
The best indicator for the detection of the end point in the titration of a weak acid and a strong base is:
A. Methyl orange ( $pH$ range $3$ to $4$ )
B. Methyl red ( $pH$ range $4$ to $6$ )
C. Thymol blue ( $pH$ range $8$ to $3$ )
D. Phenolphthalein ( $pH$ range $8$ to $10$ )
Answer
559.5k+ views
Hint:The best indicator used in the detection of the end point in the titration of a weak and a strong base is the chemical compound with formula ${C_{20}}{H_{14}}{O_8}$ . It turns colorless when applied in acidic solution and pink when applied in basic solution.
Complete answer:
Phenolphthalein is a compound with formula ${C_{20}}{H_{14}}{O_8}$ . Its IUPAC name is \[3,3 - Bis\left( {4 - hydroxyphenyl} \right) - 2 - benzofuran - 1(3H) - one\] . It appeared as a white powder. It is used in acid-base titration. In the case of acidic solution the end point is detected if the solution turns colorless. And in the case of a basic solution the endpoint is detected if the solution gets turned into a pink color solution.
If the case of titrating weak acid and strong base, phenolphthalein convert the solution color to pink which indicate the end point of the solution.
Phenolphthalein shows four different colors for detecting an aqueous solution depending on the $pH$ of the solution. As if the solution is strongly acidic then it exists in protonated form ( $H{\ln ^ + }$ ), and gives an orange coloration. if the solution is in between strongly acidic and slightly basic conditions, the lactone form is a colorless solution. The doubly deprotonated ( ${\ln ^{2 - }}$ ) phenolate form which gives the pink color to the solution. If the solution is strongly basic in nature then phenolphthalein is converted to its $\ln {(OH)^{3 - }}$ form, and then its pink color changes and fades which becomes completely colorless above $13.0pH$ .
Structure of phenolphthalein is gives as:
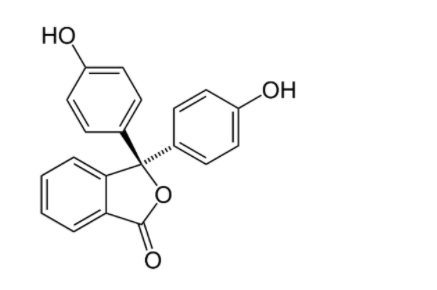
Hence, option D is correct.
Note:
Phenolphthalein is a weak acid. It can lose ${H^ + }$ ions in solution. The non-ionized phenolphthalein molecule is colorless and the protonated phenolphthalein ion is an orange. The deprotonated phenolphthalein ion is fuchsia. Sensitivity of phenolphthalein is used in other applications such as concrete that has naturally high $pH$ due to the calcium hydroxide formed when Portland cement reacts with water. As the concrete reacts with carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, $pH$ decreases to $8.5 - 9$ .
Complete answer:
Phenolphthalein is a compound with formula ${C_{20}}{H_{14}}{O_8}$ . Its IUPAC name is \[3,3 - Bis\left( {4 - hydroxyphenyl} \right) - 2 - benzofuran - 1(3H) - one\] . It appeared as a white powder. It is used in acid-base titration. In the case of acidic solution the end point is detected if the solution turns colorless. And in the case of a basic solution the endpoint is detected if the solution gets turned into a pink color solution.
If the case of titrating weak acid and strong base, phenolphthalein convert the solution color to pink which indicate the end point of the solution.
Phenolphthalein shows four different colors for detecting an aqueous solution depending on the $pH$ of the solution. As if the solution is strongly acidic then it exists in protonated form ( $H{\ln ^ + }$ ), and gives an orange coloration. if the solution is in between strongly acidic and slightly basic conditions, the lactone form is a colorless solution. The doubly deprotonated ( ${\ln ^{2 - }}$ ) phenolate form which gives the pink color to the solution. If the solution is strongly basic in nature then phenolphthalein is converted to its $\ln {(OH)^{3 - }}$ form, and then its pink color changes and fades which becomes completely colorless above $13.0pH$ .
Structure of phenolphthalein is gives as:

Hence, option D is correct.
Note:
Phenolphthalein is a weak acid. It can lose ${H^ + }$ ions in solution. The non-ionized phenolphthalein molecule is colorless and the protonated phenolphthalein ion is an orange. The deprotonated phenolphthalein ion is fuchsia. Sensitivity of phenolphthalein is used in other applications such as concrete that has naturally high $pH$ due to the calcium hydroxide formed when Portland cement reacts with water. As the concrete reacts with carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, $pH$ decreases to $8.5 - 9$ .
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




