
The block of mass M moving on the frictionless horizontal surface collides with a spring of spring constant K and compresses it by length L. The maximum momentum of the block after collision is:
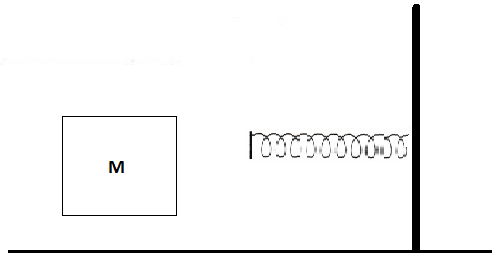
A. Zero
B. \[\dfrac{{M{L^2}}}{K}\]
C. \[\sqrt {MK} L\]
D. \[\dfrac{{K{L^2}}}{{2M}}\]

Answer
609.6k+ views
Hint: In this question, we will use the principle of conservation of mechanical energy. This principle states that if only the conservative forces doing work on the body, then its mechanical energy ( kinetic energy + potential energy ) remains constant i.e. K.E + P.E = E(constant).
Complete step-by-step solution -
Formula used: K.E = $\dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2}$, P.E of stretched string = $\dfrac{1}{2}k{x^2}$, P = mv and $K.E + P.E = E({\text{constant)}}$.
We know that, if only the conservative forces are doing work on the body, then its mechanical energy ( kinetic energy + potential energy ) remains constant. It can be written as:
$ \Rightarrow K.E + P.E = E({\text{constant)}}$.
$ \Rightarrow $ $\vartriangle K + \vartriangle U = 0$
$ \Rightarrow $ $\vartriangle K = - \vartriangle U$.
If the initial velocity of the moving block is v, then the kinetic energy will be,
$ \Rightarrow K.E = \dfrac{1}{2}Mv_{\max }^2$.
As we know that the potential energy of a stretched string is $\dfrac{1}{2}k{x^2}$.
So the potential energy due to the spring is = $\dfrac{1}{2}K{L^2}$.
So now, according to the principle of conservation of energy,
Energy can neither be created nor destroyed. It may be transformed from one form to another.
So, when the spring gets compressed by length L,
K.E lost by mass M = P.E stored in the compressed spring.
$ \Rightarrow $ K.E = P.E
We have $K.E = \dfrac{1}{2}Mv_{\max }^2$ and P.E =$\dfrac{1}{2}K{L^2}$, hence
$ \Rightarrow $ $\dfrac{1}{2}Mv_{\max }^2$ =$\dfrac{1}{2}K{L^2}$.
Solving this, we get
$
\Rightarrow v_{\max }^2 = \dfrac{{K{L^2}}}{M}. \\
\Rightarrow {v_{\max }} = \sqrt {\dfrac{{K{L^2}}}{M}} = \sqrt {\dfrac{K}{M}} L \\
$
Now, the maximum momentum of the block,
$
\Rightarrow {P_{\max }} = M{v_{\max }} \\
\Rightarrow {P_{\max }} = M\sqrt {\dfrac{K}{M}} L \\
\Rightarrow {P_{\max }} = \sqrt {MK} L \\
$
Here, we can see that the maximum momentum of the block after collision is \[\sqrt {MK} L\].
Therefore, the correct answer is option (C).
Note: In this type of question we will use the law of conservation of energy. First we have to find the initial kinetic energy and then we have to find the potential energy of the stretched string. Then by using the principle of conservation of energy, we will equate both the energies and then we will get the value of maximum velocity. And then by using that velocity we can get the value of maximum momentum.
Complete step-by-step solution -
Formula used: K.E = $\dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2}$, P.E of stretched string = $\dfrac{1}{2}k{x^2}$, P = mv and $K.E + P.E = E({\text{constant)}}$.
We know that, if only the conservative forces are doing work on the body, then its mechanical energy ( kinetic energy + potential energy ) remains constant. It can be written as:
$ \Rightarrow K.E + P.E = E({\text{constant)}}$.
$ \Rightarrow $ $\vartriangle K + \vartriangle U = 0$
$ \Rightarrow $ $\vartriangle K = - \vartriangle U$.
If the initial velocity of the moving block is v, then the kinetic energy will be,
$ \Rightarrow K.E = \dfrac{1}{2}Mv_{\max }^2$.
As we know that the potential energy of a stretched string is $\dfrac{1}{2}k{x^2}$.
So the potential energy due to the spring is = $\dfrac{1}{2}K{L^2}$.
So now, according to the principle of conservation of energy,
Energy can neither be created nor destroyed. It may be transformed from one form to another.
So, when the spring gets compressed by length L,
K.E lost by mass M = P.E stored in the compressed spring.
$ \Rightarrow $ K.E = P.E
We have $K.E = \dfrac{1}{2}Mv_{\max }^2$ and P.E =$\dfrac{1}{2}K{L^2}$, hence
$ \Rightarrow $ $\dfrac{1}{2}Mv_{\max }^2$ =$\dfrac{1}{2}K{L^2}$.
Solving this, we get
$
\Rightarrow v_{\max }^2 = \dfrac{{K{L^2}}}{M}. \\
\Rightarrow {v_{\max }} = \sqrt {\dfrac{{K{L^2}}}{M}} = \sqrt {\dfrac{K}{M}} L \\
$
Now, the maximum momentum of the block,
$
\Rightarrow {P_{\max }} = M{v_{\max }} \\
\Rightarrow {P_{\max }} = M\sqrt {\dfrac{K}{M}} L \\
\Rightarrow {P_{\max }} = \sqrt {MK} L \\
$
Here, we can see that the maximum momentum of the block after collision is \[\sqrt {MK} L\].
Therefore, the correct answer is option (C).
Note: In this type of question we will use the law of conservation of energy. First we have to find the initial kinetic energy and then we have to find the potential energy of the stretched string. Then by using the principle of conservation of energy, we will equate both the energies and then we will get the value of maximum velocity. And then by using that velocity we can get the value of maximum momentum.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




