
The chords of an ellipse are drawn through the positive end of the minor axis. Then, the mid-point lies on :
a) circle
b) parabola
c) ellipse
d) hyperbola
Answer
531.9k+ views
Hint: For these kinds of questions, we make use of the concepts of ellipse. First we consider the general equation of the ellipse taken in its standard form where it’s major axis is the $x$-axis and its minor axis is the $y$-axis. Then we make use of the formula of the chord equation which is made up using the mid-points we assume. Later on we substitute the coordinates of the end of the minor axis since it is mentioned in the question that a chord is drawn through it which means the chord passes through that point.
Complete step-by-step solution:
The general equation of the ellipse taken in its standard form where it’s major axis is the $x$-axis and its minor axis is the $y$-axis is $\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1$.
Let us take a look at the picture of the ellipse to get a clear understanding .
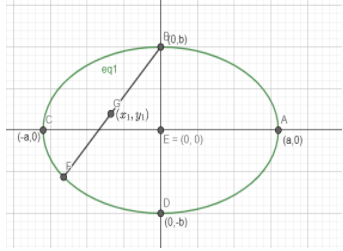
Let BF be the chord of the ellipse which has the mid-point $\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)$ .
The equation of the ellipse with the mid-point $\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)$ is ${{S}_{1}}={{S}_{11}}$ , where ${{S}_{1}}=\dfrac{x{{x}_{1}}}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{y{{y}_{1}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1$ and ${{S}_{11}}=\dfrac{{{x}_{1}}^{2}}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{{{y}_{1}}^{2}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1$ .
Let us substitute and see what we get: the equation of the chord of the ellipse is.
Upon doing so, we get the following :
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{S}_{1}}={{S}_{11}} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{x{{x}_{1}}}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{y{{y}_{1}}}{{{b}^{2}}}-1=\dfrac{{{x}_{1}}^{2}}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{{{y}_{1}}^{2}}{{{b}^{2}}}-1 \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{x{{x}_{1}}}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{y{{y}_{1}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=\dfrac{{{x}_{1}}^{2}}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{{{y}_{1}}^{2}}{{{b}^{2}}} \\
\end{align}$
The chord of the equation of the ellipse with point $\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)$ is $\dfrac{x{{x}_{1}}}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{y{{y}_{1}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=\dfrac{{{x}_{1}}^{2}}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{{{y}_{1}}^{2}}{{{b}^{2}}}$.
Now it is given in the question that this chord is drawn through the positive end of the minor axis. The positive end of the minor axis is $\left( 0,b \right)$. Let us substitute in the equation of the chord of the ellipse.
Upon doing so, we get the following :
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{x{{x}_{1}}}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{y{{y}_{1}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=\dfrac{{{x}_{1}}^{2}}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{{{y}_{1}}^{2}}{{{b}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{\left( 0 \right){{x}_{1}}}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{\left( b \right){{y}_{1}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=\dfrac{{{x}_{1}}^{2}}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{{{y}_{1}}^{2}}{{{b}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{b{{y}_{1}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=\dfrac{{{x}_{1}}^{2}}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{{{y}_{1}}^{2}}{{{b}^{2}}} \\
\end{align}$
Let us replace $\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)$ with $\left( x,y \right)$ respectively.
Upon doing so, we get the following :
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{x{{x}_{1}}}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{y{{y}_{1}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=\dfrac{{{x}_{1}}^{2}}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{{{y}_{1}}^{2}}{{{b}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{\left( 0 \right){{x}_{1}}}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{\left( b \right){{y}_{1}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=\dfrac{{{x}_{1}}^{2}}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{{{y}_{1}}^{2}}{{{b}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{b{{y}_{1}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=\dfrac{{{x}_{1}}^{2}}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{{{y}_{1}}^{2}}{{{b}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{by}{{{b}^{2}}}=\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}} \\
\end{align}\]
This is the equation of an ellipse.
