
The centroid of the triangle formed by the feet of the normals from the point \[\left( {h,k} \right)\] to the parabola\[{y^2} + 4ax = 0\],\[\left( {a > 0} \right)\] lies on
A.\[X - axis\]
B.\[Y - axis\]
C.\[x = h\]
D.\[y - k\]
Answer
568.5k+ views
Hint: Here in this question firstly we will find the value of the coordinate of the point lies on the parabola. Then we will find out the equation of the normal of the parabola. From the equation of the normal of the parabola we will find out the sum of the roots of the equation. Then we will find out the coordinates of the centroid of the triangle as coordinates of the centroid.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The given equation of the parabola is \[{y^2} + 4ax = 0\].
We will first find the coordinates of any points that lie on the parabola. So the coordinates of the point on the parabola \[{y^2} = - 4ax\] will be \[\left( { - a{t^2},2at} \right)\].
Now we have to find the equation of the normal of the parabola. We know that the equation of the normal of the parabola is \[\left( {y - {y_1}} \right) = - \dfrac{{{y_1}}}{{2a}}\left( {x - {x_1}} \right)\].
Substituting the value of the point \[\left( { - a{t^2},2at} \right)\] in the equation of the normal, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \left( {y - 2at} \right) = - \dfrac{{2at}}{{2a}}\left( {x - \left( { - a{t^2}} \right)} \right)\]
Simplifying the above equation, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \left( {y - 2at} \right) = - t\left( {x + a{t^2}} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow y - xt = 2at + a{t^3}\]
It is given in the equation that the normal is passing through the point\[\left( {h,k} \right)\].
We can represent the parabola and triangle as shown below:
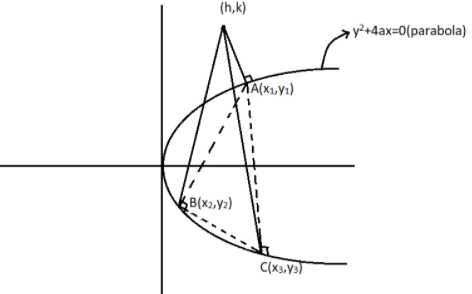
So, it will satisfy the equation of the normal. Therefore, we get
\[ \Rightarrow k - ht = 2at + a{t^3}\]
\[ \Rightarrow a{t^3} + \left( {2a + h} \right)t - k = 0\]
The above formed equation is the cubic equation whose three roots \[{t_1},{t_2},{t_3}\] are the parameters of the feet of the three normals and from the equation we can get the sum of all the roots.
Sum of the roots\[ = {t_1} + {t_2} + {t_3} = - \dfrac{{{\rm{coefficient\, of }}{\,t^2}}}{{{\rm{coefficient\, of\, }}{\,t^3}}} = 0\]
Now, we have to find out the coordinates of the centroid of the triangle. We know that the coordinates of the centroid of the triangle formed by the feet of the normals will be the average of the coordinates. Therefore the coordinates will be \[\left( {\dfrac{{{x_1} + {x_2} + {x_3}}}{3},\dfrac{{{y_1} + {y_2} + {y_3}}}{3}} \right)\]. So by putting the value of the coordinates of the point\[\left( { - a{t^2},2at} \right)\], we will get the value of the coordinates of the centroid of the triangle. Therefore,
\[\left( {\dfrac{{ - a{t_1}^2 - a{t_2}^2 - a{t_3}^2}}{3},\dfrac{{2a{t_1} + 2a{t_2} + 2a{t_3}}}{3}} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow \left( { - \dfrac{a}{3}\left( {{t_1}^2 + {t_2}^2 + {t_3}^2} \right),\dfrac{{2a}}{3}\left( {{t_1} + {t_2} + {t_3}} \right)} \right)\]
Substituting the value of \[{t_1} + {t_2} + {t_3}\] in the above equation, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \left( { - \dfrac{a}{3}\left( {{t_1}^2 + {t_2}^2 + {t_3}^2} \right),\dfrac{{2a}}{3}\left( 0 \right)} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow \left( { - \dfrac{a}{3}\left( {{t_1}^2 + {t_2}^2 + {t_3}^2} \right),0} \right)\]
We can clearly see that the value of the \[y\] coordinate is zero. So the centroid lies on the \[X\]-axis.
