
The area velocity of the angular momentum of the planet is related by which of the following relations?
$A.\dfrac{{\vartriangle \bar A}}{{\vartriangle t}} = \dfrac{{\bar L}}{{2{m_p}}}$
$B.\dfrac{{\vartriangle \bar A}}{{\vartriangle t}} = \dfrac{{\bar L}}{{{m_p}}}$
$C.\dfrac{{\vartriangle \bar A}}{{\vartriangle t}} = \dfrac{{2\bar L}}{{{m_p}}}$
$D.\dfrac{{\vartriangle \bar A}}{{\vartriangle t}} = \dfrac{{\bar L}}{{\sqrt {2{m_p}} }}$
Answer
611.7k+ views
- Hint – Here we will proceed by using the concept of area velocity is the area swept out per unit time by a particle moving along a curve.
Complete step-by-step solution -
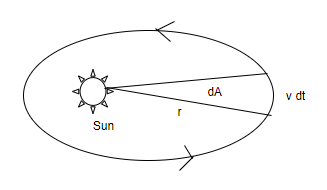
The concept of area velocity is closely linked with the concept of angular momentum. Kepler’s second law states that the area of velocity of a planet, with the sun takes as origin, is constant
Let us consider,
${m_p} = $ mass of the planet.
The angular momentum known as a law of area, $L = {m_p}vr$
$vr = \dfrac{L}{{{m_p}}}$ ….. (1)
Time period, $t = \dfrac{{2\pi r}}{v}$
Total area swapped in time $t,A = \pi {r^2}$
Area velocity, $\dfrac{A}{t} = \dfrac{{\dfrac{{\pi {r^2}}}{{2\pi r}}}}{v} = \dfrac{{vr}}{2}$
From equation 1 we get,
$\dfrac{A}{t} = \dfrac{L}{{2{m_p}}}$
In vector form, a real velocity is given by
$\dfrac{{\bar A}}{t} = \dfrac{{\bar L}}{{2{m_p}}}$
Therefore, A is the correct option.
Note – Whenever we come up with this type of problem, one must know that conservation of areal velocity is a general property of central force motion, and, within the context of classical mechanics, is equivalent to the conservation of angular momentum.
Complete step-by-step solution -

The concept of area velocity is closely linked with the concept of angular momentum. Kepler’s second law states that the area of velocity of a planet, with the sun takes as origin, is constant
Let us consider,
${m_p} = $ mass of the planet.
The angular momentum known as a law of area, $L = {m_p}vr$
$vr = \dfrac{L}{{{m_p}}}$ ….. (1)
Time period, $t = \dfrac{{2\pi r}}{v}$
Total area swapped in time $t,A = \pi {r^2}$
Area velocity, $\dfrac{A}{t} = \dfrac{{\dfrac{{\pi {r^2}}}{{2\pi r}}}}{v} = \dfrac{{vr}}{2}$
From equation 1 we get,
$\dfrac{A}{t} = \dfrac{L}{{2{m_p}}}$
In vector form, a real velocity is given by
$\dfrac{{\bar A}}{t} = \dfrac{{\bar L}}{{2{m_p}}}$
Therefore, A is the correct option.
Note – Whenever we come up with this type of problem, one must know that conservation of areal velocity is a general property of central force motion, and, within the context of classical mechanics, is equivalent to the conservation of angular momentum.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




