
The compound $buta - 1,2 - dien$ consists of:
A.only $sp - $ hybridized carbon atom
B.only $s{p^2}$ hybridized carbon atom
C.both $sp$ and $s{p^2}$ hybridized carbon atom
D.$sp$ , $s{p^2}$ and $s{p^3}$ hybridized carbon atom
Answer
576.9k+ views
Hint:Hybridization can be defined as the mixing of two atomic orbitals with the same energy levels to give a new degenerated type of orbitals. There are different types of hybridization namely: $sp,s{p^2},s{p^3},s{p^3}d$and $s{p^3}{d^2}$ .
Complete step by step answer:
-Hybridization can be defined as the mixing of two atomic orbitals with the same energy levels to give a new degenerated type of orbitals. There are different types of hybridization namely: $sp,s{p^2},s{p^3},s{p^3}d$ and $s{p^3}{d^2}$ .
-We will discuss about each hybridization as follows:
-$sp$ hybridization: In this type of hybridization, one $s$ orbital and one $p$ orbital are mixed together to form a completely new orbital called $sp$ orbital.
It forms linear molecules.
Example of $sp$ hybridization: $Be{F_2},BeC{l_2}$ .
-$s{p^2}$ hybridization: In this type of hybridization, one $s$ orbital and two $p$ orbital are mixed together to form a completely new orbital called $s{p^2}$ orbital.
It forms a trigonal symmetry.
Example of $s{p^2}$ hybridization:$B{F_3},B{H_3}$ .
-$s{p^3}$ hybridization: In this type of hybridization, one $s$ orbital and three $p$ orbital are mixed together to form a completely new orbital called $s{p^3}$ orbital.
It forms a tetrahedron.
Example of $s{p^2}$ hybridization: ethane,methane.
-$s{p^3}d$ hybridization: In this type of hybridization, one $s$ orbital , three $p$ orbital and one $d$ orbital are mixed together to form a completely new orbital called $s{p^3}d $orbital.
It forms a trigonal bipyramidal.
Example of $s{p^2}$hybridization: $PC{l_5}$
-$s{p^3}d$ hybridization: In this type of hybridization, one $s$ orbital , three $p$ orbital and two $d$ orbital are mixed together to form a completely new orbital called $s{p^3}{d^2} $orbital.
It forms an octahedron.
Now, we will discuss about the compound $buta - 1,2 - dien$ :
It is an organic compound and it is the isomer of $1,3 - butadiene$ .
The structure of $buta - 1,2 - dien$ is given below:
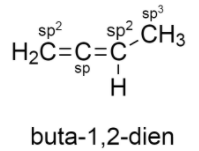
It consists of two double bonds and two sigma bonds.
-$C{H_2}$ is attached to three atoms: two of hydrogen, one to carbon atom. Thus it is $s{p^2}$ hybridized.
-The carbon adjacent to the $C{H_2}$ group also has two double bonds which means it is $sp$ hybridized.
-The carbon that is attached to $C{H_3}$ is $s{p^2}$ hybridized because it is bonded to two carbon atoms and one hydrogen atom.
The carbon atom of $C{H_3}$ is $s{p^3}$ hybridized.
So the correct is option D) $sp$ , $s{p^2}$ and $s{p^3}$ hybridized carbon atoms.
Note:
The basic criteria to check for hybridisation of carbon atoms is to look at the number of bonds it has like if a carbon atom has triple bond it is sp hybridised , if it has double bond it is $s{p^2}$ hybridised and if a carbon atom has only single bonds it is $s{p^3}$ hybridised .
Complete step by step answer:
-Hybridization can be defined as the mixing of two atomic orbitals with the same energy levels to give a new degenerated type of orbitals. There are different types of hybridization namely: $sp,s{p^2},s{p^3},s{p^3}d$ and $s{p^3}{d^2}$ .
-We will discuss about each hybridization as follows:
-$sp$ hybridization: In this type of hybridization, one $s$ orbital and one $p$ orbital are mixed together to form a completely new orbital called $sp$ orbital.
It forms linear molecules.
Example of $sp$ hybridization: $Be{F_2},BeC{l_2}$ .
-$s{p^2}$ hybridization: In this type of hybridization, one $s$ orbital and two $p$ orbital are mixed together to form a completely new orbital called $s{p^2}$ orbital.
It forms a trigonal symmetry.
Example of $s{p^2}$ hybridization:$B{F_3},B{H_3}$ .
-$s{p^3}$ hybridization: In this type of hybridization, one $s$ orbital and three $p$ orbital are mixed together to form a completely new orbital called $s{p^3}$ orbital.
It forms a tetrahedron.
Example of $s{p^2}$ hybridization: ethane,methane.
-$s{p^3}d$ hybridization: In this type of hybridization, one $s$ orbital , three $p$ orbital and one $d$ orbital are mixed together to form a completely new orbital called $s{p^3}d $orbital.
It forms a trigonal bipyramidal.
Example of $s{p^2}$hybridization: $PC{l_5}$
-$s{p^3}d$ hybridization: In this type of hybridization, one $s$ orbital , three $p$ orbital and two $d$ orbital are mixed together to form a completely new orbital called $s{p^3}{d^2} $orbital.
It forms an octahedron.
Now, we will discuss about the compound $buta - 1,2 - dien$ :
It is an organic compound and it is the isomer of $1,3 - butadiene$ .
The structure of $buta - 1,2 - dien$ is given below:

It consists of two double bonds and two sigma bonds.
-$C{H_2}$ is attached to three atoms: two of hydrogen, one to carbon atom. Thus it is $s{p^2}$ hybridized.
-The carbon adjacent to the $C{H_2}$ group also has two double bonds which means it is $sp$ hybridized.
-The carbon that is attached to $C{H_3}$ is $s{p^2}$ hybridized because it is bonded to two carbon atoms and one hydrogen atom.
The carbon atom of $C{H_3}$ is $s{p^3}$ hybridized.
So the correct is option D) $sp$ , $s{p^2}$ and $s{p^3}$ hybridized carbon atoms.
Note:
The basic criteria to check for hybridisation of carbon atoms is to look at the number of bonds it has like if a carbon atom has triple bond it is sp hybridised , if it has double bond it is $s{p^2}$ hybridised and if a carbon atom has only single bonds it is $s{p^3}$ hybridised .
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




