
The base of an equilateral triangle with side 2a lies along the y -axis such that the midpoint of the base is at the origin. Find vertices of the triangle.
Answer
574.5k+ views
Hint: We know that in geometry, an equilateral triangle is a triangle in which all three sides are equal. We all are familiar with the Euclidean geometry that says, an equilateral triangle is also equiangular; that is, all three internal angles are also congruent to each other and are each 60°. It is also a regular polygon, so it is also referred to as a regular triangle.
We know that the equation of a line is with one known point and the slope of line given is as follows:
\[\dfrac{y-b}{x-a}=m\]
(Where m is the slope of the line and (a, b) is the known point that lies on the line)
Complete step by step answer:
As given in the question, we have to find the 3 vertices of the given equilateral triangle.
Now, as the mid-point of the base of the equilateral triangle is the origin (0, 0) and as the side of the equilateral triangle is given as 2a. It is also given that both the endpoints lie on the y-axis. Hence, by symmetry we can say that these two vertices have the coordinates (0, a) and (0, -a).
Now, as we know that, all the angles of an equilateral triangle are equal to 60°.
So, the equation of the line that is one side of the equilateral triangle and which is having (0, -a) point and the third vertex can be written as follows:
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{y-(-a)}{x-0}=\tan {{30}^{\circ }} \\
&\Rightarrow y+a=x\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}} \\
&\Rightarrow \sqrt{3}\left( y+a \right)=x \\
\end{align}\] Since, $slope=\tan \theta $
Now, from the concept of symmetry, we can say that the third vertex also lies on the x-axis, so, we will place$y=0$,
\[\begin{align}
& \sqrt{3}\left( y+a \right)=x \\
&\Rightarrow \sqrt{3}a=x \\
\end{align}\]
Hence, the third vertex is
\[\left( \sqrt{3}a,0 \right)\] .
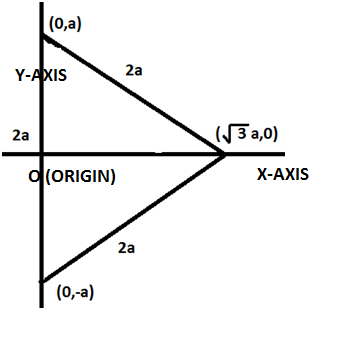
Hence, $\left( \sqrt{3}a,0 \right),\left( 0,a \right),\left( 0,-a \right)$ are the coordinates of the three vertices of the equilateral triangle.
Note: We can make an error if we don’t know the formula to get the slope of a line that is,
The equation of a line is with one known point and the slope of line given is as follows:
\[\dfrac{y-b}{x-a}=m\]
(Where m is the slope of the line and (a, b) is the known point that lies on the line)
Also, assessing the question that the midpoint of one side of the equilateral triangle will be the origin is very essential as without this information, one can never get to the correct answer.
We know that the equation of a line is with one known point and the slope of line given is as follows:
\[\dfrac{y-b}{x-a}=m\]
(Where m is the slope of the line and (a, b) is the known point that lies on the line)
Complete step by step answer:
As given in the question, we have to find the 3 vertices of the given equilateral triangle.
Now, as the mid-point of the base of the equilateral triangle is the origin (0, 0) and as the side of the equilateral triangle is given as 2a. It is also given that both the endpoints lie on the y-axis. Hence, by symmetry we can say that these two vertices have the coordinates (0, a) and (0, -a).
Now, as we know that, all the angles of an equilateral triangle are equal to 60°.
So, the equation of the line that is one side of the equilateral triangle and which is having (0, -a) point and the third vertex can be written as follows:
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{y-(-a)}{x-0}=\tan {{30}^{\circ }} \\
&\Rightarrow y+a=x\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}} \\
&\Rightarrow \sqrt{3}\left( y+a \right)=x \\
\end{align}\] Since, $slope=\tan \theta $
Now, from the concept of symmetry, we can say that the third vertex also lies on the x-axis, so, we will place$y=0$,
\[\begin{align}
& \sqrt{3}\left( y+a \right)=x \\
&\Rightarrow \sqrt{3}a=x \\
\end{align}\]
Hence, the third vertex is
\[\left( \sqrt{3}a,0 \right)\] .

Hence, $\left( \sqrt{3}a,0 \right),\left( 0,a \right),\left( 0,-a \right)$ are the coordinates of the three vertices of the equilateral triangle.
Note: We can make an error if we don’t know the formula to get the slope of a line that is,
The equation of a line is with one known point and the slope of line given is as follows:
\[\dfrac{y-b}{x-a}=m\]
(Where m is the slope of the line and (a, b) is the known point that lies on the line)
Also, assessing the question that the midpoint of one side of the equilateral triangle will be the origin is very essential as without this information, one can never get to the correct answer.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




