
The area of the Quadrilateral formed by the tangents at the endpoints of the latus rectum to the ellipse:
$\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{9}+\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{5}=1$ is:
[a] $\dfrac{27}{9}$
[b] 9
[c] $\dfrac{27}{2}$
[d] 27
Answer
607.8k+ views
- Hint: The area of the Quadrilateral will be symmetric in four quadrants. Find the area of the triangle in the first quadrant and multiply it by 4 to get the desired area.
Use the equation of the tangent to the ellipse $\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1$ at .the point $\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)$ is given by $\dfrac{x{{x}_{1}}}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{y{{y}_{1}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1$.
Use the fact that latus rectum passes through focus and is perpendicular to the major-axis of the ellipse and coordinates of focus are $\left( ae,0 \right)$ and ${{b}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}\left( 1-{{e}^{2}} \right)$ where e is the eccentricity of the ellipse.
Complete step-by-step solution -
First, we will find the coordinates of the focus of the ellipse. For that, we need to find the eccentricity of the ellipse first.
We know ${{b}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}\left( 1-{{e}^{2}} \right)$.
In the given ellipse, we have${{a}^{2}}=9$ and ${{b}^{2}}=5$.
Substituting the value of ${{a}^{2}}$ and ${{b}^{2}}$ in the above equation, we get
.$5=9\left( 1-{{e}^{2}} \right)$
Dividing both sides by 9 we get
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{5}{9}=\dfrac{9}{9}\left( 1-{{e}^{2}} \right) \\
& 1-{{e}^{2}}=\dfrac{5}{9} \\
\end{align}$
Subtracting 1 from both sides, we get
$\begin{align}
& 1-{{e}^{2}}-1=\dfrac{5}{9}-1=\dfrac{-4}{9} \\
& \Rightarrow -{{e}^{2}}=\dfrac{-4}{9} \\
\end{align}$
Multiplying both sides by -1, we get
${{e}^{2}}=\dfrac{4}{9}$
Taking square root on both sides, we get
$\begin{align}
& \sqrt{{{e}^{2}}}=\sqrt{\dfrac{4}{9}} \\
& \Rightarrow e=\dfrac{2}{3} \\
\end{align}$
Hence the eccentricity of the ellipse $=\dfrac{2}{3}$
Now coordinates of focus are (ae,0)
$\begin{align}
& =\left( 3\times \dfrac{2}{3},0 \right) \\
& =\left( 2,0 \right) \\
\end{align}$
Let $\left( 2,y \right)$ be the endpoint of the latus rectum in the first quadrant.
Since $\left( 2,y \right)$ lies on the ellipse, we have
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{{{2}^{2}}}{9}+\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{5}=1 \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{4}{9}+\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{5}=1 \\
\end{align}$
Subtracting $\dfrac{4}{9}$ from both sides, we get
$\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{5}=1-\dfrac{4}{9}=\dfrac{5}{9}$
Multiplying by 5 on both sides, we get
\[{{y}^{2}}=\dfrac{25}{9}\]
Hence, we have
$y=\pm \dfrac{5}{3}$
Since the point is in the first quadrant, we have $y>0$
Hence we have $y=\dfrac{5}{3}$
Hence the coordinates of the end of the Latus rectum in the first quadrant are $\left( 2,\dfrac{5}{3} \right)$
Finding the equation of the tangent to the ellipse through $\left( 2,\dfrac{5}{3} \right)$:
We know that equation of the tangent to the ellipse $\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1$ at .the point $\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)$ is given by $\dfrac{x{{x}_{1}}}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{y{{y}_{1}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1$.
