
The circles ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}$=4 and ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}-4\lambda x+9=0$ have exactly two common tangents if $\lambda $ equals
(a) 8
(b) 2
(c) 12
(d) -112
Answer
597.9k+ views
Hint: For two circles to have exactly two common tangents, they should intersect each other at two points. Use the fact that two circles intersect each other at two points of the distance between their centres is less than the sum of the radii of the two circles and greater than the difference of the radii of the two circles, i.e. $\left| {{r}_{1}}-{{r}_{2}} \right|<{{C}_{1}}{{C}_{2}}<{{r}_{1}}+{{r}_{2}}$. Use the fact that the radius of a circle ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+2gx+2fy+c=0$ is given by $r=\sqrt{{{g}^{2}}+{{f}^{2}}-c}$. Hence form an inequation in $\lambda $. Hence find which of the options is correct
Complete step-by-step solution -
We know that the radius of the circle ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+2gx+2fy+c=0$ is given by $r=\sqrt{{{g}^{2}}+{{f}^{2}}-c}$ and the centre is given by $C\equiv \left( -g,-f \right)$
Consider the circle ${{S}_{1}}:{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}=4$
Here g = f = 0, c= -4
Hence the centre of the circle ${{S}_{1}}$ is given by ${{C}_{1}}\equiv \left( 0,0 \right)$
The radius of the circle ${{S}_{1}}$ is given by ${{r}_{1}}=\sqrt{{{g}^{2}}+{{f}^{2}}-c}=\sqrt{{{0}^{2}}+{{0}^{2}}-\left( -4 \right)}=2$
Consider the circle ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}-4\lambda x+9=0$
Here $g=-2\lambda ,f=0,c=9$
Hence the centre of the circle ${{S}_{2}}$ is given by ${{C}_{2}}\equiv \left( 2\lambda ,0 \right)$
The radius of the circle ${{S}_{2}}$ is given by ${{r}_{2}}=\sqrt{{{g}^{2}}+{{f}^{2}}-c}=\sqrt{4{{\lambda }^{2}}-9}$
The radius of the circle should be real.
Hence, we have
$\begin{align}
& 4{{\lambda }^{2}}-9>0 \\
& \Rightarrow {{\lambda }^{2}}-\dfrac{9}{4}>0 \\
& \Rightarrow \left( \lambda -\dfrac{3}{2} \right)\left( \lambda +\dfrac{3}{2} \right)>0 \\
& \Rightarrow \lambda \in \left( -\infty ,\dfrac{-3}{2} \right)\bigcup \left( \dfrac{3}{2},\infty \right)\text{ }\left( i \right) \\
\end{align}$
Now since the circles have only two common tangents, they must intersect at two points.
Hence, we have
$\left| {{r}_{1}}-{{r}_{2}} \right|<{{C}_{1}}{{C}_{2}}<{{r}_{1}}+{{r}_{2}}$
Now, we have
${{C}_{1}}{{C}_{2}}=\sqrt{{{\left( 2\lambda -0 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( 0-0 \right)}^{2}}}=2\left| \lambda \right|$
From the inequation $\left| {{r}_{1}}-{{r}_{2}} \right|<{{C}_{1}}{{C}_{2}}$, we have
$\left| \sqrt{4{{\lambda }^{2}}-9}-2 \right|<2\left| \lambda \right|$
Since both LHS and RHS are non-negative, squaring will not change the sense of the inequality sign.
Squaring both sides, we get
$\begin{align}
& 4{{\lambda }^{2}}-9+4-4\sqrt{4{{\lambda }^{2}}-9}<4{{\lambda }^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow -4\sqrt{4{{\lambda }^{2}}-9}-5<0 \\
& \Rightarrow 4\sqrt{4{{\lambda }^{2}}-9}>-5 \\
\end{align}$
This inequality is true for all possible values of $\lambda $ since the square root of a term is non-negative.
From the inequation ${{C}_{1}}{{C}_{2}}<\left| {{r}_{1}}+{{r}_{2}} \right|$, we have
$2\left| \lambda \right|<\sqrt{4{{\lambda }^{2}}-9}+2$
Since both LHS and RHS are non-negative, squaring will not change the sense of the inequality sign.
