
The centre of curvature of a _______ mirror is in front of it.
A. Convex
B. Concave
C. Convex or concave
D. None of these
Answer
522k+ views
Hint: Keep in mind where the centre of the sphere lies. Remember the basic structure and formation of both the spherical mirrors and you have your answer!
Complete step by step answer:
There are two prominent types of mirrors: Plane mirrors and Spherical mirrors
Plane mirrors have a flat reflective surface. A plane mirror always forms a virtual and upright image of the same size as the object.
A spherical mirror as the name suggests is a mirror with a curved reflecting surface. It is formed as if it is cut out of a spherical surface. Spherical mirrors have a constant radius of curvature. There are two types of spherical mirrors:
Concave mirrors
Convex mirrors
If we cut a hollow sphere into parts and paint the outer surface of the cut parts , the inner surface becomes the reflecting surface and both the parts can be termed as concave mirrors.
If we cut the hollow sphere into parts and paint the inner surfaces, the outer surface becomes the reflecting surface and such mirrors are called convex mirrors.
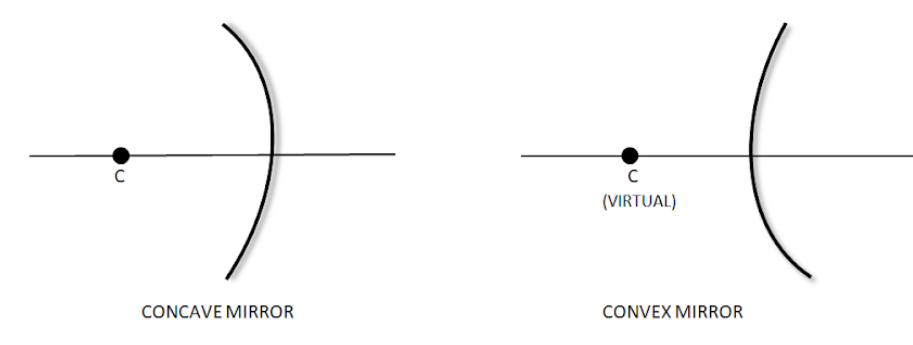
Centre of curvature of a spherical mirror is the centre of the hollow sphere of which the mirror was a part.
Centre of curvature of a concave mirror lies in front of it. Rays parallel to the principal axis pass through the focus after reflection.
Centre of curvature of a convex mirror is imaginary. In case of convex mirrors the rays appear to emerge from a virtual focus.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: Note that both are a part of the same hollow sphere but one has a real centre of curvature and the other has a virtual one. Remember that the concave mirror is a converging one with a real focus and convex is a diverging mirror with a virtual focus.
Complete step by step answer:
There are two prominent types of mirrors: Plane mirrors and Spherical mirrors
Plane mirrors have a flat reflective surface. A plane mirror always forms a virtual and upright image of the same size as the object.
A spherical mirror as the name suggests is a mirror with a curved reflecting surface. It is formed as if it is cut out of a spherical surface. Spherical mirrors have a constant radius of curvature. There are two types of spherical mirrors:
Concave mirrors
Convex mirrors
If we cut a hollow sphere into parts and paint the outer surface of the cut parts , the inner surface becomes the reflecting surface and both the parts can be termed as concave mirrors.
If we cut the hollow sphere into parts and paint the inner surfaces, the outer surface becomes the reflecting surface and such mirrors are called convex mirrors.

Centre of curvature of a spherical mirror is the centre of the hollow sphere of which the mirror was a part.
Centre of curvature of a concave mirror lies in front of it. Rays parallel to the principal axis pass through the focus after reflection.
Centre of curvature of a convex mirror is imaginary. In case of convex mirrors the rays appear to emerge from a virtual focus.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: Note that both are a part of the same hollow sphere but one has a real centre of curvature and the other has a virtual one. Remember that the concave mirror is a converging one with a real focus and convex is a diverging mirror with a virtual focus.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 8 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 8 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 8 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

Citizens of India can vote at the age of A 18 years class 8 social science CBSE

Full form of STD, ISD and PCO

Advantages and disadvantages of science

Right to vote is a AFundamental Right BFundamental class 8 social science CBSE

What are the 12 elements of nature class 8 chemistry CBSE




