
The coefficient of kinetic friction is $0.03$ in the diagram where mass ${m_2} = 20kg$ and ${m_1} = 4kg$. The acceleration of the block shall be $(g = 10m{s^{ - 2}})$.

A.$1.8m{s^{ - 2}}$
B.$0.8m{s^{ - 2}}$
C.$1.4m{s^{ - 2}}$
D.$0.4m{s^{ - 2}}$

Answer
543.6k+ views
Hint: To solve this question we must know what acceleration means. Acceleration can be defined as the rate of change of the velocity of an object with respect to time. Acceleration is a vector quantity which means they have both magnitude and direction. According to Newton's second law ‘the acceleration of an object (a) is proportional to the force (F) applied on it’, and the proportionality factor is the object's mass (m).
Complete answer:
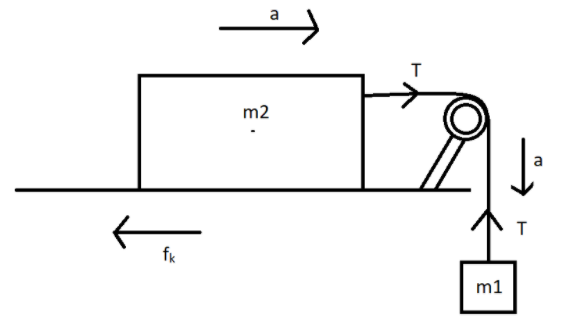
Given that,
Mass of ${m_1} = 4kg$
Mass of ${m_2} = 20kg$
Coefficient of kinetic friction is given by,
${u_k} = 0.03$
Let the acceleration of blocks be ‘a’
Now consider free body diagram of ${m_2}$
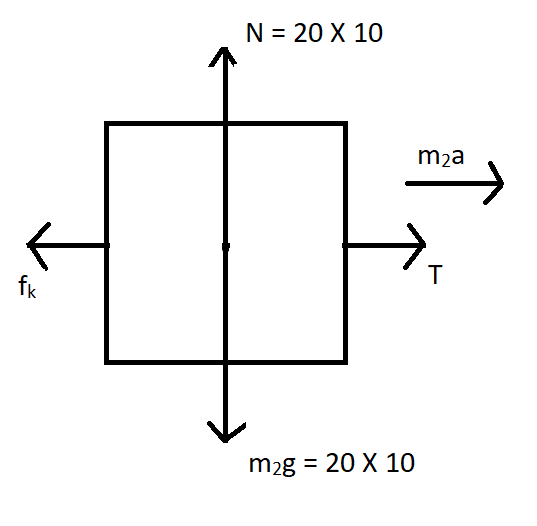
Its equation of motion is given by,
$\
{m_2}a = T - {f_k} \\
{m_2}a = T - ({u_k}N) \\
20a = T - 0.03 \times 200 \\
20a = T - 6{\text{ - - - - - - - - - - - - - equation1}} \\
\ $
Now by considering ${m_1}$ , its free body diagram is given by,

$\
{m_2}a = {m_1}g - T \\
4a = 40 - T - - - - - - - {\text{ equation 2}} \\
\ $
Hence by adding both the equation we get
$\
24a = 34 \\
a = \dfrac{{34}}{{24}} \\
a = 1.4m{s^{ - 2}} \\
\\
\ $
Hence the acceleration of the block is $1.4m{s^{ - 2}}$
Note:
The three types of acceleration are as follows-
Uniform acceleration: When an object is travelling in a straight line with an increase in velocity at equal intervals of time, then the object is said to be in uniform acceleration. Free falling of an object is said to be an example of uniform acceleration.
Non-uniform acceleration: When an object is travelling with an increase in velocity but not at the equal intervals of time is known as non-uniform acceleration. Bus moving or leaving from the bus stop is an example of non-uniform acceleration.
Instantaneous acceleration: Acceleration of an object at any instant of time is known as instantaneous acceleration.
Complete answer:

Given that,
Mass of ${m_1} = 4kg$
Mass of ${m_2} = 20kg$
Coefficient of kinetic friction is given by,
${u_k} = 0.03$
Let the acceleration of blocks be ‘a’
Now consider free body diagram of ${m_2}$

Its equation of motion is given by,
$\
{m_2}a = T - {f_k} \\
{m_2}a = T - ({u_k}N) \\
20a = T - 0.03 \times 200 \\
20a = T - 6{\text{ - - - - - - - - - - - - - equation1}} \\
\ $
Now by considering ${m_1}$ , its free body diagram is given by,

$\
{m_2}a = {m_1}g - T \\
4a = 40 - T - - - - - - - {\text{ equation 2}} \\
\ $
Hence by adding both the equation we get
$\
24a = 34 \\
a = \dfrac{{34}}{{24}} \\
a = 1.4m{s^{ - 2}} \\
\\
\ $
Hence the acceleration of the block is $1.4m{s^{ - 2}}$
Note:
The three types of acceleration are as follows-
Uniform acceleration: When an object is travelling in a straight line with an increase in velocity at equal intervals of time, then the object is said to be in uniform acceleration. Free falling of an object is said to be an example of uniform acceleration.
Non-uniform acceleration: When an object is travelling with an increase in velocity but not at the equal intervals of time is known as non-uniform acceleration. Bus moving or leaving from the bus stop is an example of non-uniform acceleration.
Instantaneous acceleration: Acceleration of an object at any instant of time is known as instantaneous acceleration.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