Squaring both sides, we get
$\begin{align}
& 4{{\lambda }^{2}}<4{{\lambda }^{2}}-9+4+4\sqrt{4{{\lambda }^{2}}-9} \\
& \Rightarrow 4\sqrt{4{{\lambda }^{2}}-9}>5 \\
\end{align}$
Squaring both sides again, we get
$\begin{align}
& 16\left( 4{{\lambda }^{2}}-9 \right)>25 \\
& \Rightarrow 4{{\lambda }^{2}}-9>\dfrac{25}{16} \\
& \Rightarrow 4{{\lambda }^{2}}>\dfrac{25+144}{16}=\dfrac{169}{16} \\
& \Rightarrow {{\lambda }^{2}}>\dfrac{169}{64} \\
& \Rightarrow \left( \lambda -\dfrac{13}{8} \right)\left( \lambda +\dfrac{13}{8} \right)>0 \\
& \Rightarrow \lambda \in \left( -\infty ,\dfrac{-13}{8} \right)\bigcup \left( \dfrac{13}{8},\infty \right)\text{ }\left( ii \right) \\
\end{align}$
From (i) and (ii), we have
$\lambda \in \left( -\infty ,\dfrac{-13}{8} \right)\bigcup \left( \dfrac{13}{8},\infty \right)$
