
The circumcentre of a triangle lies at the origin and it’s centroid is the midpoint of the line segment joining the points $\left( {{a}^{2}}+1,{{a}^{2}}+1 \right)$ and $\left( 2a,-2a \right)$,$a\ne 0$ . Then for any a, the orthocenter of this triangle lies on the line:
A) \[y-2ax=0\]
B) $y\left( {{a}^{2}}+1 \right)-x=0$
C) \[y+x\text{ }=0\]
D) \[{{\left( a-1 \right)}^{2}}x-{{\left( a+1 \right)}^{2}}y\text{ }=0\]
Answer
576.9k+ views
Hint: We know that circumcentre is the intersection point of all the perpendicular bisectors and centroid is intersection point of all the medians of the given triangle and orthocenter is the intersection of all angular bisectors of the given triangle. These points i.e. circumcentre, centroid and orthocenter are always collinear.
Complete step by step answer:
Given that the circumcentre(C) of triangle XYZ is origin which implies C = (0,0)
Also Given that the centroid (G) is the midpoint of the line segment joining the points E$\left( {{a}^{2}}+1,{{a}^{2}}+1 \right)$and F$\left( 2a,-2a \right)$ as shown in the diagram.
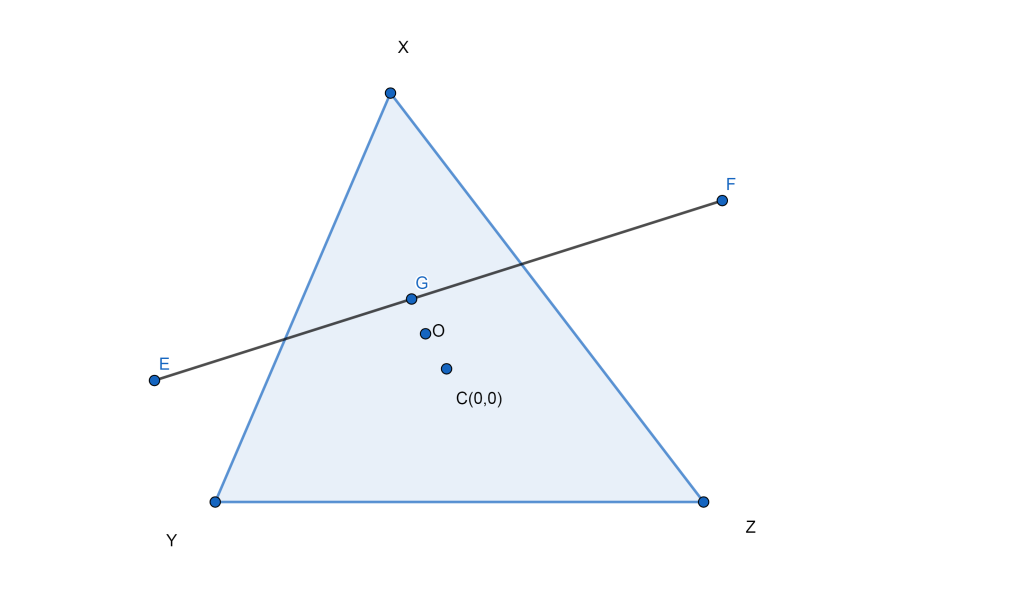
We know that midpoint of any two points(a,b) and (c,d) is ($\dfrac{a+c}{2},\dfrac{b+d}{2}$ )
which implies the centroid (G) = ($\dfrac{{{a}^{2}}+1+2a}{2},\dfrac{{{a}^{2}}+1-2a}{2}$) = ($\dfrac{{{(a+1)}^{2}}}{2},\dfrac{{{(a-1)}^{2}}}{2}$ )
[We already know that \[{{(a\pm b)}^{2}}=\text{ }{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}\pm 2ab\] ]
As we know that centroid , circumcentre , orthocenter are collinear , we can find the line that passes through these three points even when we know any of these two points.
