
The compound A is:
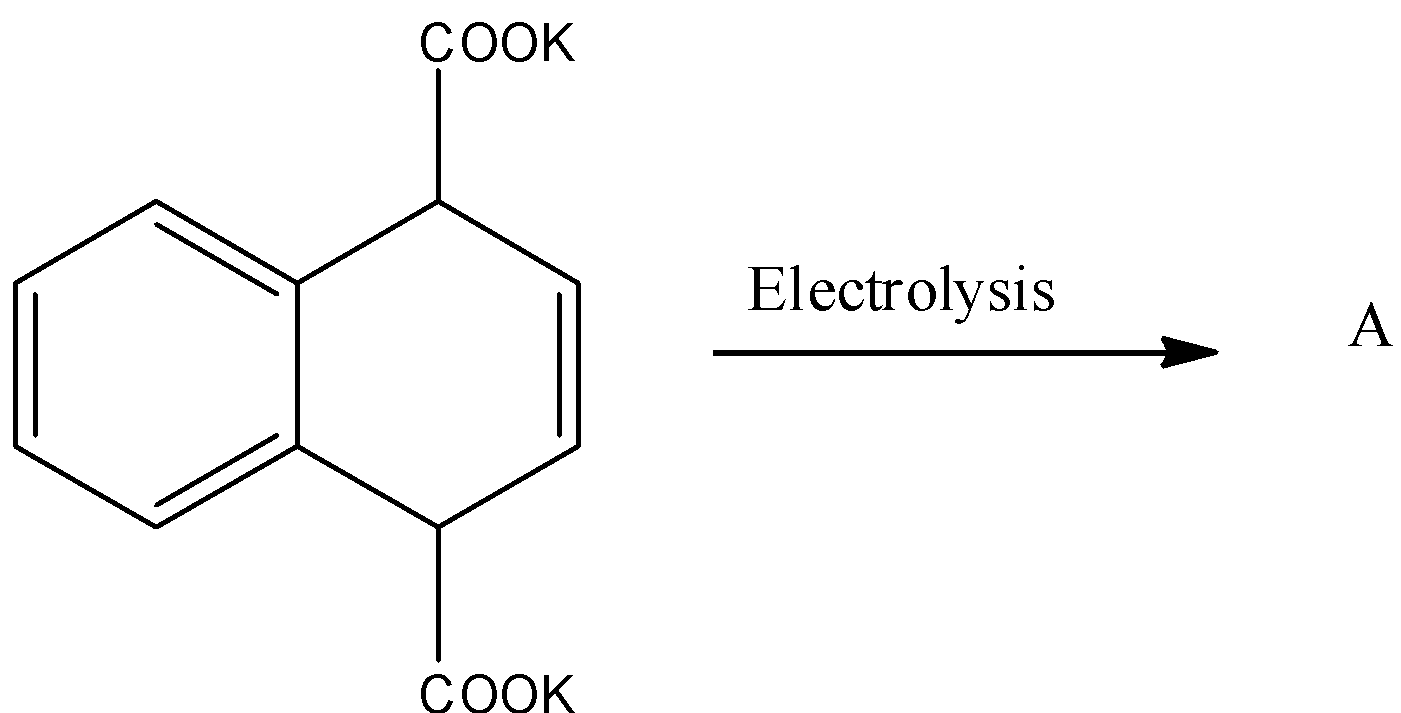
A.
