
The area of the region $A\left\{ \left( x,y \right)\in \mathbb{R}\times \mathbb{R}:0\le x\le 3,0\le y\le 4y\le {{x}^{2}}+3x \right\}$ is:
[a] $\dfrac{53}{6}$
[b] $\dfrac{59}{6}$
[c] 8
[d] $\dfrac{26}{3}$
[e] $\dfrac{135}{8}$
Answer
581.1k+ views
Hint: Observe that the region A is bounded by two curves $y={{x}^{2}}+3x,4y={{x}^{2}}+3x$. Identify the enclosed area by the two curves. Argue that the bounded area is equal to the difference between the area bounded by the curve $4y={{x}^{2}}+3x$, the x-axis and the ordinates x =0 and x= 3 and the area bounded by the curve $y={{x}^{2}}+3x$, the x-axis and the ordinates x= 0 and x= 3. Use the fact that the area bounded by the curve y = f(x) , the x-axis and the ordinates x = a and x= b is given by $A=\int_{a}^{b}{\left| f\left( x \right) \right|dx}$. Hence determine the two areas and hence the area of the region.
Complete step by step answer:
A is the region $\left\{ \left( x,y \right):0\le x\le 3,0\le y\le 4y\le {{x}^{2}}+3x \right\}$
Hence in region A, we have $4y\le {{x}^{2}}+3x$ and $y\le {{x}^{2}}+3x$
The region $4y\le {{x}^{2}}+3x$ is shown below
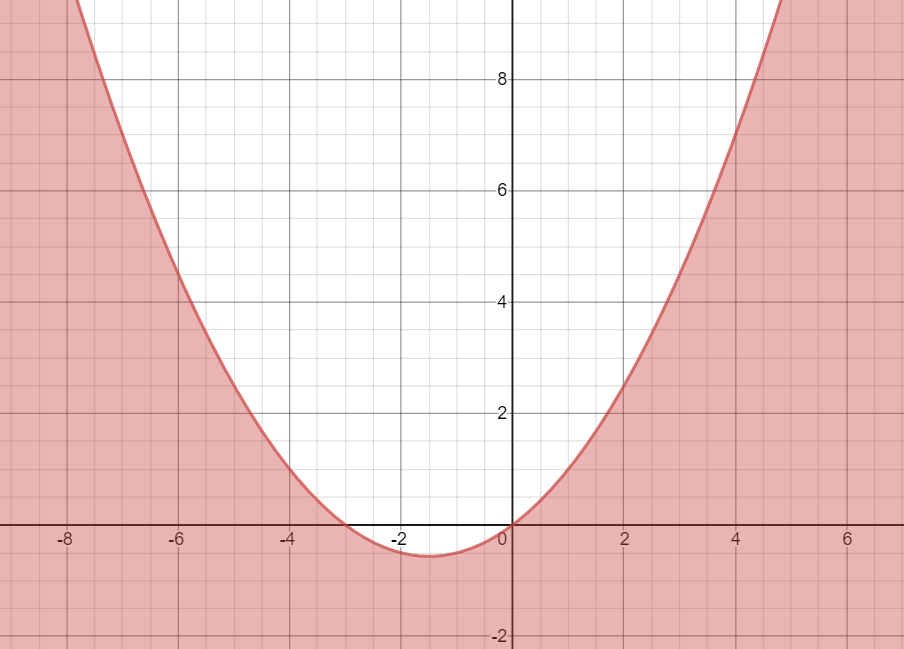
