
The average kinetic energy of the particles of a gas is most closely associated with which of the following quantity?
A) Heat capacity
B) temperature
C) specific heat
D) absolute zero
E) potential energy
Answer
587.7k+ views
Hint: The particles of a gas are supposed to have elastic collisions both with the wall of the container and the other particles ideally. They are thought of as point mass particles with a velocity range zero to infinity. Hence, their average kinetic energy is to be calculated taking care of this assumptions.
Complete step by step answer:
Step 1:
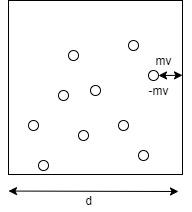
Let in an one dimensional case, a gas particle with mass $m$ collides with the wall of a container with length $d$ perpendicularly with a velocity $v$ and exerts a force $F$ as
\[
F = \dfrac{{mv - \left( { - mv} \right)}}{t} \\
\Rightarrow F = \dfrac{{2mv}}{t} \\
\]
You can find the frequency of the collision as
$\dfrac{1}{t} = \dfrac{v}{d}$
So, the average force becomes
$F = \dfrac{{m{v^2}}}{d}$
Step 2:
Calculate the total force on the wall due to all the particles
$
F = \sum {\dfrac{{m{v^2}}}{d}} \\
= \dfrac{{mN}}{L}\left[ {\dfrac{{\sum {{v^2}} }}{N}} \right] \\
= \dfrac{{mN}}{L}v_{rms}^2 \\
$
Step 3:
You can exploit the symmetry, hence for a three-dimensional case
$v_{xyz}^2 = v_x^2 + v_y^2 + v_z^2 = 3{v^2}$
Hence, you get the force $F$ as
$F = \dfrac{{mN}}{{3d}}v_{rms}^2$
Calculate the pressure on the wall of the container as
$P = \dfrac{{mN}}{{3{d^3}}}v_{rms}^2$
Now the volume of the container is the total volume of the gas particles as
$V = {d^3}$
Hence you can have
\[
P \times V = \dfrac{{mN}}{{3{d^3}}}v_{rms}^2 \times {d^3} \\
= \dfrac{{mNv_{rms}^2}}{3} \\
\]
Step 4:
The average kinetic energy of a gas particle is
$K = \dfrac{1}{2}mv_{rms}^2$
Hence, you can rewrite the relation in eq (1) as
$
PV = \dfrac{2}{3}N \times \dfrac{1}{2}mv_{rms}^2 \\
= \dfrac{2}{3}NK \\
$
Step 5:
Now from ideal gas relation you have
$PV = N{k_b}T$
where, ${k_b}$ is the universal Boltzmann constant and $T$ is the temperature of the gas.
Calculate the average translational kinetic energy of a gas particle by using the relation in eq (2)
$
\dfrac{2}{3}NK = N{k_b}T \\
\Rightarrow K = \dfrac{3}{2}{k_b}T \\
$
Hence, you can see that the average kinetic energy can be solely determined from the temperature $T$ and the universal Boltzmann constant ${k_b}$ .
Final Answer:
The average kinetic energy of the particles of a gas is most closely associated with (B) temperature.
Note: The assumption of elastic collision is to be carefully taken in case of calculation of change of the momentum. The pressure should be calculated on the wall of the container due to the force exerted by the particles. The collisional effects between the molecules are not considered significant as they can be average out to zero in the long run. The other quantities like heat capacity and specific heat can affect the average kinetic energy but not a bit as significant as the temperature as you saw from the derivation.
Complete step by step answer:
Step 1:

Let in an one dimensional case, a gas particle with mass $m$ collides with the wall of a container with length $d$ perpendicularly with a velocity $v$ and exerts a force $F$ as
\[
F = \dfrac{{mv - \left( { - mv} \right)}}{t} \\
\Rightarrow F = \dfrac{{2mv}}{t} \\
\]
You can find the frequency of the collision as
$\dfrac{1}{t} = \dfrac{v}{d}$
So, the average force becomes
$F = \dfrac{{m{v^2}}}{d}$
Step 2:
Calculate the total force on the wall due to all the particles
$
F = \sum {\dfrac{{m{v^2}}}{d}} \\
= \dfrac{{mN}}{L}\left[ {\dfrac{{\sum {{v^2}} }}{N}} \right] \\
= \dfrac{{mN}}{L}v_{rms}^2 \\
$
Step 3:
You can exploit the symmetry, hence for a three-dimensional case
$v_{xyz}^2 = v_x^2 + v_y^2 + v_z^2 = 3{v^2}$
Hence, you get the force $F$ as
$F = \dfrac{{mN}}{{3d}}v_{rms}^2$
Calculate the pressure on the wall of the container as
$P = \dfrac{{mN}}{{3{d^3}}}v_{rms}^2$
Now the volume of the container is the total volume of the gas particles as
$V = {d^3}$
Hence you can have
\[
P \times V = \dfrac{{mN}}{{3{d^3}}}v_{rms}^2 \times {d^3} \\
= \dfrac{{mNv_{rms}^2}}{3} \\
\]
Step 4:
The average kinetic energy of a gas particle is
$K = \dfrac{1}{2}mv_{rms}^2$
Hence, you can rewrite the relation in eq (1) as
$
PV = \dfrac{2}{3}N \times \dfrac{1}{2}mv_{rms}^2 \\
= \dfrac{2}{3}NK \\
$
Step 5:
Now from ideal gas relation you have
$PV = N{k_b}T$
where, ${k_b}$ is the universal Boltzmann constant and $T$ is the temperature of the gas.
Calculate the average translational kinetic energy of a gas particle by using the relation in eq (2)
$
\dfrac{2}{3}NK = N{k_b}T \\
\Rightarrow K = \dfrac{3}{2}{k_b}T \\
$
Hence, you can see that the average kinetic energy can be solely determined from the temperature $T$ and the universal Boltzmann constant ${k_b}$ .
Final Answer:
The average kinetic energy of the particles of a gas is most closely associated with (B) temperature.
Note: The assumption of elastic collision is to be carefully taken in case of calculation of change of the momentum. The pressure should be calculated on the wall of the container due to the force exerted by the particles. The collisional effects between the molecules are not considered significant as they can be average out to zero in the long run. The other quantities like heat capacity and specific heat can affect the average kinetic energy but not a bit as significant as the temperature as you saw from the derivation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