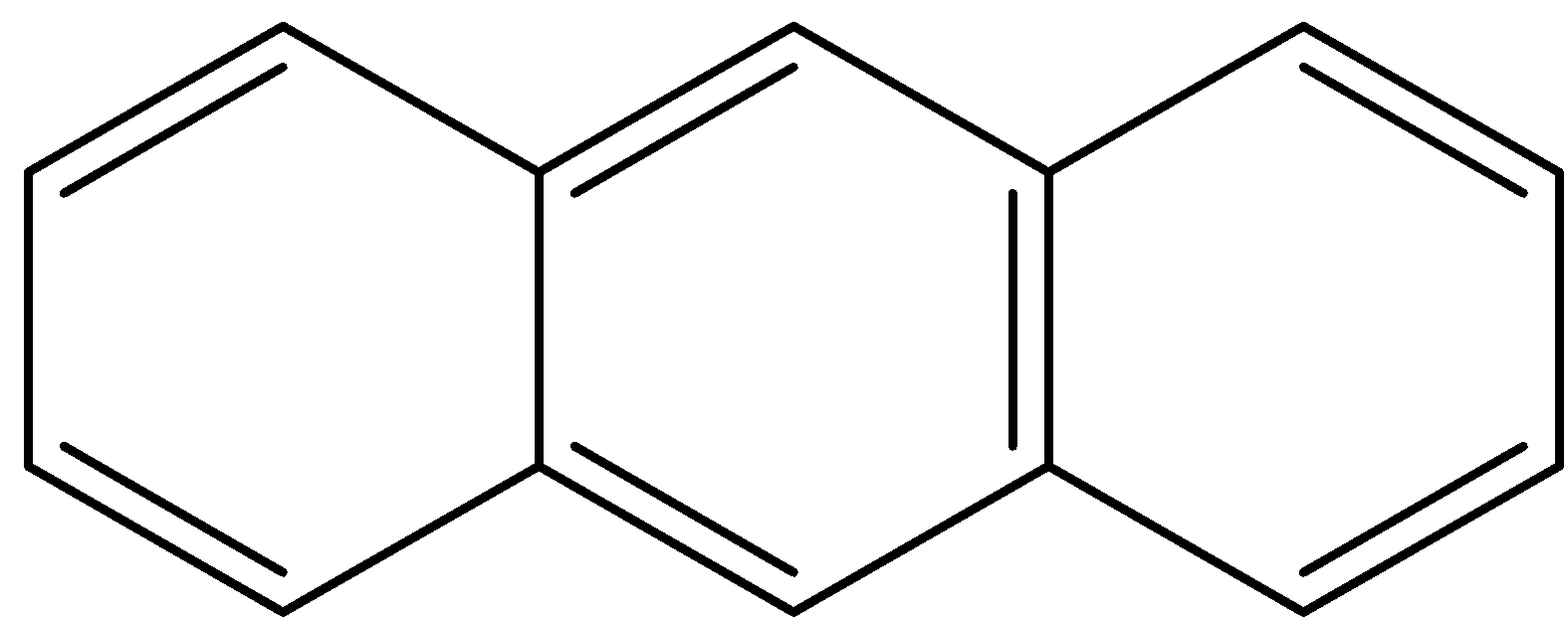
B.
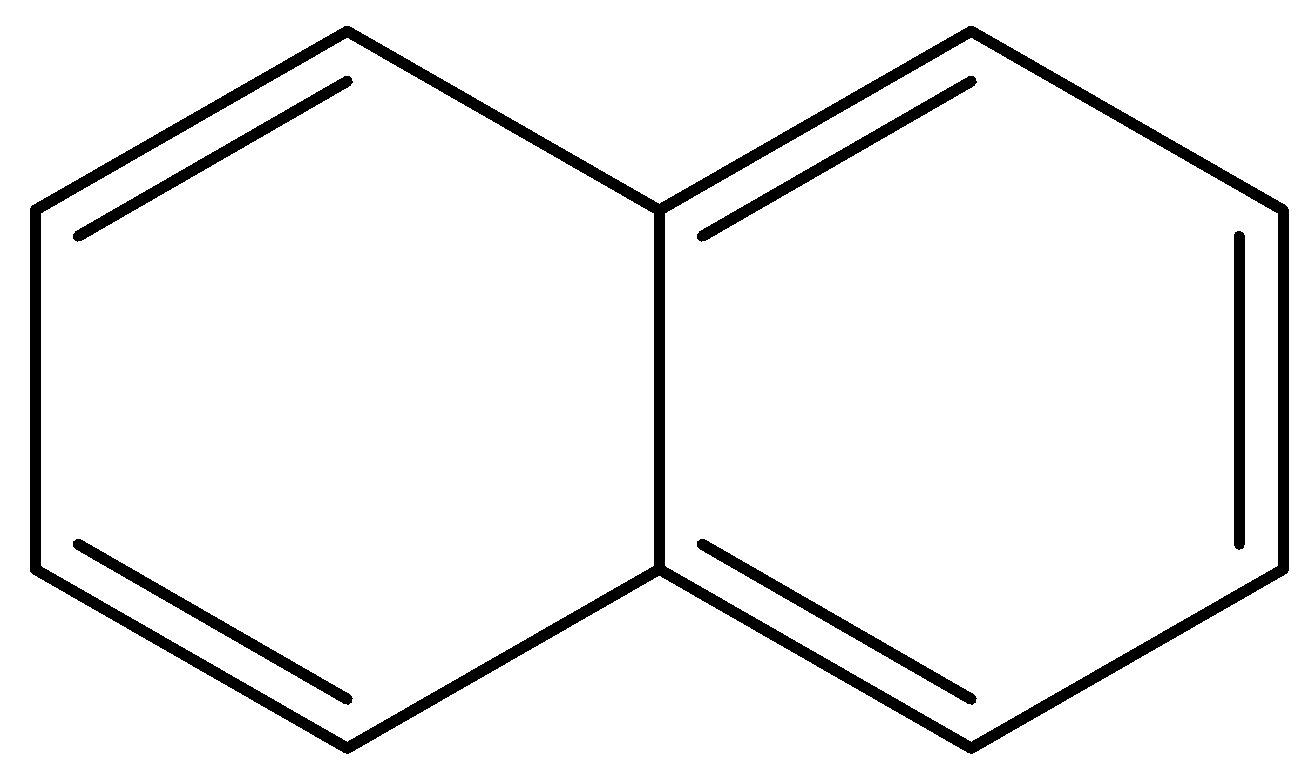
C.