The region $y\le {{x}^{2}}+3x$ is shown below
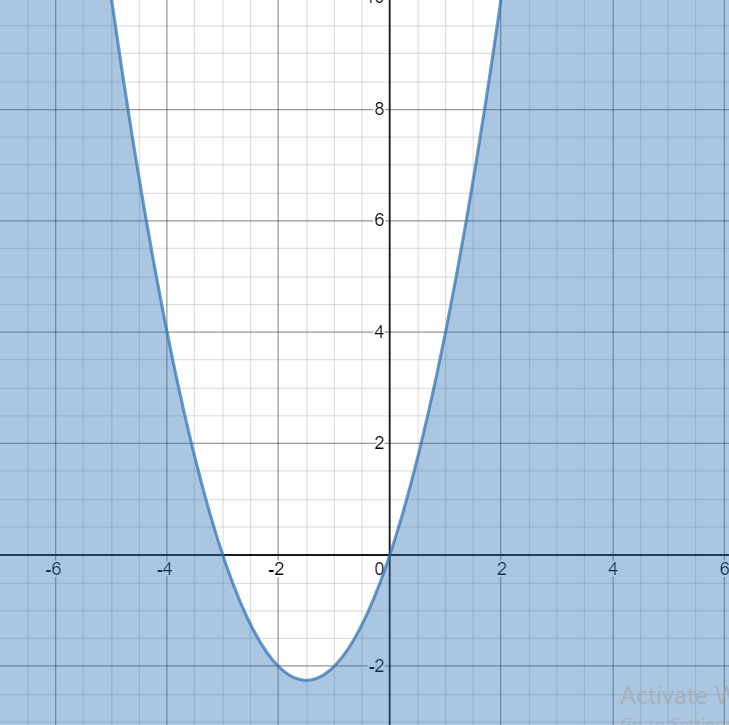
Also, we have $0\le x\le 3$
Hence the region A is given by the intersection of these two regions in the interval [0,3]
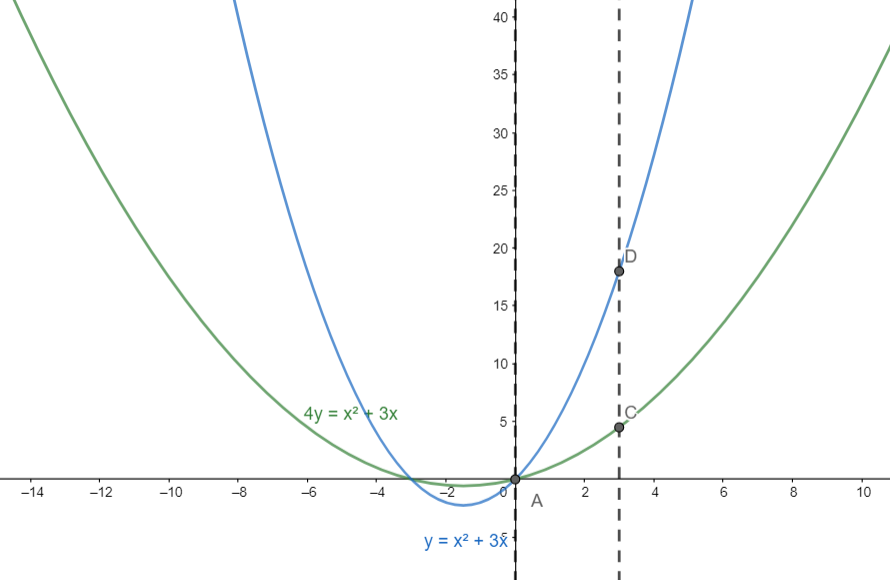
Hence the region R is the region ACDA in the above diagram.
Finding the coordinates of C:
C is the point of intersection of the curve $4y={{x}^{2}}+3x$ and $x=3$
Solving simultaneously, we get
$4y={{3}^{2}}+3\Rightarrow 4y=12$
Dividing both sides by 4, we get
y = 3
Hence, we have
$C\equiv \left( 3,3 \right)$
Finding the coordinates of D:
D is the point of intersection of the curves $y={{x}^{2}}+3x$ and x = 3
Solving simultaneously, we get
$y={{3}^{2}}+3\Rightarrow y=12$
Hence, we have
Observe that the area of the region A is the difference between the area bounded by the curve \[4y={{x}^{2}}+3x\], the x-axis and the ordinates x =0 and x= 3 and the area bounded by the curve $y={{x}^{2}}+3x$, the x-axis and the ordinates x= 0 and x= 3.
Now, we know that the area bounded by the curve y = f(x), the x-axis and the ordinates x = a and x= b is given by $A=\int_{a}^{b}{\left| f\left( x \right) \right|dx}$.
