
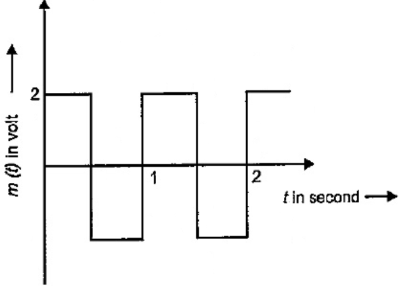
The carrier wave is represented by C (t) = 5 Sin (10πt) volt. A modulating signal is a square wave as shown in the figure. Determine the modulation index.

Answer
608.7k+ views
- Hint: To find the modulation index, we apply the formula of it using the required variables given in the equation of the carrier wave and the figure. We look at the general form of the carrier wave to derive the amplitude from the given equation.
Complete step-by-step solution -
Given data,
Carrier wave, C (t) = 5 Sin (10πt)
A carrier wave is a wave of constant frequency. It has the properties of a sine wave. We know the general equation of a sine wave is C = A sin (ωt), where A is the amplitude of the wave.
Comparing this general equation to the given carrier wave equation, C (t) = 5 Sin (10πt)
We can say that the amplitude of the carrier wave is ${{\text{A}}_{\text{c}}} = 5$.
Now let us look at the modulating wave given in the figure,
We know the amplitude of a wave is the maximum value a particle in a wave reaches from its equilibrium position.
Therefore from the figure we could say that the amplitude of the modulating wave is${{\text{A}}_{\text{m}}} = 2$.
Modulating Index is defined as the range of the modulated variable of a carrier signal varies around its unmodulated level.
It is given by the formula
${\text{M}}{\text{.I = }}{\mu _{\text{a}}} = \dfrac{{{{\text{A}}_{\text{m}}}}}{{{{\text{A}}_{\text{c}}}}}$
$ \Rightarrow {\text{M}}{\text{.I = }}\dfrac{2}{5} = 0.4$
The modulation index of the wave is 0.4
Note – In order to answer this type of question the key is to know the general form of a carrier wave is a sine wave, using this we find its amplitude. Also looking at the graph we infer the amplitude of the modulating wave. We do not consider the sign while counting the amplitude, we only consider its magnitude. There are different modulation indexes for amplitude modulation and frequency modulation respectively.
Complete step-by-step solution -
Given data,
Carrier wave, C (t) = 5 Sin (10πt)
A carrier wave is a wave of constant frequency. It has the properties of a sine wave. We know the general equation of a sine wave is C = A sin (ωt), where A is the amplitude of the wave.
Comparing this general equation to the given carrier wave equation, C (t) = 5 Sin (10πt)
We can say that the amplitude of the carrier wave is ${{\text{A}}_{\text{c}}} = 5$.
Now let us look at the modulating wave given in the figure,
We know the amplitude of a wave is the maximum value a particle in a wave reaches from its equilibrium position.
Therefore from the figure we could say that the amplitude of the modulating wave is${{\text{A}}_{\text{m}}} = 2$.
Modulating Index is defined as the range of the modulated variable of a carrier signal varies around its unmodulated level.
It is given by the formula
${\text{M}}{\text{.I = }}{\mu _{\text{a}}} = \dfrac{{{{\text{A}}_{\text{m}}}}}{{{{\text{A}}_{\text{c}}}}}$
$ \Rightarrow {\text{M}}{\text{.I = }}\dfrac{2}{5} = 0.4$
The modulation index of the wave is 0.4
Note – In order to answer this type of question the key is to know the general form of a carrier wave is a sine wave, using this we find its amplitude. Also looking at the graph we infer the amplitude of the modulating wave. We do not consider the sign while counting the amplitude, we only consider its magnitude. There are different modulation indexes for amplitude modulation and frequency modulation respectively.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE

Explain sex determination in humans with line diag class 12 biology CBSE

Organisms of a higher trophic level which feed on several class 12 biology CBSE




