
The blades of the windmill sweep out a circle of area A.
A) If the wind flows at a velocity $v$ perpendicular to the circle what is the mass of the air passing through it in time $t$
B) What is the kinetic energy of the air
C) Assume that the windmill converts $25\% $ of the wind energy into electrical energy and that $A = 30{m^2}$ , $v = 36km/h$ and the density of air is $1.2kg/{m^3}$ what is the electrical power produced
Answer
564.9k+ views
Hint:To calculate the mass of air passed in time $t$ can calculate by calculating how much volume of air pass through area $A$ and it multiply b density of air
When we find mass of the air then we can calculate the kinetic energy of air simply applying the formula of K.E. To calculate power we know power is work done per unit time or can say energy per unit time by applying these things we can get all answers.
Step by step solution:
In question it is given the area sweep by windmill is $A$ and the velocity of air is $v$
Let us assume in time $t$ the air travel a distance $d$ as shown in diagram
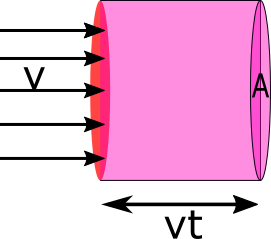
$ \Rightarrow d = v \times t$
$ \Rightarrow d = vt$
Volume of air passed in time $t$ from area a can given by
$V = area \times d$
$ \Rightarrow V = Avt$
So mass of air passed from area a in time $t$ can given as
$ \Rightarrow m = \rho \times V$
$ \Rightarrow m = \rho Avt$ .............. (1)
This is the mass of air which passed from area $A$ in time $t$
(b)
To calculate kinetic energy we know formula of K.E
$ \Rightarrow K.E = \dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2}$
From equation 1 put the value of mass of air
$ \Rightarrow K.E = \dfrac{1}{2}\rho Avt \times {v^2}$
$ \Rightarrow K.E = \dfrac{1}{2}\rho A{v^3}t$ ......... (2)
This is the kinetic energy of air
(c)
We know the power is defined as work down (energy) per unit time
$P = \dfrac{{K.E}}{t}$
So from equation (2)
$ \Rightarrow P = \dfrac{{\dfrac{1}{2}\rho A{v^3}t}}{t}$
$ \Rightarrow P = \dfrac{1}{2}\rho A{v^3}$
This is the power given by air to windmill but windmill can convert only $25\% $ into electrical energy
So the electrical Power can give as
$ \Rightarrow {P_{electric}} = 25\% \times P$
\[ \Rightarrow {P_{electric}} = \dfrac{1}{2}\rho A{v^3} \times \dfrac{{25}}{{100}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {P_{electric}} = \dfrac{1}{8}\rho A{v^3}\]
Put the given value,
\[A = 30{m^2}\] And $\rho = 1.2kg/{m^3}$ ,$v = 36km/h = 10m/\sec $
\[ \Rightarrow {P_{electric}} = \dfrac{1}{8} \times 1.2 \times 30 \times {10^3}\]
We know ${10^3}watt = 1kwatt$
\[ \Rightarrow {P_{electric}} = 4.5kwatt\]
Hence power converted into electrical power is 4.5 kW.
Note:
Here we use to calculate the volume of air which crosses the area $A$ in time $t$.
As we know the velocity of air is $v$ m/s so it can travel $vt$ distance in time $t$ because $d = vt$
If we want to find volume of air which crosses this area in same time then we have to multiply distance by area of circle because:
Volume= area × length
Here area is $A$ and length is $d = vt$
So volume of air passed from area $A$ in time $t$ is $V = Avt$
When we find mass of the air then we can calculate the kinetic energy of air simply applying the formula of K.E. To calculate power we know power is work done per unit time or can say energy per unit time by applying these things we can get all answers.
Step by step solution:
In question it is given the area sweep by windmill is $A$ and the velocity of air is $v$
Let us assume in time $t$ the air travel a distance $d$ as shown in diagram

$ \Rightarrow d = v \times t$
$ \Rightarrow d = vt$
Volume of air passed in time $t$ from area a can given by
$V = area \times d$
$ \Rightarrow V = Avt$
So mass of air passed from area a in time $t$ can given as
$ \Rightarrow m = \rho \times V$
$ \Rightarrow m = \rho Avt$ .............. (1)
This is the mass of air which passed from area $A$ in time $t$
(b)
To calculate kinetic energy we know formula of K.E
$ \Rightarrow K.E = \dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2}$
From equation 1 put the value of mass of air
$ \Rightarrow K.E = \dfrac{1}{2}\rho Avt \times {v^2}$
$ \Rightarrow K.E = \dfrac{1}{2}\rho A{v^3}t$ ......... (2)
This is the kinetic energy of air
(c)
We know the power is defined as work down (energy) per unit time
$P = \dfrac{{K.E}}{t}$
So from equation (2)
$ \Rightarrow P = \dfrac{{\dfrac{1}{2}\rho A{v^3}t}}{t}$
$ \Rightarrow P = \dfrac{1}{2}\rho A{v^3}$
This is the power given by air to windmill but windmill can convert only $25\% $ into electrical energy
So the electrical Power can give as
$ \Rightarrow {P_{electric}} = 25\% \times P$
\[ \Rightarrow {P_{electric}} = \dfrac{1}{2}\rho A{v^3} \times \dfrac{{25}}{{100}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {P_{electric}} = \dfrac{1}{8}\rho A{v^3}\]
Put the given value,
\[A = 30{m^2}\] And $\rho = 1.2kg/{m^3}$ ,$v = 36km/h = 10m/\sec $
\[ \Rightarrow {P_{electric}} = \dfrac{1}{8} \times 1.2 \times 30 \times {10^3}\]
We know ${10^3}watt = 1kwatt$
\[ \Rightarrow {P_{electric}} = 4.5kwatt\]
Hence power converted into electrical power is 4.5 kW.
Note:
Here we use to calculate the volume of air which crosses the area $A$ in time $t$.
As we know the velocity of air is $v$ m/s so it can travel $vt$ distance in time $t$ because $d = vt$
If we want to find volume of air which crosses this area in same time then we have to multiply distance by area of circle because:
Volume= area × length
Here area is $A$ and length is $d = vt$
So volume of air passed from area $A$ in time $t$ is $V = Avt$
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