Hence the area bounded by the curve $y=\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}+3x}{3}$, the x-axis and the ordinates x = 0 and x=3, is given by
${{A}_{1}}=\int_{0}^{3}{\left| \dfrac{{{x}^{2}}+3x}{4} \right|dx}$
In the intervale (0,3), we have $\left| {{x}^{2}}+3x \right|={{x}^{2}}+3x$
Hence, we have
${{A}_{2}}=\int_{0}^{3}{\dfrac{\left( {{x}^{2}}+3x \right)}{4}dx}=\dfrac{1}{4}\left[ \left. \dfrac{{{x}^{3}}}{3}+\dfrac{3{{x}^{2}}}{2} \right|_{0}^{3} \right]=\dfrac{1}{4}\left( \dfrac{27}{3}+\dfrac{27}{2}-0-0 \right)=\dfrac{135}{24}$
Also, the area bounded by the curve $y={{x}^{2}}+3x$, the x-axis and the ordinates x = 0 and x =3, is given by
${{A}_{2}}=\int_{0}^{3}{\left| {{x}^{2}} \right|dx}$
We know that $\forall x\in \left[ 0,3 \right],\left| {{x}^{2}}+3x \right|={{x}^{2}}+3x$
Hence, we have
${{A}_{2}}=\int_{0}^{3}{\left( {{x}^{2}}+3x \right)dx}=\left[ \left. \dfrac{{{x}^{3}}}{3}+\dfrac{3{{x}^{2}}}{2} \right|_{0}^{3} \right]=\left( \dfrac{27}{3}+\dfrac{27}{2}-0-0 \right)=\dfrac{135}{6}$
Hence the area of the region A is given by $A={{A}_{2}}-{{A}_{1}}=\dfrac{135}{6}-\dfrac{135}{24}=\dfrac{135}{8}$
Hence the area of the region A is $\dfrac{135}{8}$ square units.
So, the correct answer is “Option E”.
Note: Alternative Solution:
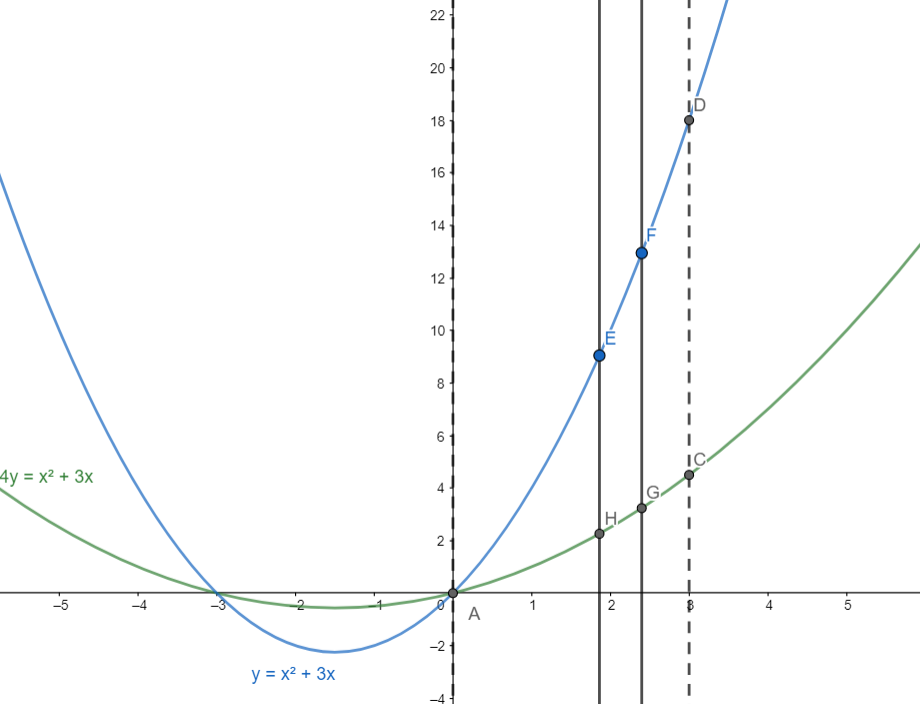
Consider the vertical strip EFGD
We have $EH={{x}^{2}}+3x-\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}+3x}{4}=\dfrac{3}{4}\left( {{x}^{2}}+3x \right)$ and $GH=dx$
Hence the area of the strip is $\dfrac{3}{4}\left( {{x}^{2}}+3x \right)dx$
The total area of A is the sum of the areas of these strips from point A to B
Hence, we have
$A=\int_{0}^{3}{\dfrac{3}{4}\left( {{x}^{2}}+3x \right)dx}=\dfrac{3}{4}\left( \dfrac{27}{3}+\dfrac{27}{2} \right)=\dfrac{135}{8}$, which is the same as obtained above.