Clearly all of the options [p],[q],[r] and [s] are in this range.
Note: To ease your understanding, here’s a plot on the number line of the possible values of $\lambda $ that we found out :
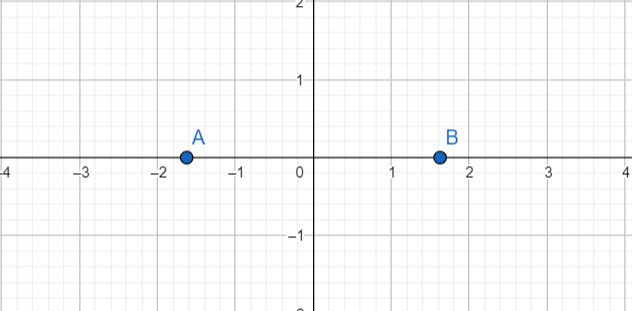
Here, A and B represent $-\dfrac{13}{8}$ and $+\dfrac{13}{8}$ respectively. The values of $\lambda $ lie on the side where the absolute of the values are >$+\dfrac{13}{8}$ .
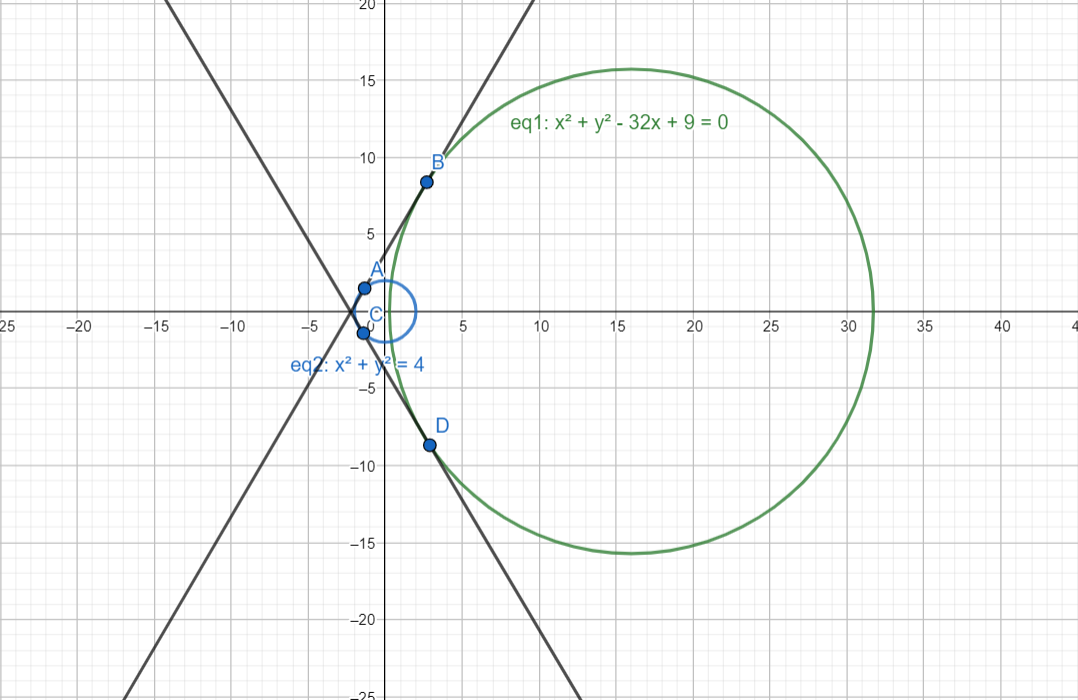
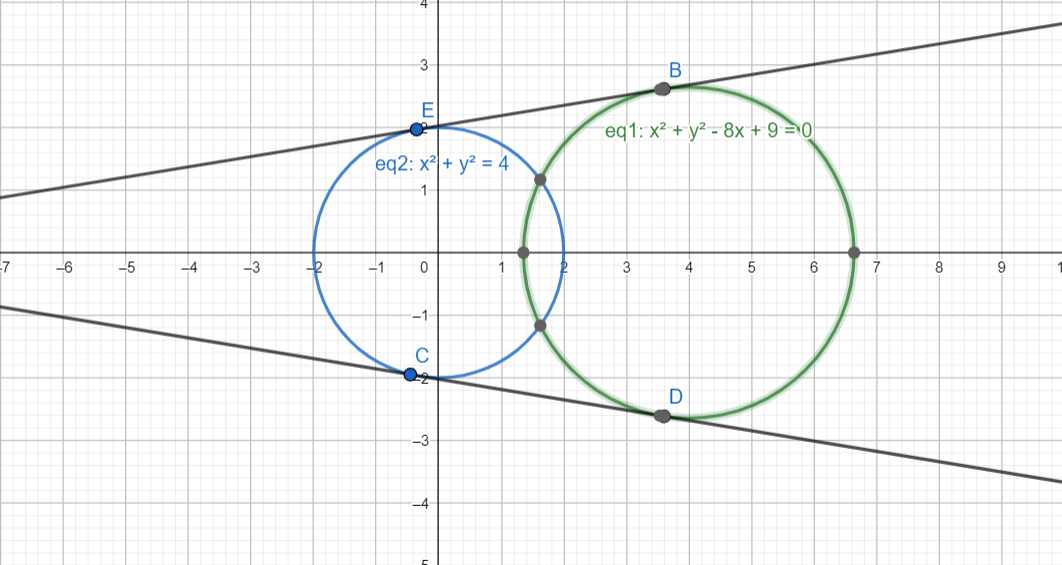
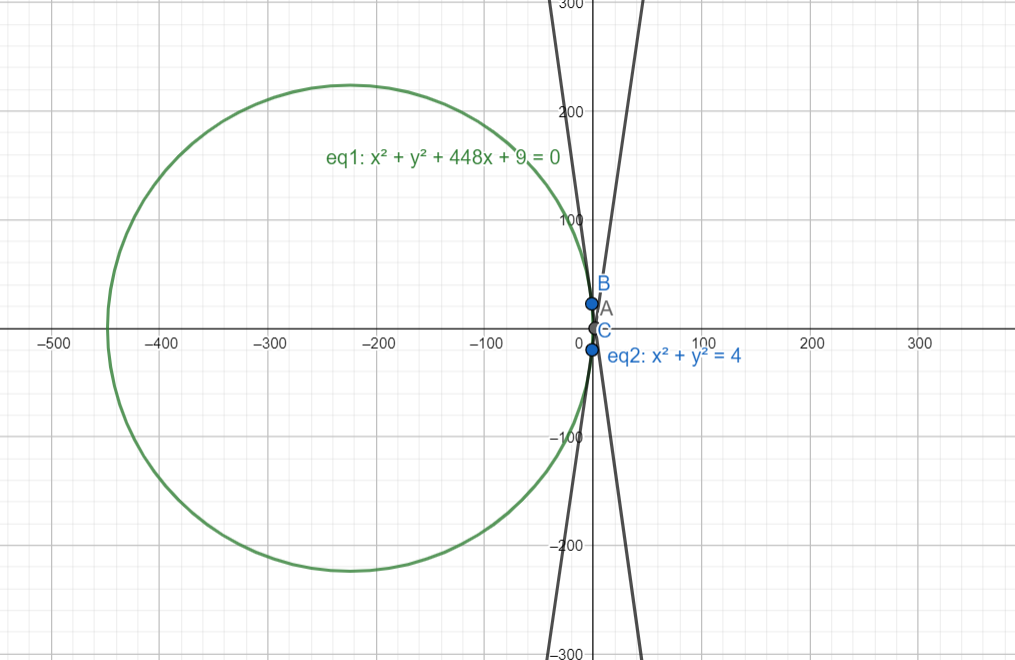
Here are the circles and their tangents with each value of $\lambda $ as given in the options :
When $\lambda $ = 8 :
When $\lambda $ = 2:
When $\lambda $ = 12 :
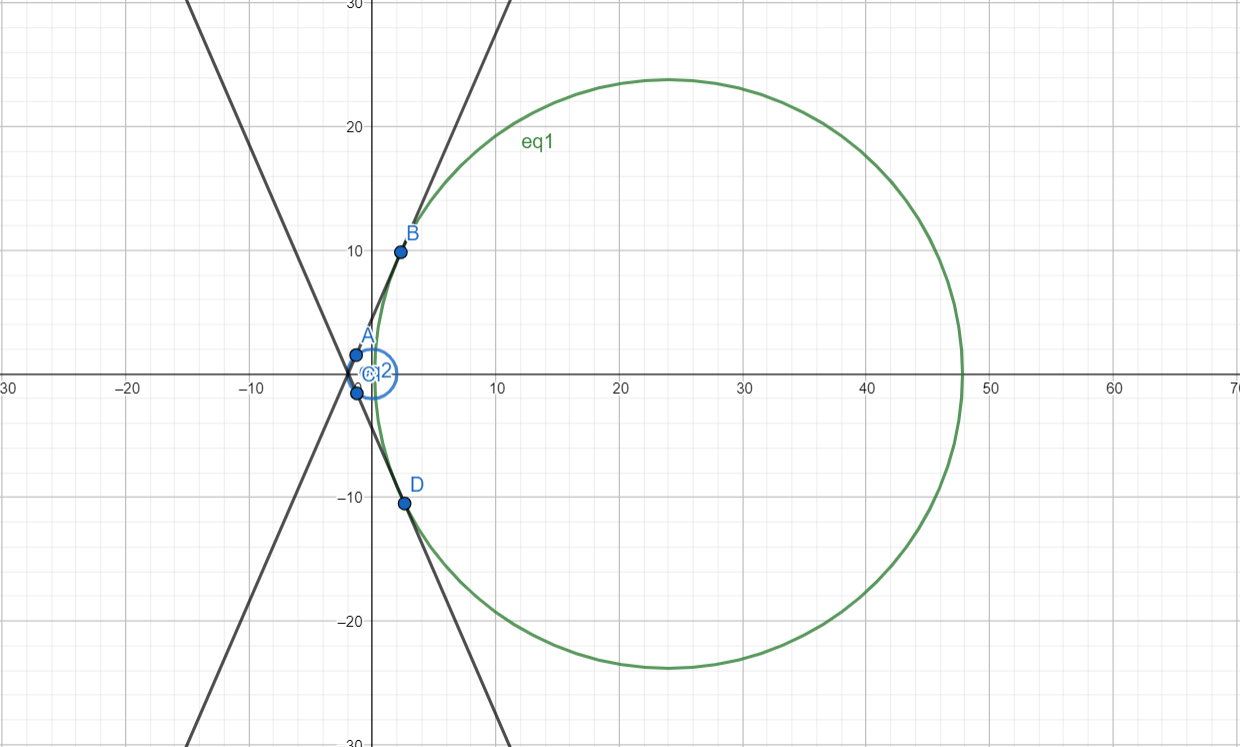
When $\lambda $ = -112 :
Complete step-by-step solution -
We know that the radius of the circle ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+2gx+2fy+c=0$ is given by $r=\sqrt{{{g}^{2}}+{{f}^{2}}-c}$ and the centre is given by $C\equiv \left( -g,-f \right)$
Consider the circle ${{S}_{1}}:{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}=4$
Here g = f = 0, c= -4
Hence the centre of the circle ${{S}_{1}}$ is given by ${{C}_{1}}\equiv \left( 0,0 \right)$
The radius of the circle ${{S}_{1}}$ is given by ${{r}_{1}}=\sqrt{{{g}^{2}}+{{f}^{2}}-c}=\sqrt{{{0}^{2}}+{{0}^{2}}-\left( -4 \right)}=2$
Consider the circle ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}-4\lambda x+9=0$
Here $g=-2\lambda ,f=0,c=9$
Hence the centre of the circle ${{S}_{2}}$ is given by ${{C}_{2}}\equiv \left( 2\lambda ,0 \right)$
The radius of the circle ${{S}_{2}}$ is given by ${{r}_{2}}=\sqrt{{{g}^{2}}+{{f}^{2}}-c}=\sqrt{4{{\lambda }^{2}}-9}$
The radius of the circle should be real.
