
The closed ascocarp is
(a) Apothecium
(b) Amphithecium
(c) Endothecium
(d) Cleistothecium
Answer
524.4k+ views
Hint: These fungi are also known as sac fungi. It is the largest phylum of fungi. They constitute a fruiting body that is closed. They are tightly bound and inside them, the various spores are embedded and are closed.
Complete answer
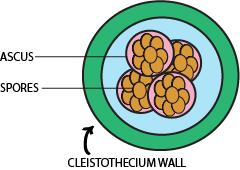
Ascomycetes are the sac fungi which is the largest phylum of fungi and constitutes a microscopic sexual structure in which the non-motile spores known as ascospores are formed. It is a monophyletic group that consists of a sexual species from other fungal taxa and are classified based on morphological and physiological similarities on bearing ascus. They constitute a fruiting body that is closed and called cleistothecium. It consists of hyphae and has around four to eight ascospores containing millions of asci in them. The fruiting body is closed completely without any opening and thus there is no contact from outside.
Additional information
-They are medicinal and important for humans such as antibiotics, for making bread, cheese, and alcoholic beverages.
-Ascomycota constitutes edible mushrooms along with around 30,000 known species.
-Ascomycetes reproduce sexually as well as asexually. Fungi have a dikaryon stage in their life cycle where the haploid spores fuse together but the zygote is not produced immediately rather a fused stage is achieved.
So, the correct answer is ‘Cleistothecium’.
Note:
Apothecium is an open, saucer-like, wide fruiting body in the Phylum Ascomycetes. It may also have a cup-shaped structure. Amphithecium is the outer layer of the sporophytes found in the bryophytes. Endothecium is the inner lining of the anther which secretes substances that help in the maturation of the pollen grains.
Complete answer
Ascomycetes are the sac fungi which is the largest phylum of fungi and constitutes a microscopic sexual structure in which the non-motile spores known as ascospores are formed. It is a monophyletic group that consists of a sexual species from other fungal taxa and are classified based on morphological and physiological similarities on bearing ascus. They constitute a fruiting body that is closed and called cleistothecium. It consists of hyphae and has around four to eight ascospores containing millions of asci in them. The fruiting body is closed completely without any opening and thus there is no contact from outside.
Additional information
-They are medicinal and important for humans such as antibiotics, for making bread, cheese, and alcoholic beverages.
-Ascomycota constitutes edible mushrooms along with around 30,000 known species.
-Ascomycetes reproduce sexually as well as asexually. Fungi have a dikaryon stage in their life cycle where the haploid spores fuse together but the zygote is not produced immediately rather a fused stage is achieved.
So, the correct answer is ‘Cleistothecium’.

Note:
Apothecium is an open, saucer-like, wide fruiting body in the Phylum Ascomycetes. It may also have a cup-shaped structure. Amphithecium is the outer layer of the sporophytes found in the bryophytes. Endothecium is the inner lining of the anther which secretes substances that help in the maturation of the pollen grains.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