So, now we will find the line passing through G and C so that the orthocenter lies on it.
We know that the equation of line that passes through (a,b) and (c,d) is
$\dfrac{y-b}{x-a}=\dfrac{d-b}{c-a}$
which implies the line passing through G ($\dfrac{{{(a+1)}^{2}}}{2},\dfrac{{{(a-1)}^{2}}}{2}$ ) and C(0,0) will be
$\dfrac{y-0}{x-0}=\dfrac{{{(a-1)}^{2}}/2-0}{{{(a+1)}^{2}}/2-0}$ ;
Which implies $\dfrac{y}{x}=\dfrac{{{(a-1)}^{2}}}{{{(a+1)}^{2}}}$;
Which implies \[{{\left( a+1 \right)}^{2}}y\text{ }=\text{ }{{\left( a-1 \right)}^{2}}x\] ;
That is also equal to \[{{\left( a-1 \right)}^{2}}x-{{\left( a+1 \right)}^{2}}y\text{ }=0\]
Therefore the orthocenter of this triangle lies on the line \[{{\left( a-1 \right)}^{2}}x-{{\left( a+1 \right)}^{2}}y\text{ }=0\]
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note:
Go through the properties of all the circles and centres corresponding to the triangle that is orthocenter , centroid, circumcenter , incenter and find the ratios through which one center cuts the other .Also check the collinearities between them. Do not draw the graph whenever you see a question related to these centers. First read the total question and then solve the problem.
Complete step by step answer:
Given that the circumcentre(C) of triangle XYZ is origin which implies C = (0,0)
Also Given that the centroid (G) is the midpoint of the line segment joining the points E$\left( {{a}^{2}}+1,{{a}^{2}}+1 \right)$and F$\left( 2a,-2a \right)$ as shown in the diagram.

We know that midpoint of any two points(a,b) and (c,d) is ($\dfrac{a+c}{2},\dfrac{b+d}{2}$ )
which implies the centroid (G) = ($\dfrac{{{a}^{2}}+1+2a}{2},\dfrac{{{a}^{2}}+1-2a}{2}$) = ($\dfrac{{{(a+1)}^{2}}}{2},\dfrac{{{(a-1)}^{2}}}{2}$ )
[We already know that \[{{(a\pm b)}^{2}}=\text{ }{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}\pm 2ab\] ]
As we know that centroid , circumcentre , orthocenter are collinear , we can find the line that passes through these three points even when we know any of these two points.
So, now we will find the line passing through G and C so that the orthocenter lies on it.
We know that the equation of line that passes through (a,b) and (c,d) is
$\dfrac{y-b}{x-a}=\dfrac{d-b}{c-a}$
which implies the line passing through G ($\dfrac{{{(a+1)}^{2}}}{2},\dfrac{{{(a-1)}^{2}}}{2}$ ) and C(0,0) will be
$\dfrac{y-0}{x-0}=\dfrac{{{(a-1)}^{2}}/2-0}{{{(a+1)}^{2}}/2-0}$ ;
Which implies $\dfrac{y}{x}=\dfrac{{{(a-1)}^{2}}}{{{(a+1)}^{2}}}$;
Which implies \[{{\left( a+1 \right)}^{2}}y\text{ }=\text{ }{{\left( a-1 \right)}^{2}}x\] ;
That is also equal to \[{{\left( a-1 \right)}^{2}}x-{{\left( a+1 \right)}^{2}}y\text{ }=0\]
Therefore the orthocenter of this triangle lies on the line \[{{\left( a-1 \right)}^{2}}x-{{\left( a+1 \right)}^{2}}y\text{ }=0\]
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note:
Go through the properties of all the circles and centres corresponding to the triangle that is orthocenter , centroid, circumcenter , incenter and find the ratios through which one center cuts the other .Also check the collinearities between them. Do not draw the graph whenever you see a question related to these centers. First read the total question and then solve the problem.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