$\therefore $ The chords of an ellipse are drawn through the positive end of the minor axis. Then, the mid-point lies on an ellipse. So the answer is option C.
Note: It is important to know the definitions and formulae of all the conic sections. We should also know the standard equation of all the curves when both the axes are the major axis . We should also be careful while solving as there is a lot of scope for calculation errors. If we couldn’t recognize the general equation of the ellipse in the above question, we can complete the squares and then it would like the equation of the ellipse.
Complete step-by-step solution:
The general equation of the ellipse taken in its standard form where it’s major axis is the $x$-axis and its minor axis is the $y$-axis is $\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1$.
Let us take a look at the picture of the ellipse to get a clear understanding .

Let BF be the chord of the ellipse which has the mid-point $\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)$ .
The equation of the ellipse with the mid-point $\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)$ is ${{S}_{1}}={{S}_{11}}$ , where ${{S}_{1}}=\dfrac{x{{x}_{1}}}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{y{{y}_{1}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1$ and ${{S}_{11}}=\dfrac{{{x}_{1}}^{2}}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{{{y}_{1}}^{2}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1$ .
Let us substitute and see what we get: the equation of the chord of the ellipse is.
Upon doing so, we get the following :
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{S}_{1}}={{S}_{11}} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{x{{x}_{1}}}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{y{{y}_{1}}}{{{b}^{2}}}-1=\dfrac{{{x}_{1}}^{2}}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{{{y}_{1}}^{2}}{{{b}^{2}}}-1 \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{x{{x}_{1}}}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{y{{y}_{1}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=\dfrac{{{x}_{1}}^{2}}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{{{y}_{1}}^{2}}{{{b}^{2}}} \\
\end{align}$
The chord of the equation of the ellipse with point $\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)$ is $\dfrac{x{{x}_{1}}}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{y{{y}_{1}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=\dfrac{{{x}_{1}}^{2}}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{{{y}_{1}}^{2}}{{{b}^{2}}}$.
Now it is given in the question that this chord is drawn through the positive end of the minor axis. The positive end of the minor axis is $\left( 0,b \right)$. Let us substitute in the equation of the chord of the ellipse.
Upon doing so, we get the following :
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{x{{x}_{1}}}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{y{{y}_{1}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=\dfrac{{{x}_{1}}^{2}}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{{{y}_{1}}^{2}}{{{b}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{\left( 0 \right){{x}_{1}}}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{\left( b \right){{y}_{1}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=\dfrac{{{x}_{1}}^{2}}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{{{y}_{1}}^{2}}{{{b}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{b{{y}_{1}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=\dfrac{{{x}_{1}}^{2}}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{{{y}_{1}}^{2}}{{{b}^{2}}} \\
\end{align}$
Let us replace $\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)$ with $\left( x,y \right)$ respectively.
Upon doing so, we get the following :
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{x{{x}_{1}}}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{y{{y}_{1}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=\dfrac{{{x}_{1}}^{2}}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{{{y}_{1}}^{2}}{{{b}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{\left( 0 \right){{x}_{1}}}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{\left( b \right){{y}_{1}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=\dfrac{{{x}_{1}}^{2}}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{{{y}_{1}}^{2}}{{{b}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{b{{y}_{1}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=\dfrac{{{x}_{1}}^{2}}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{{{y}_{1}}^{2}}{{{b}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{by}{{{b}^{2}}}=\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}} \\
\end{align}\]
This is the equation of an ellipse.
$\therefore $ The chords of an ellipse are drawn through the positive end of the minor axis. Then, the mid-point lies on an ellipse. So the answer is option C.
Note: It is important to know the definitions and formulae of all the conic sections. We should also know the standard equation of all the curves when both the axes are the major axis . We should also be careful while solving as there is a lot of scope for calculation errors. If we couldn’t recognize the general equation of the ellipse in the above question, we can complete the squares and then it would like the equation of the ellipse.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