Using the above property, we have
Equation of tangent $\dfrac{2x}{9}+\dfrac{5y}{3\times 5}=1$
i.e. $\dfrac{2x}{9}+\dfrac{y}{3}=1$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{x}{\dfrac{9}{2}}+\dfrac{y}{3}=1$
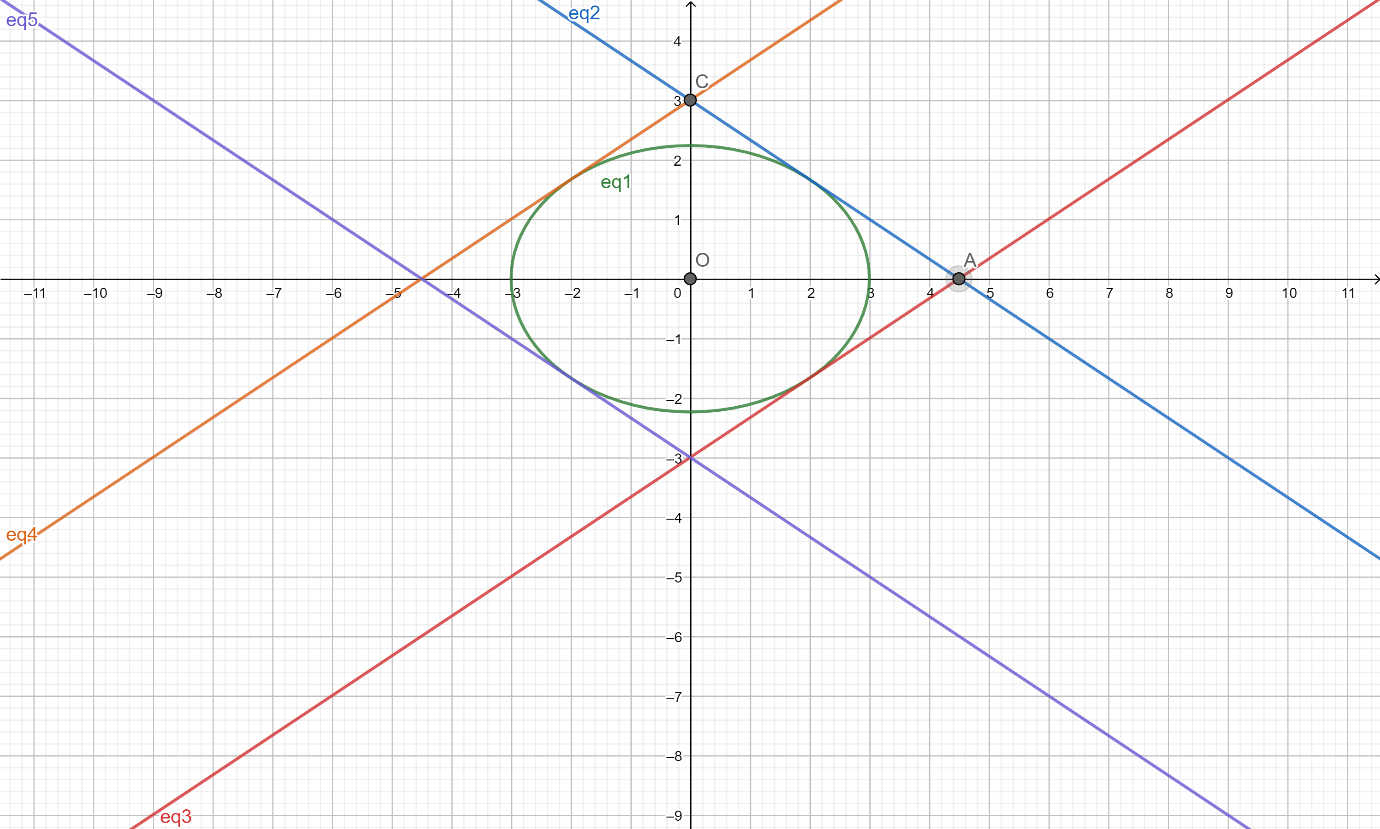
Hence the tangent intersects the x-axis at $A\left( \dfrac{9}{2},0 \right)$ and the y-axis at \[C\left( 0,3 \right)\].
As is evident from the graph area of the Quadrilateral = $4\times ar\left( \Delta AOC \right)$
$ar\left( \Delta AOC \right)=\dfrac{1}{2}OA\times OC=\dfrac{1}{2}\times \dfrac{9}{2}\times 3=\dfrac{27}{4}$
Hence area of the Quadrilateral = $4\times \dfrac{27}{4}=27$
Hence area of the Quadrilateral = 27 sq-units.
Hence option [d] is correct
Note: This question can be solved directly using the fact that area of Quadrilateral formed by the tangents at the endpoints of latus recti $=\dfrac{2{{a}^{2}}}{e}$
Using the above property we have area of Quadrilateral $=\dfrac{2\times 9}{\dfrac{2}{3}}=27$ which is same as obtained above
Use the equation of the tangent to the ellipse $\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1$ at .the point $\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)$ is given by $\dfrac{x{{x}_{1}}}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{y{{y}_{1}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1$.
