom.
The reaction is as follows:
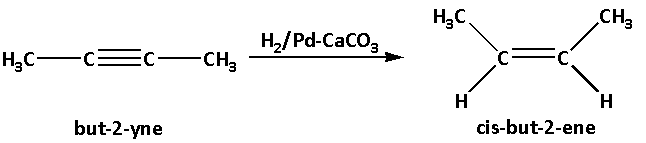
But-2-yne then reacts and undergoes hydrogenation i.e. but-2-yne reacts with hydrogen in presence of palladium deposited on calcium carbonate as a catalyst. This leads to formation of cis-but-2-ene.
In the reaction, palladium deposited on calcium carbonate is used as a catalyst. This is known as Lindar’s catalyst. Lindar’s catalyst reduces alkynes and produces cis-alkene.
The reaction is as follows:
Thus, the reaction sequence is as follows:
 \[{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}} - {\text{C}} \equiv {\text{CH}}\xrightarrow[{{\text{One equib}}{\text{.}}}]{{{\text{Na/liq}}{\text{.N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}} - {\text{C}} \equiv {{\text{C}}^ + }\xrightarrow{{{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}} - {\text{I}}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}} - {\text{C}} \equiv {\text{C}} - {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}\xrightarrow{{{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{/Pd}} - {\text{CaC}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}} - \left( {\text{H}} \right){\text{C}} = {\text{C}}\left( {\text{H}} \right) - {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}\]
\[{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}} - {\text{C}} \equiv {\text{CH}}\xrightarrow[{{\text{One equib}}{\text{.}}}]{{{\text{Na/liq}}{\text{.N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}} - {\text{C}} \equiv {{\text{C}}^ + }\xrightarrow{{{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}} - {\text{I}}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}} - {\text{C}} \equiv {\text{C}} - {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}\xrightarrow{{{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{/Pd}} - {\text{CaC}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}} - \left( {\text{H}} \right){\text{C}} = {\text{C}}\left( {\text{H}} \right) - {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}\]
Thus, compound ‘C’ is cis-but-2-ene.
Therefore, option (B) is correct.
Note: In the reaction, palladium deposited on calcium carbonate is used as a catalyst. This is known as Lindar’s catalyst. Lindar’s catalyst reduces alkynes and produces cis-alkene. Lindar’s catalysts are heterogeneous catalyst in which palladium is deposited on calcium carbonate or barium sulphate.
Complete solution:
We are given a reaction sequence as follows:
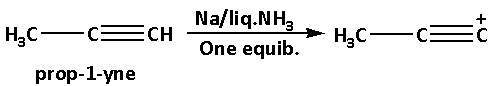
\[{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}} - {\text{C}} \equiv {\text{CH}}\xrightarrow[{{\text{One equib}}{\text{.}}}]{{{\text{Na/liq}}{\text{.N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}}}{\text{A}}\xrightarrow{{{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}} - {\text{I}}}}{\text{B}}\xrightarrow{{{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{/Pd}} - {\text{CaC}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}}}{\text{C}}\]
Initially we have prop-1-yne. Prop-1-yne reacts with sodium metal in liquid ammonia and gives product B.
Prop-1-yne reacts with sodium metal in liquid ammonia and produces a deprotonated product. In this reaction, a proton i.e. one hydrogen atom gets eliminated from prop-1-yne.
The reaction of prop-1-yne with sodium metal in liquid ammonia is as follows:
The deprotonated product reacts with methyl iodide and produces but-2-yne. In this reaction, the methyl group $\left( { - {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}} \right)$ gets attached to the positively charged carbon atom.
The reaction is as follows:

But-2-yne then reacts and undergoes hydrogenation i.e. but-2-yne reacts with hydrogen in presence of palladium deposited on calcium carbonate as a catalyst. This leads to formation of cis-but-2-ene.
In the reaction, palladium deposited on calcium carbonate is used as a catalyst. This is known as Lindar’s catalyst. Lindar’s catalyst reduces alkynes and produces cis-alkene.
The reaction is as follows:
Thus, the reaction sequence is as follows:

Thus, compound ‘C’ is cis-but-2-ene.
Therefore, option (B) is correct.
Note: In the reaction, palladium deposited on calcium carbonate is used as a catalyst. This is known as Lindar’s catalyst. Lindar’s catalyst reduces alkynes and produces cis-alkene. Lindar’s catalysts are heterogeneous catalyst in which palladium is deposited on calcium carbonate or barium sulphate.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