Hence, we have
$\begin{align}
& 4{{\lambda }^{2}}-9>0 \\
& \Rightarrow {{\lambda }^{2}}-\dfrac{9}{4}>0 \\
& \Rightarrow \left( \lambda -\dfrac{3}{2} \right)\left( \lambda +\dfrac{3}{2} \right)>0 \\
& \Rightarrow \lambda \in \left( -\infty ,\dfrac{-3}{2} \right)\bigcup \left( \dfrac{3}{2},\infty \right)\text{ }\left( i \right) \\
\end{align}$
Now since the circles have only two common tangents, they must intersect at two points.
Hence, we have
$\left| {{r}_{1}}-{{r}_{2}} \right|<{{C}_{1}}{{C}_{2}}<{{r}_{1}}+{{r}_{2}}$
Now, we have
${{C}_{1}}{{C}_{2}}=\sqrt{{{\left( 2\lambda -0 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( 0-0 \right)}^{2}}}=2\left| \lambda \right|$
From the inequation $\left| {{r}_{1}}-{{r}_{2}} \right|<{{C}_{1}}{{C}_{2}}$, we have
$\left| \sqrt{4{{\lambda }^{2}}-9}-2 \right|<2\left| \lambda \right|$
Since both LHS and RHS are non-negative, squaring will not change the sense of the inequality sign.
Squaring both sides, we get
$\begin{align}
& 4{{\lambda }^{2}}-9+4-4\sqrt{4{{\lambda }^{2}}-9}<4{{\lambda }^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow -4\sqrt{4{{\lambda }^{2}}-9}-5<0 \\
& \Rightarrow 4\sqrt{4{{\lambda }^{2}}-9}>-5 \\
\end{align}$
This inequality is true for all possible values of $\lambda $ since the square root of a term is non-negative.
From the inequation ${{C}_{1}}{{C}_{2}}<\left| {{r}_{1}}+{{r}_{2}} \right|$, we have
$2\left| \lambda \right|<\sqrt{4{{\lambda }^{2}}-9}+2$
Since both LHS and RHS are non-negative, squaring will not change the sense of the inequality sign.
Squaring both sides, we get
$\begin{align}
& 4{{\lambda }^{2}}<4{{\lambda }^{2}}-9+4+4\sqrt{4{{\lambda }^{2}}-9} \\
& \Rightarrow 4\sqrt{4{{\lambda }^{2}}-9}>5 \\
\end{align}$
Squaring both sides again, we get
$\begin{align}
& 16\left( 4{{\lambda }^{2}}-9 \right)>25 \\
& \Rightarrow 4{{\lambda }^{2}}-9>\dfrac{25}{16} \\
& \Rightarrow 4{{\lambda }^{2}}>\dfrac{25+144}{16}=\dfrac{169}{16} \\
& \Rightarrow {{\lambda }^{2}}>\dfrac{169}{64} \\
& \Rightarrow \left( \lambda -\dfrac{13}{8} \right)\left( \lambda +\dfrac{13}{8} \right)>0 \\
& \Rightarrow \lambda \in \left( -\infty ,\dfrac{-13}{8} \right)\bigcup \left( \dfrac{13}{8},\infty \right)\text{ }\left( ii \right) \\
\end{align}$
From (i) and (ii), we have
$\lambda \in \left( -\infty ,\dfrac{-13}{8} \right)\bigcup \left( \dfrac{13}{8},\infty \right)$
Clearly all of the options [p],[q],[r] and [s] are in this range.
Note: To ease your understanding, here’s a plot on the number line of the possible values of $\lambda $ that we found out :

Here, A and B represent $-\dfrac{13}{8}$ and $+\dfrac{13}{8}$ respectively. The values of $\lambda $ lie on the side where the absolute of the values are >$+\dfrac{13}{8}$ .
Here are the circles and their tangents with each value of $\lambda $ as given in the options :
When $\lambda $ = 8 :

When $\lambda $ = 2:

When $\lambda $ = 12 :

When $\lambda $ = -112 :

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




