
The bisectors of angles B and C of an isosceles triangle with AB=AC, intersect each other at point O. Produce BO to M. Prove that $\angle MOC = \angle ABC$
Answer
584.7k+ views
Hint:
We know that angles opposite to equal sides are also equal in a triangle then we can write, $\angle ACB = \angle ABC$. Now on dividing the angles by one-half, we get-$\angle OCB = \angle OBC$ as OB and OC are bisectors of angle B and C. Then we know that the sum of two interior angles is equal to the exterior angle of the triangle so we can use this for $\vartriangle OBC$. Then, put $\angle OCB = \angle OBC$ and add them. Since OB is bisectors of angle B. Then we can write-$\angle OBC = \dfrac{1}{2}\angle ABC$.
Complete step by step solution:
Let ABC be the isosceles triangle where AB=AC and the bisectors of angles B and C intersect each other at point O. BO is produced to M at line AC.
We have to prove-$\angle MOC = \angle ABC$
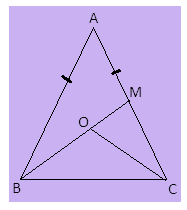
In triangle ABC, AB=AC
We know that angles opposite to equal sides are also equal. Then we can write-
$ \Rightarrow \angle ACB = \angle ABC$ -- (i)
On dividing eq. (i) by $\dfrac{1}{2}$, we get-
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}\angle ACB = \dfrac{1}{2}\angle ABC$ -- eq. (ii)
From the diagram, it is clear that $\dfrac{1}{2}\angle ACB = \angle OCB$ and $\dfrac{1}{2}\angle ABC = \angle OBC$ as OB and OC are bisectors of angle B and C.
On substituting these values in eq. (ii), we get-
$ \Rightarrow \angle OCB = \angle OBC$ -- (iii)
Now we know that the sum of two interior angles is equal to the exterior angle of the triangle.
Then In $\vartriangle OBC$, we can write-
$ \Rightarrow \angle OBC + \angle OCB = \angle MOC$
Then from, eq. (iii), we get-
$ \Rightarrow \angle OBC + \angle OBC = \angle MOC$
Then we can write,
$ \Rightarrow 2\angle OBC = \angle MOC$
But $\dfrac{1}{2}\angle ABC = \angle OBC$ so on substituting this value, we get-
$ \Rightarrow \angle ABC = \angle MOC$
Hence Proved.
Note:
The properties of an Isosceles triangle are-
1) Two sides of the triangle are equal to each other and one side is unequal. This unequal side is the base of the triangle.
2) The two base angles of the isosceles triangle are equal. The angle which is not equal to the others is called the apex angle.
3) The altitude drawn from the apex bisects the isosceles triangle divides the triangle into two equal right-angled triangles.
We know that angles opposite to equal sides are also equal in a triangle then we can write, $\angle ACB = \angle ABC$. Now on dividing the angles by one-half, we get-$\angle OCB = \angle OBC$ as OB and OC are bisectors of angle B and C. Then we know that the sum of two interior angles is equal to the exterior angle of the triangle so we can use this for $\vartriangle OBC$. Then, put $\angle OCB = \angle OBC$ and add them. Since OB is bisectors of angle B. Then we can write-$\angle OBC = \dfrac{1}{2}\angle ABC$.
Complete step by step solution:
Let ABC be the isosceles triangle where AB=AC and the bisectors of angles B and C intersect each other at point O. BO is produced to M at line AC.
We have to prove-$\angle MOC = \angle ABC$

In triangle ABC, AB=AC
We know that angles opposite to equal sides are also equal. Then we can write-
$ \Rightarrow \angle ACB = \angle ABC$ -- (i)
On dividing eq. (i) by $\dfrac{1}{2}$, we get-
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}\angle ACB = \dfrac{1}{2}\angle ABC$ -- eq. (ii)
From the diagram, it is clear that $\dfrac{1}{2}\angle ACB = \angle OCB$ and $\dfrac{1}{2}\angle ABC = \angle OBC$ as OB and OC are bisectors of angle B and C.
On substituting these values in eq. (ii), we get-
$ \Rightarrow \angle OCB = \angle OBC$ -- (iii)
Now we know that the sum of two interior angles is equal to the exterior angle of the triangle.
Then In $\vartriangle OBC$, we can write-
$ \Rightarrow \angle OBC + \angle OCB = \angle MOC$
Then from, eq. (iii), we get-
$ \Rightarrow \angle OBC + \angle OBC = \angle MOC$
Then we can write,
$ \Rightarrow 2\angle OBC = \angle MOC$
But $\dfrac{1}{2}\angle ABC = \angle OBC$ so on substituting this value, we get-
$ \Rightarrow \angle ABC = \angle MOC$
Hence Proved.
Note:
The properties of an Isosceles triangle are-
1) Two sides of the triangle are equal to each other and one side is unequal. This unequal side is the base of the triangle.
2) The two base angles of the isosceles triangle are equal. The angle which is not equal to the others is called the apex angle.
3) The altitude drawn from the apex bisects the isosceles triangle divides the triangle into two equal right-angled triangles.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




