
The centre of the circle is $\left( a+2,a-1 \right)$. Find the value of “a” if the circle passes through $\left( 2,-2 \right)$ and $\left( 8,-2 \right)$.
Answer
587.7k+ views
Hint: We have given the centre of the circle which is equal to $\left( a+2,a-1 \right)$. And it is also given that the circle passes through two points $\left( 2,-2 \right)$ and $\left( 8,-2 \right)$ so these two points are lying on the circle and we know that the length from the centre to any point on the circle is equal and is known as radius. Find the distance between the centre and the two points which are lying on the circle and then equate both the distances and find the value of “a”. The distance between the two points is calculated by using the distance formula which is equal to $\sqrt{{{\left( {{x}_{2}}-{{x}_{1}} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( {{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{1}} \right)}^{2}}}$. In this formula, $\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)\And \left( {{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}} \right)$ are the coordinates of two points.
Complete step by step answer:
We have given the centre of the circle as $\left( a+2,a-1 \right)$. Let us name this point as “O”. We have also given two points $\left( 2,-2 \right)$ and $\left( 8,-2 \right)$ through which the circle passes. Let us name these points as A and B respectively.
In the below diagram, we have shown a circle with centre O and the two points A and B are lying on the circle.
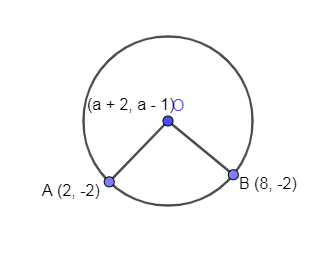
In the above diagram, we have shown the distance between O, A as OA and O, B as OB.
We know that, distance from the centre of the circle to any point on the circle is always equal so we are going to find the distances OA and OB and then equate them.
Distances between O, A and O, B are calculated using distance formula.
Let us suppose two points P $\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)$ and Q $\left( {{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}} \right)$ and the distance between them using distance formula is equal to:
$\sqrt{{{\left( {{x}_{2}}-{{x}_{1}} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( {{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{1}} \right)}^{2}}}$
Similarly, we are going to find the distance between O $\left( a+2,a-1 \right)$ and point A (2, -2).
\[\begin{align}
& OA=\sqrt{{{\left( 2-\left( a+2 \right) \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( -2-\left( a-1 \right) \right)}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow OA=\sqrt{{{\left( 2-a-2 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( -2-a+1 \right)}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow OA=\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{\left( -1-a \right)}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow OA=\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{\left( a+1 \right)}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow OA=\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{a}^{2}}+1+2a} \\
& \Rightarrow OA=\sqrt{2{{a}^{2}}+2a+1} \\
\end{align}\]
Now, we are going to find the distance between O $\left( a+2,a-1 \right)$ and point B (8, -2).
\[\begin{align}
& OB=\sqrt{{{\left( 8-\left( a+2 \right) \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( -2-\left( a-1 \right) \right)}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow OB=\sqrt{{{\left( 8-a-2 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( -2-a+1 \right)}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow OB=\sqrt{{{\left( 6-a \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( -a-1 \right)}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow OB=\sqrt{36+{{a}^{2}}-12a+{{\left( a+1 \right)}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow OB=\sqrt{36+{{a}^{2}}-12a+{{a}^{2}}+1+2a} \\
& \Rightarrow OB=\sqrt{2{{a}^{2}}-10a+37} \\
\end{align}\]
Equating OA and OB we get,
$\begin{align}
& OA=OB \\
& \Rightarrow \sqrt{2{{a}^{2}}+2a+1}=\sqrt{2{{a}^{2}}-10a+37} \\
\end{align}$
Squaring on both the sides we get,
$2{{a}^{2}}+2a+1=2{{a}^{2}}-10a+37$
In the above equation, $2{{a}^{2}}$ will be cancelled out on both the sides and we are left with the following:
$\begin{align}
& 2a+1=-10a+37 \\
& \Rightarrow 12a=36 \\
& \Rightarrow a=\dfrac{36}{12}=3 \\
\end{align}$
Hence, we got the value of “a” as 3.
Note: You can check whether the obtained value of “a” is correct or not by substituting this value of “a” in the centre of the circle and then see whether the distance from O to points A and B are equal or not.
