
The coefficients of static and dynamic friction are \[0.7\]and \[0.4\]. The minimum force required to create motion is applied on a body and if it is further continued, the acceleration attained by the body of mass $1\;kg$ in $ms^{-2}$ is:
A. $7$
B.$4$
C.$3$
D.$0$
Answer
533.4k+ views
Hint: We know that friction is a resistive force, which opposes the motion of an object. It is also a contact force which acts due to the relative motion of the object with respect to the surface on which it tries to move. There are different types of friction, which depends on the surface or substance used and the type of motion which is observed.
Formula used:
$F=ma$ and $f=\mu N$
Complete step-by-step solution:
We know that dry friction is observed due to the relative motion of two solid objects like a ball and a road. This is again classified as static friction, this is the minimum force required to move a stationary object and kinetic friction, and this the friction offered due to motion of the objects. Kinetic friction can either be due to sliding or rolling of an object over the other surface.
From the definition of friction, we can also say that the net work done by any system which experiences friction as $W=F_{net}-f$ where, $W$ is the work done by the system due to force $F_{net}$ and friction $f$
Here, when the body is at rest, it experiences static friction $f_s$ , and when the an external force $F$ tries to accelerate the body by $a$, then the body experiences $f_k$ as shown in the figure below:
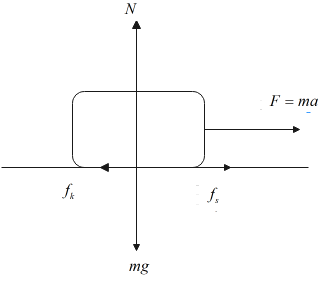
Then, we can say that $f_s-f_k=F$
$\implies \mu_smg+\mu_kmg=ma$
$\implies (\mu_s-\mu_k)g=a$
$\implies a=(0.7-.04)10=3$
$\therefore a=3ms^{-2}$
Hence the correct answer is option C.$3$
Note: Friction is a non-conservative force which depends on the trajectory or the path taken. Also due to friction, some kinetic energy of the object is lost or dissipated as heat energy. Friction is useful in a few cases and is also unnecessary in a few other cases, depending on the situation.
Formula used:
$F=ma$ and $f=\mu N$
Complete step-by-step solution:
We know that dry friction is observed due to the relative motion of two solid objects like a ball and a road. This is again classified as static friction, this is the minimum force required to move a stationary object and kinetic friction, and this the friction offered due to motion of the objects. Kinetic friction can either be due to sliding or rolling of an object over the other surface.
From the definition of friction, we can also say that the net work done by any system which experiences friction as $W=F_{net}-f$ where, $W$ is the work done by the system due to force $F_{net}$ and friction $f$
Here, when the body is at rest, it experiences static friction $f_s$ , and when the an external force $F$ tries to accelerate the body by $a$, then the body experiences $f_k$ as shown in the figure below:

Then, we can say that $f_s-f_k=F$
$\implies \mu_smg+\mu_kmg=ma$
$\implies (\mu_s-\mu_k)g=a$
$\implies a=(0.7-.04)10=3$
$\therefore a=3ms^{-2}$
Hence the correct answer is option C.$3$
Note: Friction is a non-conservative force which depends on the trajectory or the path taken. Also due to friction, some kinetic energy of the object is lost or dissipated as heat energy. Friction is useful in a few cases and is also unnecessary in a few other cases, depending on the situation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




