
The bond order of $C_{2}^{+}$ is
(A) 1
(B) 2
(C) $\dfrac{3}{2}$
(D) $\dfrac{1}{2}$
Answer
540.3k+ views
Hint: To solve this question, we first need to know what is bond order. The number of chemical bonds through which a pair of atoms are bonded is known as the bond order. The bond order of a molecule can be determined through the concept of molecular orbital theory.
Complete answer:
Now, to determine the bond order of $C_{2}^{+}$, we first need to draw its molecular orbital diagram.
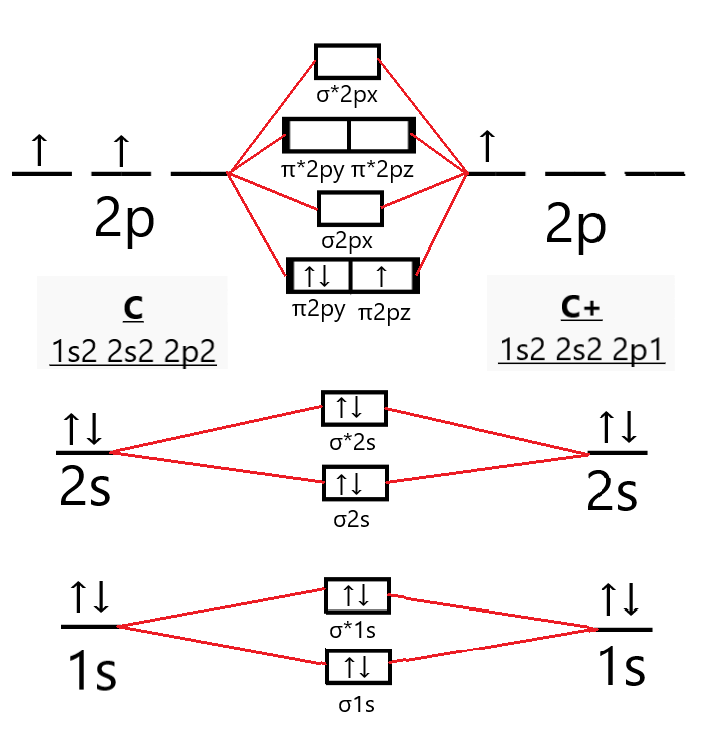
So, the electronic configuration of the $C_{2}^{+}$ molecule according to the molecular orbital theory is
\[C_{2}^{+}={{(\sigma 1s)}^{2}}{{(\sigma *1s)}^{2}}{{(\sigma 2s)}^{2}}{{(\sigma *2s)}^{2}}{{(\pi 2py)}^{2}}{{(\pi 2pz)}^{1}}\]
Where $\sigma /\pi $ orbitals depict bonding molecular orbitals whereas $\pi */\sigma *$ depict antibonding molecular orbitals.
Now, the bond order of a molecule is given by the formula
\[BO=\dfrac{1}{2}[{{N}_{b}}-{{N}_{a}}]\]
Where the number of electrons in the bonding orbitals is denoted by ${{N}_{b}}$ and the number of electrons in the antibonding orbitals is denoted by ${{N}_{a}}$.
From the molecular orbital diagram of the $C_{2}^{+}$ molecule we can see that it has 7 electrons in its bonding orbitals (${{N}_{b}}$) and 4 electrons in its antibonding orbitals (${{N}_{a}}$).
So, its bond order will be
\[\begin{align}
& B{{O}_{C_{2}^{+}}}=\dfrac{1}{2}[7-4] \\
& B{{O}_{C_{2}^{+}}}=\dfrac{3}{2} \\
\end{align}\]
Hence the correct answer is option (C) $\dfrac{3}{2}$.
Additional Information:
When a molecule has an unpaired electron in its orbital, it has a net spin value and hence is paramagnetic.
Whereas if a molecule does not have an unpaired electron in its orbital, it has a 0 net spin value and hence is diamagnetic.
In $C_{2}^{+}$, the $\pi 2pz$ orbital has an unpaired electron; hence the molecule is paramagnetic.
Note:
It should be noted that the stability of a bond can be indicated by bond order. The higher the bond order of a molecule, the more the atoms are held together tightly due to an increase in attraction between its electrons.
Complete answer:
Now, to determine the bond order of $C_{2}^{+}$, we first need to draw its molecular orbital diagram.

So, the electronic configuration of the $C_{2}^{+}$ molecule according to the molecular orbital theory is
\[C_{2}^{+}={{(\sigma 1s)}^{2}}{{(\sigma *1s)}^{2}}{{(\sigma 2s)}^{2}}{{(\sigma *2s)}^{2}}{{(\pi 2py)}^{2}}{{(\pi 2pz)}^{1}}\]
Where $\sigma /\pi $ orbitals depict bonding molecular orbitals whereas $\pi */\sigma *$ depict antibonding molecular orbitals.
Now, the bond order of a molecule is given by the formula
\[BO=\dfrac{1}{2}[{{N}_{b}}-{{N}_{a}}]\]
Where the number of electrons in the bonding orbitals is denoted by ${{N}_{b}}$ and the number of electrons in the antibonding orbitals is denoted by ${{N}_{a}}$.
From the molecular orbital diagram of the $C_{2}^{+}$ molecule we can see that it has 7 electrons in its bonding orbitals (${{N}_{b}}$) and 4 electrons in its antibonding orbitals (${{N}_{a}}$).
So, its bond order will be
\[\begin{align}
& B{{O}_{C_{2}^{+}}}=\dfrac{1}{2}[7-4] \\
& B{{O}_{C_{2}^{+}}}=\dfrac{3}{2} \\
\end{align}\]
Hence the correct answer is option (C) $\dfrac{3}{2}$.
Additional Information:
When a molecule has an unpaired electron in its orbital, it has a net spin value and hence is paramagnetic.
Whereas if a molecule does not have an unpaired electron in its orbital, it has a 0 net spin value and hence is diamagnetic.
In $C_{2}^{+}$, the $\pi 2pz$ orbital has an unpaired electron; hence the molecule is paramagnetic.
Note:
It should be noted that the stability of a bond can be indicated by bond order. The higher the bond order of a molecule, the more the atoms are held together tightly due to an increase in attraction between its electrons.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

Actinoid contraction is more than lanthanoid contraction class 11 chemistry CBSE

The transition element that has lowest enthalpy of class 11 chemistry CBSE

Can anyone list 10 advantages and disadvantages of friction

State the laws of reflection of light




