
The bond dissociation energy of B – F in $B{{F}_{3}}$ is 646KJ/mol whereas that of C – F in $C{{F}_{4}}$ is 515KJ/mol. Comment on the above statements.
[A] Stronger $\sigma $ bond between B and F in $B{{F}_{3}}$ as compared to that between C and F in $C{{F}_{4}}$
[B] Significant $p\pi -p\pi $ interaction between B and F in $B{{F}_{3}}$ whereas no possibility of such interaction between C and F in $C{{F}_{4}}$
[C] Lower degree of $p\pi -p\pi $ interaction between B and F in $B{{F}_{3}}$than that between C and F in $C{{F}_{4}}$
[D] Smaller size of B atom as compared to C atom.
Answer
585.6k+ views
HINT: Bond dissociation energy is the energy required for the breaking of a bond. A sigma and a pi-bond required higher dissociation energy than a sigma-bond. See the bonding in the given compounds to answer the question.
COMPLETE STEP BY STEP SOLUTION: To solve this question, firstly we have to understand what bond dissociation energy is.
The energy required for the breaking of a bond is known as the bond dissociation energy. It gives us the strength of a chemical bond. Stronger the bond, higher is the energy required to break the bond and thus higher is the bond dissociation energy.
Now, in the question it is given to us that the bond dissociation energy of B – F in $B{{F}_{3}}$ is 646KJ/mol whereas that of C – F in $C{{F}_{4}}$ is 515KJ/mol so we can understand that the B – F bond is stronger than the C – F bond.
So, let us now discuss the reason for the higher bond dissociation energy of B – F bond.
In $B{{F}_{3}}$, after bonding with the 3 fluorine atoms, boron still has empty p-orbitals which can be undergo a back bonding with the energetically available p-orbitals of fluorine whereas in $C{{F}_{4}}$, all the p-orbitals of carbon are engaged in bonding with the fluorine atoms and there is no possibility of back-bonding. We can represent the back bonding of B – F as-
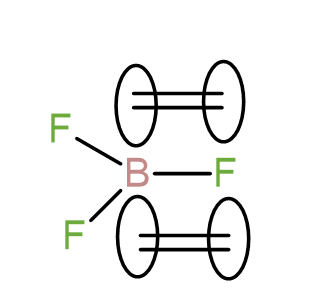
Due to this back bonding, the bond strength of B – F bond increases leading to increase in the bond dissociation energy.
We can understand from the above discussion that due to the presence of vacant p-orbitals boron can undergo back bonding with fluorine atoms leading to higher bond dissociation energy.
Therefore, the correct answer is option [B] Significant $p\pi -p\pi $ interaction between B and F in $B{{F}_{3}}$ whereas no possibility of such interaction between C and F in $C{{F}_{4}}$.
NOTE: Bonds can be broken either homolytically or heterolytically. Bond dissociation energy usually refers to the homolytic case. Here, two electrons which were engaged in the formation of the bond go back to their original atoms as the bond breaks.
COMPLETE STEP BY STEP SOLUTION: To solve this question, firstly we have to understand what bond dissociation energy is.
The energy required for the breaking of a bond is known as the bond dissociation energy. It gives us the strength of a chemical bond. Stronger the bond, higher is the energy required to break the bond and thus higher is the bond dissociation energy.
Now, in the question it is given to us that the bond dissociation energy of B – F in $B{{F}_{3}}$ is 646KJ/mol whereas that of C – F in $C{{F}_{4}}$ is 515KJ/mol so we can understand that the B – F bond is stronger than the C – F bond.
So, let us now discuss the reason for the higher bond dissociation energy of B – F bond.
In $B{{F}_{3}}$, after bonding with the 3 fluorine atoms, boron still has empty p-orbitals which can be undergo a back bonding with the energetically available p-orbitals of fluorine whereas in $C{{F}_{4}}$, all the p-orbitals of carbon are engaged in bonding with the fluorine atoms and there is no possibility of back-bonding. We can represent the back bonding of B – F as-

Due to this back bonding, the bond strength of B – F bond increases leading to increase in the bond dissociation energy.
We can understand from the above discussion that due to the presence of vacant p-orbitals boron can undergo back bonding with fluorine atoms leading to higher bond dissociation energy.
Therefore, the correct answer is option [B] Significant $p\pi -p\pi $ interaction between B and F in $B{{F}_{3}}$ whereas no possibility of such interaction between C and F in $C{{F}_{4}}$.
NOTE: Bonds can be broken either homolytically or heterolytically. Bond dissociation energy usually refers to the homolytic case. Here, two electrons which were engaged in the formation of the bond go back to their original atoms as the bond breaks.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