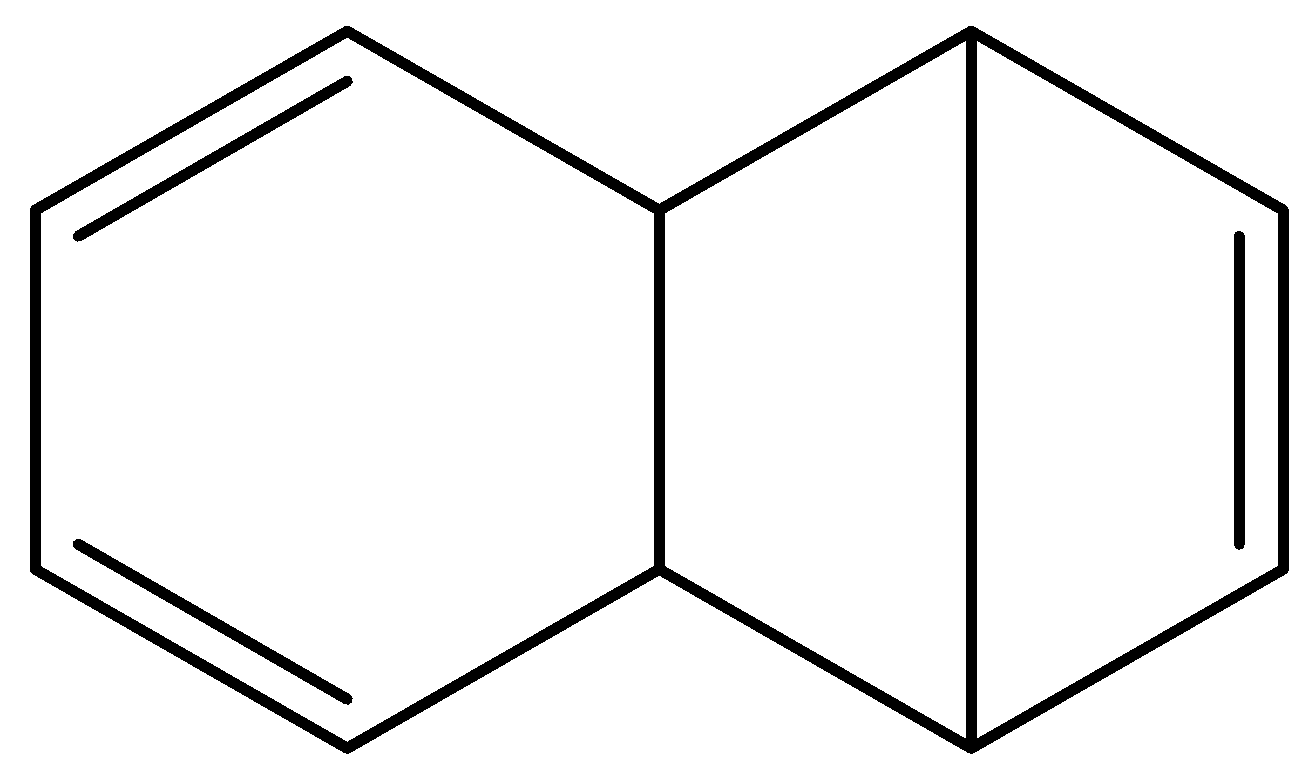
D.
