
The Atwood machine in the figure has a third mass attached to it by a limp string. After being released, the 2m mass falls a distance x before the limp string becomes taut. Thereafter both the mass on the left rise at the same speed. What is the final speed? Assume that the pulley is ideal.
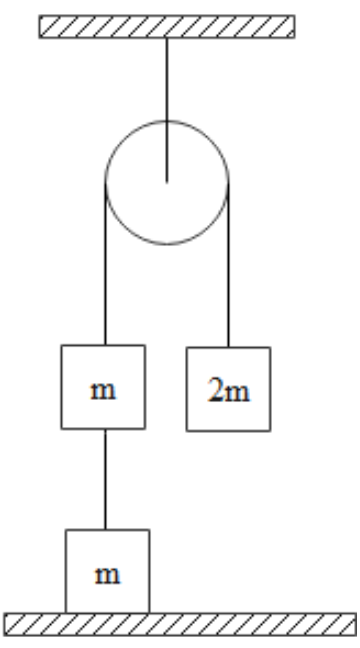

Answer
579.3k+ views
Hint: We will be using the impulse equation and the force equation for the pulley to get the final speed. The ideal pulley concept is used. A free body diagram can be drawn to understand how the force equation can be formed. Newton’s law has been used to calculate the force exerted by the mass.
Formula used: Force \[F=ma\]
Impulse \[\Delta p=F\Delta t\]
Complete step-by-step solution:
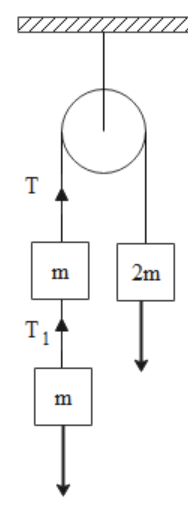
Let us first consider the system when the string is limp. If we consider a to be the acceleration of the masses before the string becomes taut then we can write the following expression for the motion of the system.
$\begin{align}
&2mg - mg = \left( {2m + m} \right)a \\
&\Rightarrow mg = 3ma \\
& \Rightarrow a = \dfrac{g}{3} \\
\end{align} $
This is the value of the acceleration of masses m and 2m before the string becomes taut. Now let us use the following equation of motion to find out the velocity, which is given as
${v^2} - {u^2} = 2aS$
The initial velocity of these masses is zero; $u = 0$. Therefore, we can write that
$\begin{gathered}
{v^2} = \dfrac{2}{3}gx \\
v = \sqrt {\dfrac{{2gx}}{3}} \\
\end{gathered} $
Here x is the distance to which the mass 2m will fall before the string tightens up.
Now let the tension ${T_1}$ due to the second mass m is acting on the system when the string becomes taut. When this tension develops, it acts as an impulse for some time dt. We are given that all the masses move with uniform velocity after the string becomes taut, so let this velocity be c.
Now, we can write the following expression using the impulse-momentum theorem where the impulse J acting on the system is equal to the change in momentum of the system.
$J = Fdt = \Delta mv$
Writing this expression for all the masses we get
For the second mass m on the bottom, ${T_1}dt = mc$ …(i)
Here ${T_1}$ is the tensional force acting on this mass.
For the mass m above it, $\left( {T - {T_1}} \right)dt = mc - mv{\text{ }}...{\text{(ii)}}$
Here $T - {T_1}$ is the tensional force acting on two masses.
And similarly, for the mass 2m, $ - Tdt = 2mc - 2mv{\text{ }}...{\text{(iii)}}$
Adding these three equations we get
$\begin{gathered}
0 = 4mc - 3mv \\
\Rightarrow c = \dfrac{3}{4}v \\
\end{gathered} $
Inserting the value of v obtained earlier, we get
$c = \dfrac{3}{4}\sqrt {\dfrac{{2gx}}{3}} = \sqrt {\dfrac{{9 \times 2gx}}{{16 \times 3}}} = \sqrt {\dfrac{{3gx}}{8}} $
This is the final speed of the masses and the required answer.
Note: Impulse acting on a system can be defined as the sudden change in force occurring in a very short interval of time. In the given system, the impulse occurs due to the tension developed in the pulley when the lower string becomes taut.
Formula used: Force \[F=ma\]
Impulse \[\Delta p=F\Delta t\]
Complete step-by-step solution:

Let us first consider the system when the string is limp. If we consider a to be the acceleration of the masses before the string becomes taut then we can write the following expression for the motion of the system.
$\begin{align}
&2mg - mg = \left( {2m + m} \right)a \\
&\Rightarrow mg = 3ma \\
& \Rightarrow a = \dfrac{g}{3} \\
\end{align} $
This is the value of the acceleration of masses m and 2m before the string becomes taut. Now let us use the following equation of motion to find out the velocity, which is given as
${v^2} - {u^2} = 2aS$
The initial velocity of these masses is zero; $u = 0$. Therefore, we can write that
$\begin{gathered}
{v^2} = \dfrac{2}{3}gx \\
v = \sqrt {\dfrac{{2gx}}{3}} \\
\end{gathered} $
Here x is the distance to which the mass 2m will fall before the string tightens up.
Now let the tension ${T_1}$ due to the second mass m is acting on the system when the string becomes taut. When this tension develops, it acts as an impulse for some time dt. We are given that all the masses move with uniform velocity after the string becomes taut, so let this velocity be c.
Now, we can write the following expression using the impulse-momentum theorem where the impulse J acting on the system is equal to the change in momentum of the system.
$J = Fdt = \Delta mv$
Writing this expression for all the masses we get
For the second mass m on the bottom, ${T_1}dt = mc$ …(i)
Here ${T_1}$ is the tensional force acting on this mass.
For the mass m above it, $\left( {T - {T_1}} \right)dt = mc - mv{\text{ }}...{\text{(ii)}}$
Here $T - {T_1}$ is the tensional force acting on two masses.
And similarly, for the mass 2m, $ - Tdt = 2mc - 2mv{\text{ }}...{\text{(iii)}}$
Adding these three equations we get
$\begin{gathered}
0 = 4mc - 3mv \\
\Rightarrow c = \dfrac{3}{4}v \\
\end{gathered} $
Inserting the value of v obtained earlier, we get
$c = \dfrac{3}{4}\sqrt {\dfrac{{2gx}}{3}} = \sqrt {\dfrac{{9 \times 2gx}}{{16 \times 3}}} = \sqrt {\dfrac{{3gx}}{8}} $
This is the final speed of the masses and the required answer.
Note: Impulse acting on a system can be defined as the sudden change in force occurring in a very short interval of time. In the given system, the impulse occurs due to the tension developed in the pulley when the lower string becomes taut.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