We have obtained the value of “a” as 3. Putting this value of “a” in O $\left( a+2,a-1 \right)$ we get,
$\begin{align}
& O\left( 3+2,3-1 \right) \\
& =O\left( 5,2 \right) \\
\end{align}$
Now, finding the distance between O $\left( 5,2 \right)$ and point A (2, -2) we get,
$\begin{align}
& \sqrt{{{\left( 2-5 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( -2-2 \right)}^{2}}} \\
& =\sqrt{9+16} \\
& =\sqrt{25}=5 \\
\end{align}$
Finding the distance between O $\left( 5,2 \right)$ and point A (8, -2) we get,
$\begin{align}
& \sqrt{{{\left( 8-5 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( -2-2 \right)}^{2}}} \\
& =\sqrt{9+16} \\
& =\sqrt{25}=5 \\
\end{align}$
As you can see that we are getting the same distances from point O to A and to B so the point O that we have calculated above is correct.
Complete step by step answer:
We have given the centre of the circle as $\left( a+2,a-1 \right)$. Let us name this point as “O”. We have also given two points $\left( 2,-2 \right)$ and $\left( 8,-2 \right)$ through which the circle passes. Let us name these points as A and B respectively.
In the below diagram, we have shown a circle with centre O and the two points A and B are lying on the circle.

In the above diagram, we have shown the distance between O, A as OA and O, B as OB.
We know that, distance from the centre of the circle to any point on the circle is always equal so we are going to find the distances OA and OB and then equate them.
Distances between O, A and O, B are calculated using distance formula.
Let us suppose two points P $\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)$ and Q $\left( {{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}} \right)$ and the distance between them using distance formula is equal to:
$\sqrt{{{\left( {{x}_{2}}-{{x}_{1}} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( {{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{1}} \right)}^{2}}}$
Similarly, we are going to find the distance between O $\left( a+2,a-1 \right)$ and point A (2, -2).
\[\begin{align}
& OA=\sqrt{{{\left( 2-\left( a+2 \right) \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( -2-\left( a-1 \right) \right)}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow OA=\sqrt{{{\left( 2-a-2 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( -2-a+1 \right)}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow OA=\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{\left( -1-a \right)}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow OA=\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{\left( a+1 \right)}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow OA=\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{a}^{2}}+1+2a} \\
& \Rightarrow OA=\sqrt{2{{a}^{2}}+2a+1} \\
\end{align}\]
Now, we are going to find the distance between O $\left( a+2,a-1 \right)$ and point B (8, -2).
\[\begin{align}
& OB=\sqrt{{{\left( 8-\left( a+2 \right) \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( -2-\left( a-1 \right) \right)}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow OB=\sqrt{{{\left( 8-a-2 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( -2-a+1 \right)}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow OB=\sqrt{{{\left( 6-a \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( -a-1 \right)}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow OB=\sqrt{36+{{a}^{2}}-12a+{{\left( a+1 \right)}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow OB=\sqrt{36+{{a}^{2}}-12a+{{a}^{2}}+1+2a} \\
& \Rightarrow OB=\sqrt{2{{a}^{2}}-10a+37} \\
\end{align}\]
Equating OA and OB we get,
$\begin{align}
& OA=OB \\
& \Rightarrow \sqrt{2{{a}^{2}}+2a+1}=\sqrt{2{{a}^{2}}-10a+37} \\
\end{align}$
Squaring on both the sides we get,
$2{{a}^{2}}+2a+1=2{{a}^{2}}-10a+37$
In the above equation, $2{{a}^{2}}$ will be cancelled out on both the sides and we are left with the following:
$\begin{align}
& 2a+1=-10a+37 \\
& \Rightarrow 12a=36 \\
& \Rightarrow a=\dfrac{36}{12}=3 \\
\end{align}$
Hence, we got the value of “a” as 3.
Note: You can check whether the obtained value of “a” is correct or not by substituting this value of “a” in the centre of the circle and then see whether the distance from O to points A and B are equal or not.
We have obtained the value of “a” as 3. Putting this value of “a” in O $\left( a+2,a-1 \right)$ we get,
$\begin{align}
& O\left( 3+2,3-1 \right) \\
& =O\left( 5,2 \right) \\
\end{align}$
Now, finding the distance between O $\left( 5,2 \right)$ and point A (2, -2) we get,
$\begin{align}
& \sqrt{{{\left( 2-5 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( -2-2 \right)}^{2}}} \\
& =\sqrt{9+16} \\
& =\sqrt{25}=5 \\
\end{align}$
Finding the distance between O $\left( 5,2 \right)$ and point A (8, -2) we get,
$\begin{align}
& \sqrt{{{\left( 8-5 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( -2-2 \right)}^{2}}} \\
& =\sqrt{9+16} \\
& =\sqrt{25}=5 \\
\end{align}$
As you can see that we are getting the same distances from point O to A and to B so the point O that we have calculated above is correct.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

How do I convert ms to kmh Give an example class 11 physics CBSE