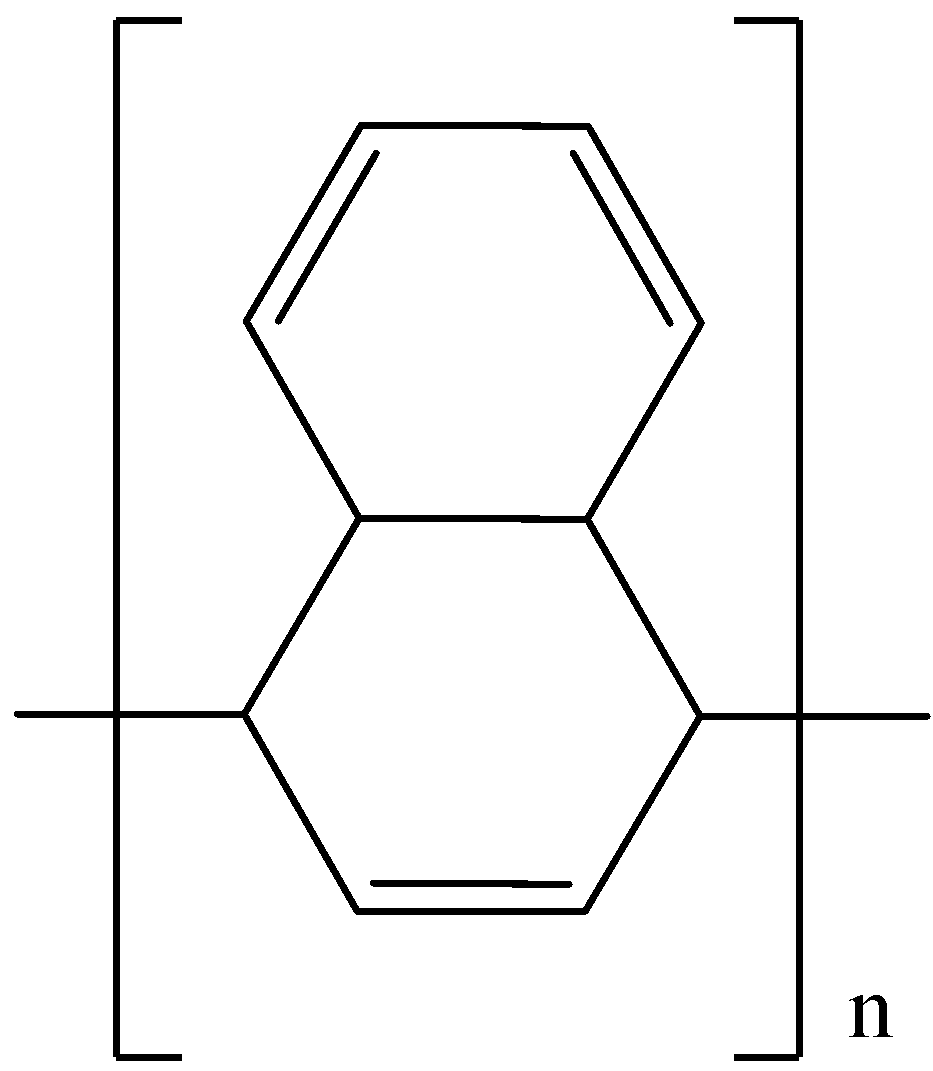





Answer
576.6k+ views
Hint:. In Kolbe electrolysis the potassium salts of the carboxylic acids undergo decarboxylation and form free radicals. The formed free radicals from the carboxylic salts undergo dimerization and form symmetrical dimers or polymer products.
Complete step by step answer:
- In the question it is given that potassium salt of carboxylic acid undergoes electrolysis.
- We have to find the product A in the given reaction.
- The reaction is as follows.
