
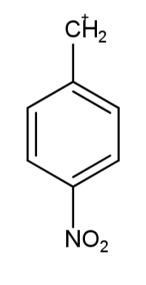
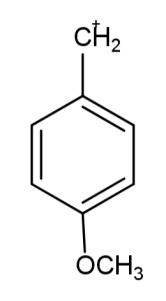
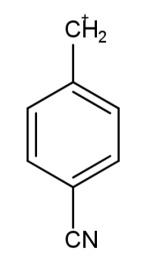
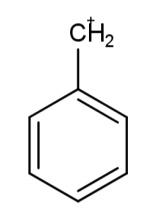
The carbocation which is most stable is:
A.
B.
C.
D.




Answer
521.4k+ views
Hint: Carbon having a positive charge is called a carbocation, while when it contains a negative charge it is called a carbanion. These are reactive intermediates and the majority of the reactions occur by the formation of carbocation and carbanions. These species are highly reactive and short living therefore carries out a reaction.
Complete answer:
A carbocation is a highly reactive and unstable substance that is an intermediate that is formed in the middle of various reactions. Through the carbocation formation, the organic compounds are able to react and form different products. A carbon, when forms a cation with 6 electrons in its valence shell, is formed by the heterolytic cleavage of a covalent bond that leads to the formation of carbocations.
The factors that define the stability of the carbocation are the multiplicity in the bonds and the presence of the number of carbon atoms, this leads to the increase in the electron density that leads to more delocalization of electrons and hence more stability. The electron donating groups like methoxy and alkyl groups increase the electron density, while the electron withdrawing groups like nitro and cyanide groups decrease the density of electrons leading to less stabilization. So, carbocation in the second option has the most stability due to the methoxy group attached.
Hence, the most stable carbocation is option B.
Note: A
As the number of carbon atoms affects stability of carbocation, the order of stability of carbocation becomes, $3{}^\circ >2{}^\circ >1{}^\circ >0{}^\circ $ these are the degree of carbons. For a carbanion the order is opposite as that of the carbocation. This is because carbanions consist of a negative charge.
Complete answer:
A carbocation is a highly reactive and unstable substance that is an intermediate that is formed in the middle of various reactions. Through the carbocation formation, the organic compounds are able to react and form different products. A carbon, when forms a cation with 6 electrons in its valence shell, is formed by the heterolytic cleavage of a covalent bond that leads to the formation of carbocations.
The factors that define the stability of the carbocation are the multiplicity in the bonds and the presence of the number of carbon atoms, this leads to the increase in the electron density that leads to more delocalization of electrons and hence more stability. The electron donating groups like methoxy and alkyl groups increase the electron density, while the electron withdrawing groups like nitro and cyanide groups decrease the density of electrons leading to less stabilization. So, carbocation in the second option has the most stability due to the methoxy group attached.
Hence, the most stable carbocation is option B.
Note: A
As the number of carbon atoms affects stability of carbocation, the order of stability of carbocation becomes, $3{}^\circ >2{}^\circ >1{}^\circ >0{}^\circ $ these are the degree of carbons. For a carbanion the order is opposite as that of the carbocation. This is because carbanions consist of a negative charge.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




