
The cardiac cycle in a normal subject is about-
(a) 0.5 second
(b) 0.8 second
(c) 1.0 second
(d) 1.2 second
Answer
573.3k+ views
Hint: Events of the cardiac cycle can be split into diastole and systole. Ventricular filling is represented by diastole and ventricular contraction/ejection is represented by systole. Systole and diastole, albeit with very distinct pressures, occur in both the right and left heart (see hemodynamics below). There are 65 to 75 heartbeats (cardiac cycles) per minute for the average adult human at rest.
Complete answer:
A heart cycle contains all of the activities that occur during one heartbeat and has three stages. Atrial systole (0.15 sec) is the first step in which all atria are in systole (contracted) and diastole (relaxed) ventricles. The rising blood pressure contributes to the entry of blood through opened AV valves into two ventricles while the semilunar valves are closed. This is accompanied by ventricular systole, where both ventricles are in systole while the atria are in diastole (0.30 sec). Rising blood pressure in the ventricles pushes the blood through opened semilunar valves to penetrate the pulmonary trunk and aorta while the atrioventricular valves are closed.
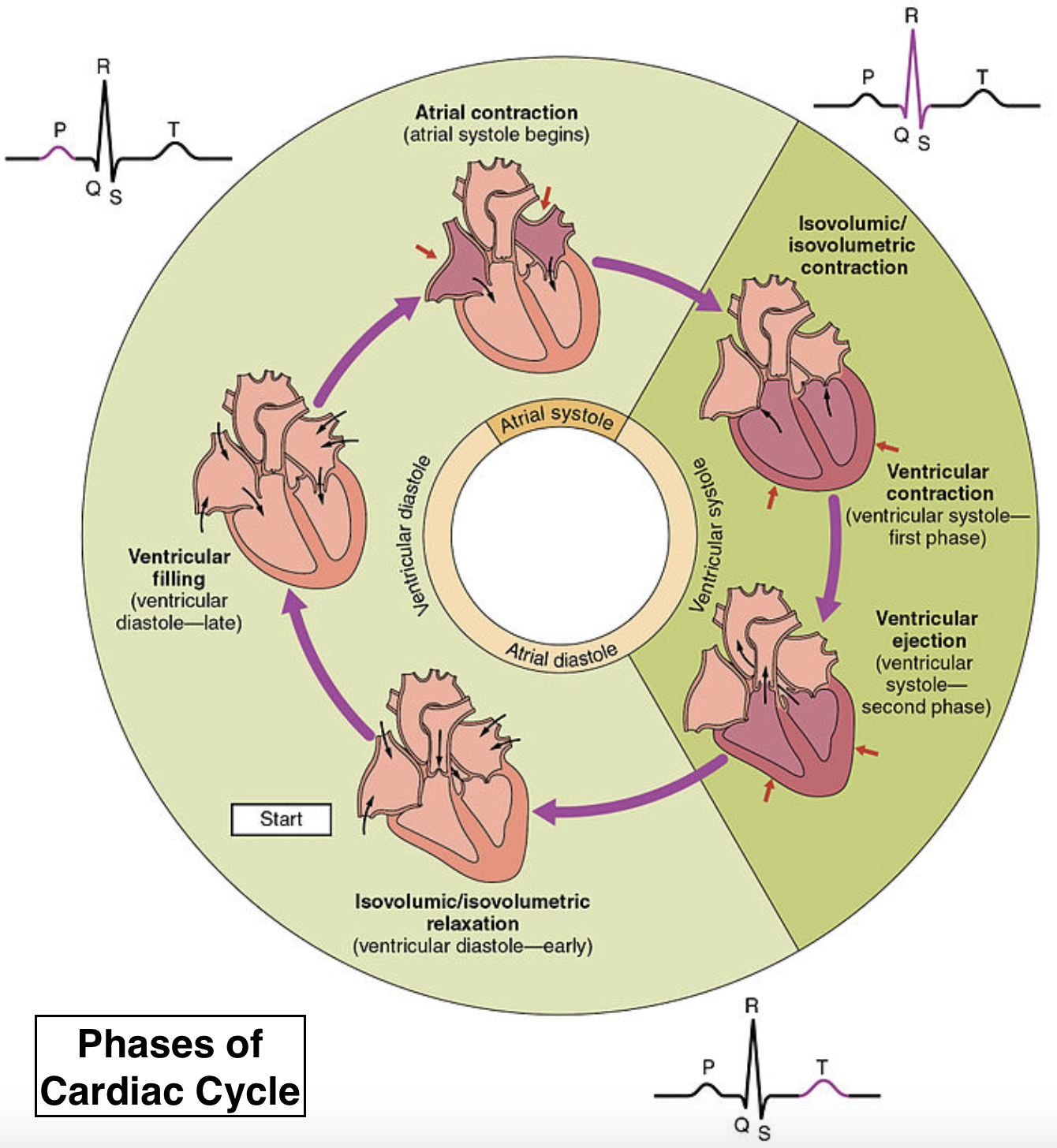
The last stage is atrial and ventricular diastole (0.40 sec) in which the two atria and the two ventricles are in diastole with low blood pressure. The superior and inferior venae cavae and the pulmonary veins fill the blood in the right and left atria, which then passively flows into the ventricles. Both auriculoventricular valves are open at this moment, and the semilunar valves are closed. Thus, atrial systole (0.15 sec) + ventricular systole (0.30 sec) + atrial and ventricular diastole (0.40 sec) = 0.85 sec is the length of one cardiac cycle.