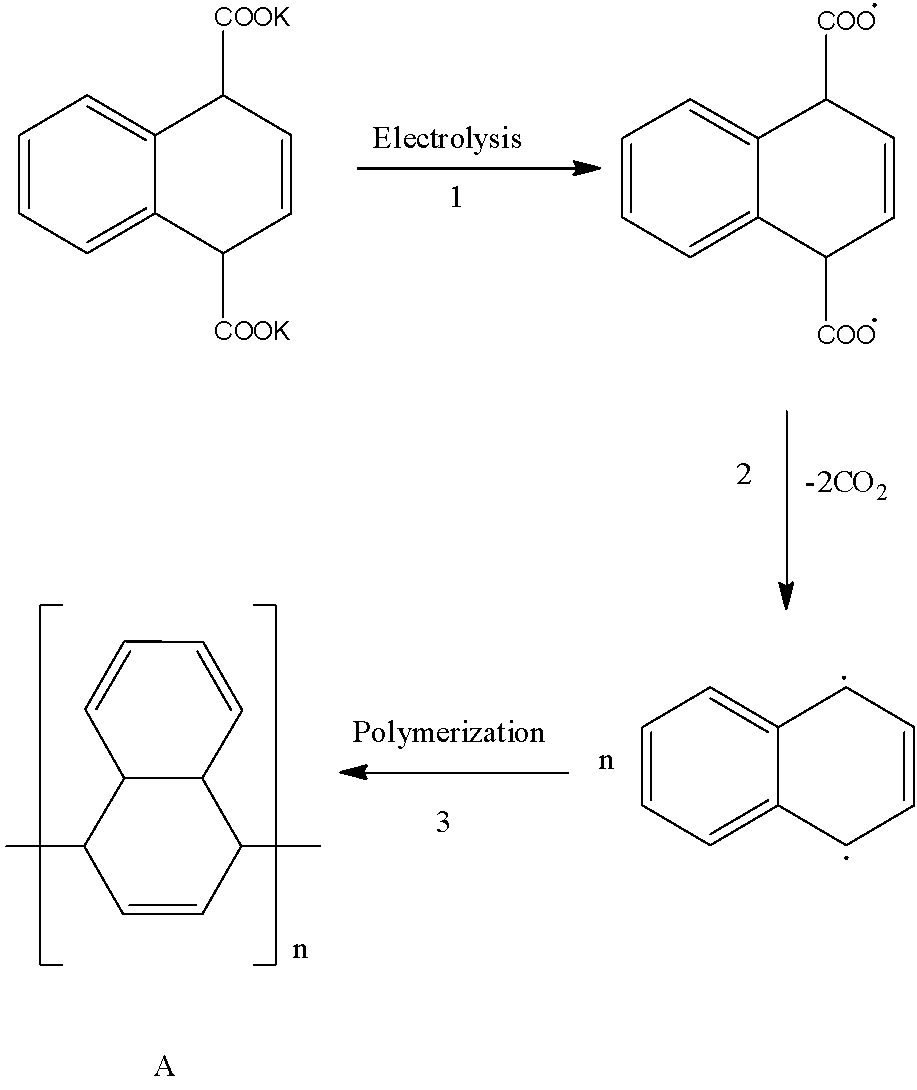
- In the first step the given compound containing potassium salt of dicarboxylic acid releases potassium in the form of free radicals and forms dicarboxylic free radicals as the product.
- The product formed in the first step the formed dicarboxylic free radicals product undergoes decarboxylation and forms a compound having two free radicals on the ring at two different places.
- The product formed in the second step undergoes polymerization and forms the product A as the major product in the third step.
- Therefore the given organic compound containing two potassium salts of carboxylic acid undergoes Kolbe electrolysis and forms a polymerized derivative as the product.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: Generally in organic chemistry Kolbe electrolysis is used to prepare symmetrical dimers by using potassium salt of carboxylic acid through free radical mechanism. The Kolbe reaction is also called a decarboxylative dimerization reaction. To undergo Kolbe electrolysis the organic compound should contain two carboxylic functional groups at two different positions in its structure.
Complete step by step answer:
- In the question it is given that potassium salt of carboxylic acid undergoes electrolysis.
- We have to find the product A in the given reaction.
- The reaction is as follows.

- In the first step the given compound containing potassium salt of dicarboxylic acid releases potassium in the form of free radicals and forms dicarboxylic free radicals as the product.
- The product formed in the first step the formed dicarboxylic free radicals product undergoes decarboxylation and forms a compound having two free radicals on the ring at two different places.
- The product formed in the second step undergoes polymerization and forms the product A as the major product in the third step.
- Therefore the given organic compound containing two potassium salts of carboxylic acid undergoes Kolbe electrolysis and forms a polymerized derivative as the product.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: Generally in organic chemistry Kolbe electrolysis is used to prepare symmetrical dimers by using potassium salt of carboxylic acid through free radical mechanism. The Kolbe reaction is also called a decarboxylative dimerization reaction. To undergo Kolbe electrolysis the organic compound should contain two carboxylic functional groups at two different positions in its structure.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous class 12 chemistry CBSE