Hence, the centroid of the triangle formed by the feet of the normals from the point\[\left( {h,k} \right)\]to the parabola \[{y^2} + 4ax = 0\],\[\left( {a > 0} \right)\] lies on \[X - axis\].
So, option A is the correct option.
Note: Here, we have to simplify the equation by modifying the equation. When we modify the equation we have to do it according to the data given in the question. We have to note that the coordinates of the centroid of the triangle is equal to the average of the coordinates of the point lying on the parabola. The centroid of a triangle is the point of the intersection of the three medians of the triangle. We should know that the equation of the normal of the parabola should satisfy any point which lies on the curve of parabola.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The given equation of the parabola is \[{y^2} + 4ax = 0\].
We will first find the coordinates of any points that lie on the parabola. So the coordinates of the point on the parabola \[{y^2} = - 4ax\] will be \[\left( { - a{t^2},2at} \right)\].
Now we have to find the equation of the normal of the parabola. We know that the equation of the normal of the parabola is \[\left( {y - {y_1}} \right) = - \dfrac{{{y_1}}}{{2a}}\left( {x - {x_1}} \right)\].
Substituting the value of the point \[\left( { - a{t^2},2at} \right)\] in the equation of the normal, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \left( {y - 2at} \right) = - \dfrac{{2at}}{{2a}}\left( {x - \left( { - a{t^2}} \right)} \right)\]
Simplifying the above equation, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \left( {y - 2at} \right) = - t\left( {x + a{t^2}} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow y - xt = 2at + a{t^3}\]
It is given in the equation that the normal is passing through the point\[\left( {h,k} \right)\].
We can represent the parabola and triangle as shown below:

So, it will satisfy the equation of the normal. Therefore, we get
\[ \Rightarrow k - ht = 2at + a{t^3}\]
\[ \Rightarrow a{t^3} + \left( {2a + h} \right)t - k = 0\]
The above formed equation is the cubic equation whose three roots \[{t_1},{t_2},{t_3}\] are the parameters of the feet of the three normals and from the equation we can get the sum of all the roots.
Sum of the roots\[ = {t_1} + {t_2} + {t_3} = - \dfrac{{{\rm{coefficient\, of }}{\,t^2}}}{{{\rm{coefficient\, of\, }}{\,t^3}}} = 0\]
Now, we have to find out the coordinates of the centroid of the triangle. We know that the coordinates of the centroid of the triangle formed by the feet of the normals will be the average of the coordinates. Therefore the coordinates will be \[\left( {\dfrac{{{x_1} + {x_2} + {x_3}}}{3},\dfrac{{{y_1} + {y_2} + {y_3}}}{3}} \right)\]. So by putting the value of the coordinates of the point\[\left( { - a{t^2},2at} \right)\], we will get the value of the coordinates of the centroid of the triangle. Therefore,
\[\left( {\dfrac{{ - a{t_1}^2 - a{t_2}^2 - a{t_3}^2}}{3},\dfrac{{2a{t_1} + 2a{t_2} + 2a{t_3}}}{3}} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow \left( { - \dfrac{a}{3}\left( {{t_1}^2 + {t_2}^2 + {t_3}^2} \right),\dfrac{{2a}}{3}\left( {{t_1} + {t_2} + {t_3}} \right)} \right)\]
Substituting the value of \[{t_1} + {t_2} + {t_3}\] in the above equation, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \left( { - \dfrac{a}{3}\left( {{t_1}^2 + {t_2}^2 + {t_3}^2} \right),\dfrac{{2a}}{3}\left( 0 \right)} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow \left( { - \dfrac{a}{3}\left( {{t_1}^2 + {t_2}^2 + {t_3}^2} \right),0} \right)\]
We can clearly see that the value of the \[y\] coordinate is zero. So the centroid lies on the \[X\]-axis.
Hence, the centroid of the triangle formed by the feet of the normals from the point\[\left( {h,k} \right)\]to the parabola \[{y^2} + 4ax = 0\],\[\left( {a > 0} \right)\] lies on \[X - axis\].
So, option A is the correct option.
Note: Here, we have to simplify the equation by modifying the equation. When we modify the equation we have to do it according to the data given in the question. We have to note that the coordinates of the centroid of the triangle is equal to the average of the coordinates of the point lying on the parabola. The centroid of a triangle is the point of the intersection of the three medians of the triangle. We should know that the equation of the normal of the parabola should satisfy any point which lies on the curve of parabola.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




