
The combined equation of the three sides of a triangle is \[({{x}^{2}}-{{y}^{2}})(2x+3y-6)=0\]. If \[\left( -2,a \right)\] is an interior point and \[\left( b,1 \right)\] is an exterior point of the triangle then
(a) \[2 < a < \dfrac{10}{3}\]
(b) \[-2 < a < \dfrac{10}{3}\]
(c) \[-1 < b < \dfrac{9}{2}\]
(d) \[-1 < b < 1\]
Answer
601.8k+ views
Hint: Convert the given family of lines into separate lines. Find out the inequality for point \[\left( -2,a \right)\] to be interior point, and then use the opposite inequality for point \[\left( b,1 \right)\], as this is exterior point.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The combined equation of the three sides of a triangle is \[({{x}^{2}}-{{y}^{2}})(2x+3y-6)=0\].
This can be written as,
\[(x-y)(x+y)(2x+3y-6)=0\]
Therefore, the three sides of the triangle are,
\[x-y=0,x+y=0,2x+3y-6=0\]
Plotting the equations, we get
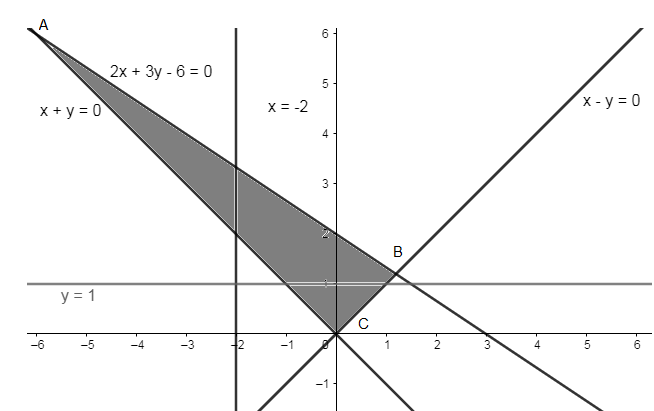
As \[\left( -2,a \right)\] is an interior point, so the interior point will lie on the equation \[x=-2\].
As the equation \[x=-2\] passes through the lines AB and AC. So, substituting the value of ‘x’ in these equations, we get
\[x+y=0\Rightarrow -2+y=0\]
\[\Rightarrow y=2\]
As here we are considering interior points, so \[2Similarly,
\[2x+3y-6=0\Rightarrow 2(-2)+3y=6\]
\[\Rightarrow -4+3y=6\Rightarrow 3y=6+4\]
\[\Rightarrow y=\dfrac{10}{3}\]
So, the value of ‘a’ for it to be inside the triangle will be,
\[2< a <\dfrac{10}{3}\]
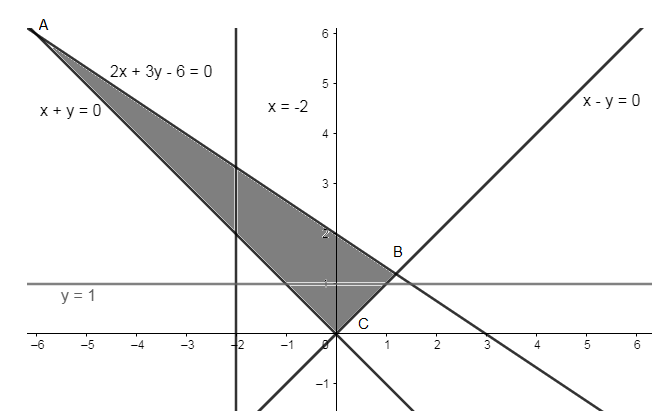
As \[\left( b,1 \right)\] is an exterior point, so the exterior point will lie on the equation \[y=1\].
As the equation \[y=1\] passes through the lines BC and AC. So, substituting the value of ‘y’ in these equations, we get
\[x+y=0\Rightarrow x+1=0\]
\[\Rightarrow x=-1\]
As here we are considering exterior points, so \[-1Similarly,
\[x-y=0\Rightarrow x-1=0\]
\[\Rightarrow x=1\]
So, the value of ‘b’ for it to be outside the triangle will be,
\[-1 < b < 1\]
Hence the correct options are (a) and (d).
Note: We can solve this by finding the equations of all the three sides then applying the condition for two points lying on same side, i.e., if two points A and B lie on same side of the line L, then the formula will be,\[{{L}_{A}}{{L}_{B}}<0\]. This will be a lengthy process.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The combined equation of the three sides of a triangle is \[({{x}^{2}}-{{y}^{2}})(2x+3y-6)=0\].
This can be written as,
\[(x-y)(x+y)(2x+3y-6)=0\]
Therefore, the three sides of the triangle are,
\[x-y=0,x+y=0,2x+3y-6=0\]
Plotting the equations, we get

As \[\left( -2,a \right)\] is an interior point, so the interior point will lie on the equation \[x=-2\].
As the equation \[x=-2\] passes through the lines AB and AC. So, substituting the value of ‘x’ in these equations, we get
\[x+y=0\Rightarrow -2+y=0\]
\[\Rightarrow y=2\]
As here we are considering interior points, so \[2
\[2x+3y-6=0\Rightarrow 2(-2)+3y=6\]
\[\Rightarrow -4+3y=6\Rightarrow 3y=6+4\]
\[\Rightarrow y=\dfrac{10}{3}\]
So, the value of ‘a’ for it to be inside the triangle will be,
\[2< a <\dfrac{10}{3}\]

As \[\left( b,1 \right)\] is an exterior point, so the exterior point will lie on the equation \[y=1\].
As the equation \[y=1\] passes through the lines BC and AC. So, substituting the value of ‘y’ in these equations, we get
\[x+y=0\Rightarrow x+1=0\]
\[\Rightarrow x=-1\]
As here we are considering exterior points, so \[-1
\[x-y=0\Rightarrow x-1=0\]
\[\Rightarrow x=1\]
So, the value of ‘b’ for it to be outside the triangle will be,
\[-1 < b < 1\]
Hence the correct options are (a) and (d).
Note: We can solve this by finding the equations of all the three sides then applying the condition for two points lying on same side, i.e., if two points A and B lie on same side of the line L, then the formula will be,\[{{L}_{A}}{{L}_{B}}<0\]. This will be a lengthy process.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