Complete step by step answer:
A is the region $\left\{ \left( x,y \right):0\le x\le 3,0\le y\le 4y\le {{x}^{2}}+3x \right\}$
Hence in region A, we have $4y\le {{x}^{2}}+3x$ and $y\le {{x}^{2}}+3x$
The region $4y\le {{x}^{2}}+3x$ is shown below

The region $y\le {{x}^{2}}+3x$ is shown below

Also, we have $0\le x\le 3$
Hence the region A is given by the intersection of these two regions in the interval [0,3]

Hence the region R is the region ACDA in the above diagram.
Finding the coordinates of C:
C is the point of intersection of the curve $4y={{x}^{2}}+3x$ and $x=3$
Solving simultaneously, we get
$4y={{3}^{2}}+3\Rightarrow 4y=12$
Dividing both sides by 4, we get
y = 3
Hence, we have
$C\equiv \left( 3,3 \right)$
Finding the coordinates of D:
D is the point of intersection of the curves $y={{x}^{2}}+3x$ and x = 3
Solving simultaneously, we get
$y={{3}^{2}}+3\Rightarrow y=12$
Hence, we have
Observe that the area of the region A is the difference between the area bounded by the curve \[4y={{x}^{2}}+3x\], the x-axis and the ordinates x =0 and x= 3 and the area bounded by the curve $y={{x}^{2}}+3x$, the x-axis and the ordinates x= 0 and x= 3.
Now, we know that the area bounded by the curve y = f(x), the x-axis and the ordinates x = a and x= b is given by $A=\int_{a}^{b}{\left| f\left( x \right) \right|dx}$.
Hence the area bounded by the curve $y=\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}+3x}{3}$, the x-axis and the ordinates x = 0 and x=3, is given by
${{A}_{1}}=\int_{0}^{3}{\left| \dfrac{{{x}^{2}}+3x}{4} \right|dx}$
In the intervale (0,3), we have $\left| {{x}^{2}}+3x \right|={{x}^{2}}+3x$
Hence, we have
${{A}_{2}}=\int_{0}^{3}{\dfrac{\left( {{x}^{2}}+3x \right)}{4}dx}=\dfrac{1}{4}\left[ \left. \dfrac{{{x}^{3}}}{3}+\dfrac{3{{x}^{2}}}{2} \right|_{0}^{3} \right]=\dfrac{1}{4}\left( \dfrac{27}{3}+\dfrac{27}{2}-0-0 \right)=\dfrac{135}{24}$
Also, the area bounded by the curve $y={{x}^{2}}+3x$, the x-axis and the ordinates x = 0 and x =3, is given by
${{A}_{2}}=\int_{0}^{3}{\left| {{x}^{2}} \right|dx}$
We know that $\forall x\in \left[ 0,3 \right],\left| {{x}^{2}}+3x \right|={{x}^{2}}+3x$
Hence, we have
${{A}_{2}}=\int_{0}^{3}{\left( {{x}^{2}}+3x \right)dx}=\left[ \left. \dfrac{{{x}^{3}}}{3}+\dfrac{3{{x}^{2}}}{2} \right|_{0}^{3} \right]=\left( \dfrac{27}{3}+\dfrac{27}{2}-0-0 \right)=\dfrac{135}{6}$
Hence the area of the region A is given by $A={{A}_{2}}-{{A}_{1}}=\dfrac{135}{6}-\dfrac{135}{24}=\dfrac{135}{8}$
Hence the area of the region A is $\dfrac{135}{8}$ square units.
So, the correct answer is “Option E”.
Note: Alternative Solution:

Consider the vertical strip EFGD
We have $EH={{x}^{2}}+3x-\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}+3x}{4}=\dfrac{3}{4}\left( {{x}^{2}}+3x \right)$ and $GH=dx$
Hence the area of the strip is $\dfrac{3}{4}\left( {{x}^{2}}+3x \right)dx$
The total area of A is the sum of the areas of these strips from point A to B
Hence, we have
$A=\int_{0}^{3}{\dfrac{3}{4}\left( {{x}^{2}}+3x \right)dx}=\dfrac{3}{4}\left( \dfrac{27}{3}+\dfrac{27}{2} \right)=\dfrac{135}{8}$, which is the same as obtained above.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

RNA and DNA are chiral molecules their chirality is class 12 chemistry CBSE




