
The carboxyl functional group (—COOH) is present in:
A) Picric acid
B) Barbituric acid
C) Ascorbic acid
D) Aspirin
Answer
598.2k+ views
Hint: A carboxylic acid is a functional group in which the carbon atoms bonded to the oxygen atom by a double bond. The hydroxyl group $\text{-OH}$ is bounded by a single bond. The fourth bond is bonded to the alkyl or the aryl group. However, some compounds contain the acidic proton which is bonded to oxygen or nitrogen can act as an acid too.
Complete step by step solution:
A carboxylic acid is an organic compound that has a carboxyl group $\text{(-COOH)}$ that is attached to the R-group. The R can be alkyl or aryl. The general formula is $\text{(R-COOH)}$.
Let us have a look at each option to get the answer:
Picric acid is a derivative of phenol. Phenol is a weak acid due to the presence of the hydroxyl group on it. Which dissociates to form ${{\text{H}}^{\text{+}}}$ ions in the solution. The picric acid which is a trinitro derivative of phenol has high acidic strength. The structure is as shown below,
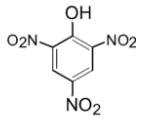
It does not contain the carboxylic acid $\text{(-COOH)}$ group in it. Thus picric acid is not a carboxylic acid.
Hence, option (A) cannot be true.
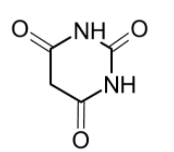
Barbituric acid is acid. It has a pyrimidine heterocyclic structure. It contains the carbonyl group and the $\text{-NH}$ group. Therefore the $\text{ }\!\!\alpha\!\!\text{ -Carbon}$ have the reactive hydrogen atoms which are acidic. These protons on the amino groups give the acidic strength to the barbituric acid. Since I do not contain the carboxylic acid $\text{(-COOH)}$ group, the option (B) cannot be true.
Ascorbic acid is also found to be acidic. It vigorously generates the ascorbate anion in the solution when one of the hydroxyl groups get deprotonated. The structure of ascorbic acid is as shown below,
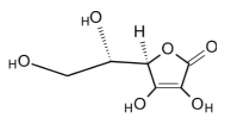
It exhibits the acidic properties due to the presence of acidic protons on the hydroxyl group. But it does not have a carboxylic acid group $\text{(-COOH)}$.hence the ascorbic acid cannot be treated as the carboxylic acid and thus, option (C) cannot be true.
The aspirin is also called as the acetylsalicylic acid or 2-acetoxybenzoic acid. It is a salicylic acid derivative where the hydroxyl group of salicylic acid undergoes the acetylation. It contains three groups:
1) Carboxylic acid functional group (R-COOH)
2) Ester functional group (R-O-CO-R')
3) Aromatic group (benzene ring)
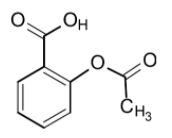
The acidity of the aspirin arises due to the loss of a proton. It is a weak acid.
It contains the carboxylic acid group.
Hence, the option (D) is the correct option.
Note: The acidity can arise due to the acidic proton which can be bonded to the electronegative atom. For example, the phenols are acidic since the hydrogen is bonded to the oxygen which withdraws the electron density. The amino group can also donate its proton.
Complete step by step solution:
A carboxylic acid is an organic compound that has a carboxyl group $\text{(-COOH)}$ that is attached to the R-group. The R can be alkyl or aryl. The general formula is $\text{(R-COOH)}$.
Let us have a look at each option to get the answer:
Picric acid is a derivative of phenol. Phenol is a weak acid due to the presence of the hydroxyl group on it. Which dissociates to form ${{\text{H}}^{\text{+}}}$ ions in the solution. The picric acid which is a trinitro derivative of phenol has high acidic strength. The structure is as shown below,

It does not contain the carboxylic acid $\text{(-COOH)}$ group in it. Thus picric acid is not a carboxylic acid.
Hence, option (A) cannot be true.
Barbituric acid is acid. It has a pyrimidine heterocyclic structure. It contains the carbonyl group and the $\text{-NH}$ group. Therefore the $\text{ }\!\!\alpha\!\!\text{ -Carbon}$ have the reactive hydrogen atoms which are acidic. These protons on the amino groups give the acidic strength to the barbituric acid. Since I do not contain the carboxylic acid $\text{(-COOH)}$ group, the option (B) cannot be true.

Ascorbic acid is also found to be acidic. It vigorously generates the ascorbate anion in the solution when one of the hydroxyl groups get deprotonated. The structure of ascorbic acid is as shown below,

It exhibits the acidic properties due to the presence of acidic protons on the hydroxyl group. But it does not have a carboxylic acid group $\text{(-COOH)}$.hence the ascorbic acid cannot be treated as the carboxylic acid and thus, option (C) cannot be true.
The aspirin is also called as the acetylsalicylic acid or 2-acetoxybenzoic acid. It is a salicylic acid derivative where the hydroxyl group of salicylic acid undergoes the acetylation. It contains three groups:
1) Carboxylic acid functional group (R-COOH)
2) Ester functional group (R-O-CO-R')
3) Aromatic group (benzene ring)

The acidity of the aspirin arises due to the loss of a proton. It is a weak acid.
It contains the carboxylic acid group.
Hence, the option (D) is the correct option.
Note: The acidity can arise due to the acidic proton which can be bonded to the electronegative atom. For example, the phenols are acidic since the hydrogen is bonded to the oxygen which withdraws the electron density. The amino group can also donate its proton.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Coming together federation is practiced in A India class 12 social science CBSE

Write the formula to find the shortest distance between class 12 maths CBSE