Use the fact that latus rectum passes through focus and is perpendicular to the major-axis of the ellipse and coordinates of focus are $\left( ae,0 \right)$ and ${{b}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}\left( 1-{{e}^{2}} \right)$ where e is the eccentricity of the ellipse.
Complete step-by-step solution -

First, we will find the coordinates of the focus of the ellipse. For that, we need to find the eccentricity of the ellipse first.
We know ${{b}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}\left( 1-{{e}^{2}} \right)$.
In the given ellipse, we have${{a}^{2}}=9$ and ${{b}^{2}}=5$.
Substituting the value of ${{a}^{2}}$ and ${{b}^{2}}$ in the above equation, we get
.$5=9\left( 1-{{e}^{2}} \right)$
Dividing both sides by 9 we get
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{5}{9}=\dfrac{9}{9}\left( 1-{{e}^{2}} \right) \\
& 1-{{e}^{2}}=\dfrac{5}{9} \\
\end{align}$
Subtracting 1 from both sides, we get
$\begin{align}
& 1-{{e}^{2}}-1=\dfrac{5}{9}-1=\dfrac{-4}{9} \\
& \Rightarrow -{{e}^{2}}=\dfrac{-4}{9} \\
\end{align}$
Multiplying both sides by -1, we get
${{e}^{2}}=\dfrac{4}{9}$
Taking square root on both sides, we get
$\begin{align}
& \sqrt{{{e}^{2}}}=\sqrt{\dfrac{4}{9}} \\
& \Rightarrow e=\dfrac{2}{3} \\
\end{align}$
Hence the eccentricity of the ellipse $=\dfrac{2}{3}$
Now coordinates of focus are (ae,0)
$\begin{align}
& =\left( 3\times \dfrac{2}{3},0 \right) \\
& =\left( 2,0 \right) \\
\end{align}$
Let $\left( 2,y \right)$ be the endpoint of the latus rectum in the first quadrant.
Since $\left( 2,y \right)$ lies on the ellipse, we have
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{{{2}^{2}}}{9}+\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{5}=1 \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{4}{9}+\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{5}=1 \\
\end{align}$
Subtracting $\dfrac{4}{9}$ from both sides, we get
$\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{5}=1-\dfrac{4}{9}=\dfrac{5}{9}$
Multiplying by 5 on both sides, we get
\[{{y}^{2}}=\dfrac{25}{9}\]
Hence, we have
$y=\pm \dfrac{5}{3}$
Since the point is in the first quadrant, we have $y>0$
Hence we have $y=\dfrac{5}{3}$
Hence the coordinates of the end of the Latus rectum in the first quadrant are $\left( 2,\dfrac{5}{3} \right)$
Finding the equation of the tangent to the ellipse through $\left( 2,\dfrac{5}{3} \right)$:
We know that equation of the tangent to the ellipse $\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1$ at .the point $\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)$ is given by $\dfrac{x{{x}_{1}}}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{y{{y}_{1}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1$.
Using the above property, we have
Equation of tangent $\dfrac{2x}{9}+\dfrac{5y}{3\times 5}=1$
i.e. $\dfrac{2x}{9}+\dfrac{y}{3}=1$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{x}{\dfrac{9}{2}}+\dfrac{y}{3}=1$
Hence the tangent intersects the x-axis at $A\left( \dfrac{9}{2},0 \right)$ and the y-axis at \[C\left( 0,3 \right)\].
As is evident from the graph area of the Quadrilateral = $4\times ar\left( \Delta AOC \right)$
$ar\left( \Delta AOC \right)=\dfrac{1}{2}OA\times OC=\dfrac{1}{2}\times \dfrac{9}{2}\times 3=\dfrac{27}{4}$
Hence area of the Quadrilateral = $4\times \dfrac{27}{4}=27$
Hence area of the Quadrilateral = 27 sq-units.
Hence option [d] is correct
Note: This question can be solved directly using the fact that area of Quadrilateral formed by the tangents at the endpoints of latus recti $=\dfrac{2{{a}^{2}}}{e}$
Using the above property we have area of Quadrilateral $=\dfrac{2\times 9}{\dfrac{2}{3}}=27$ which is same as obtained above
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Using empirical formula calculate the mode of the following class 1 statistics CBSE

What are the factors of 100 class 7 maths CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

The value of 6 more than 7 is A 1 B 1 C 13 D 13 class 7 maths CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