Additional information: The heart is a four- chambered organ called the right heart and the left heart, which consists of the right and left halves. The upper two chambers, the left, and right atria are entry points into the heart for the return of blood supply from the circulatory system, while the contractions that expel blood from the heart to supply through the circulatory system are carried out by the two lower chambers, the left, and right ventricles. Circulation is divided into the pulmonary circulation, through which the right ventricle pumps oxygen- depleted blood via the pulmonary trunk and arteries into the lungs; or systemic circulation, through which newly oxygenated blood is pumped/expelled throughout the body by the left ventricle through the aorta and all other arteries.
So, the correct answer is ‘(b) 0.8 second’.
Note:
- For a human, the typical heart is the size of a palm.
- Per day, your heart will beat about 115,000 times.
- Every day, the heart pumps about 2,000 gallons of blood.
- The rhythm of your heart is regulated by an electrical mechanism.
- And when it's removed from the body, the heart will continue pounding.
Complete answer:
A heart cycle contains all of the activities that occur during one heartbeat and has three stages. Atrial systole (0.15 sec) is the first step in which all atria are in systole (contracted) and diastole (relaxed) ventricles. The rising blood pressure contributes to the entry of blood through opened AV valves into two ventricles while the semilunar valves are closed. This is accompanied by ventricular systole, where both ventricles are in systole while the atria are in diastole (0.30 sec). Rising blood pressure in the ventricles pushes the blood through opened semilunar valves to penetrate the pulmonary trunk and aorta while the atrioventricular valves are closed.

The last stage is atrial and ventricular diastole (0.40 sec) in which the two atria and the two ventricles are in diastole with low blood pressure. The superior and inferior venae cavae and the pulmonary veins fill the blood in the right and left atria, which then passively flows into the ventricles. Both auriculoventricular valves are open at this moment, and the semilunar valves are closed. Thus, atrial systole (0.15 sec) + ventricular systole (0.30 sec) + atrial and ventricular diastole (0.40 sec) = 0.85 sec is the length of one cardiac cycle.
Additional information: The heart is a four- chambered organ called the right heart and the left heart, which consists of the right and left halves. The upper two chambers, the left, and right atria are entry points into the heart for the return of blood supply from the circulatory system, while the contractions that expel blood from the heart to supply through the circulatory system are carried out by the two lower chambers, the left, and right ventricles. Circulation is divided into the pulmonary circulation, through which the right ventricle pumps oxygen- depleted blood via the pulmonary trunk and arteries into the lungs; or systemic circulation, through which newly oxygenated blood is pumped/expelled throughout the body by the left ventricle through the aorta and all other arteries.
So, the correct answer is ‘(b) 0.8 second’.
Note:
- For a human, the typical heart is the size of a palm.
- Per day, your heart will beat about 115,000 times.
- Every day, the heart pumps about 2,000 gallons of blood.
- The rhythm of your heart is regulated by an electrical mechanism.
- And when it's removed from the body, the heart will continue pounding.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




