
The color and magnetic nature of manganite ion ($MnO_4^{2 - }$) are:
A.Green, paramagnetic
B.Purple, diamagnetic
C.Green, diamagnetic
D.Purple, paramagnetic
Answer
588k+ views
Hint: As we know the color and magnetic behavior of an ion can be determined with the help of unpaired electrons and if there is no unpaired electron then it is diamagnetic and if it contains unpaired electrons then it is paramagnetic
Complete step by step answer:
As we know manganese ($Mn$) is a d-block element having an atomic number $25$ so its outer electronic configuration is $3{d^5}4{s^2}$. The configuration is shown in the diagram below
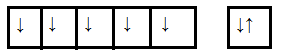
To find the unpaired electrons first, we have to find the oxidation state of $Mn$ in the case of manganite ions. Let us consider the oxidation state of $Mn$ ion in the above case is x. and we know the oxidation state of oxygen is -2. So,
$
x + 4 \times ( - 2) = - 2 \\
\Rightarrow x - 8 = - 2 \\
\Rightarrow x = 8 - 2 \\
\Rightarrow x = 6 \\
$
In the +6 oxidation state, the outer configuration of $Mn$ will be $3{d^1}$.
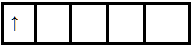
Hence there is one unpaired electron so it is paramagnetic. And due to the presence of an unpaired electron, it is purple.
So, the correct answer is Option D.
Note:
We can explain the color and magnetic properties of a compound with crystal field splitting theory. In this theory, degenerate orbitals split into higher energy levels and lower energy levels. When an electron absorbs radiation it gets to jump to the higher energy level where it becomes unstable and returns to a lower level by releasing the same amount of energy that is absorbed as a result it shows color.
Complete step by step answer:
As we know manganese ($Mn$) is a d-block element having an atomic number $25$ so its outer electronic configuration is $3{d^5}4{s^2}$. The configuration is shown in the diagram below

To find the unpaired electrons first, we have to find the oxidation state of $Mn$ in the case of manganite ions. Let us consider the oxidation state of $Mn$ ion in the above case is x. and we know the oxidation state of oxygen is -2. So,
$
x + 4 \times ( - 2) = - 2 \\
\Rightarrow x - 8 = - 2 \\
\Rightarrow x = 8 - 2 \\
\Rightarrow x = 6 \\
$
In the +6 oxidation state, the outer configuration of $Mn$ will be $3{d^1}$.

Hence there is one unpaired electron so it is paramagnetic. And due to the presence of an unpaired electron, it is purple.
So, the correct answer is Option D.
Note:
We can explain the color and magnetic properties of a compound with crystal field splitting theory. In this theory, degenerate orbitals split into higher energy levels and lower energy levels. When an electron absorbs radiation it gets to jump to the higher energy level where it becomes unstable and returns to a lower level by releasing the same amount of energy that is absorbed as a result it shows color.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




