
The area of an equilateral triangle is \[{\rm{49}}\sqrt {\rm{3}} {\rm{c}}{{\rm{m}}^{\rm{2}}}\]. Taking each angular point as the centre, circles are drawn with a radius equal to half the length of the side of the triangle. Find the area of the triangle not included in the circles. (Take \[\sqrt {\rm{3}} {\rm{ = 1}}{\rm{.732}}\])
Answer
577.2k+ views
Hint:
Here, we have to find the area of the triangle not included in the circles. Firstly we will find the side of the equilateral triangle by equating the equation of area of the equilateral triangle with its given value. Then we will find the area of each sector and then multiplying it with three as the triangle has three vertices at which the sectors are formed. Then by subtracting the area of total sectors from the total area of the equilateral triangle, we will get the area of the triangle not included in the circles.
Complete step by step solution:
It is given that area of the equilateral triangle is \[{\rm{49}}\sqrt {\rm{3}} {\rm{c}}{{\rm{m}}^{\rm{2}}}\].
We know that all the sides of an equilateral triangle is equal and all the three angle is equal to\[{60^{\circ}}\]
Let, \[{\rm{a cm}}\] be the side of the equilateral triangle
Area of the equilateral triangle \[{\rm{ = }}\dfrac{{\sqrt {\rm{3}} {{\rm{a}}^{\rm{2}}}}}{{\rm{4}}}{\rm{ = 49}}\sqrt {\rm{3}} \]
So, by solving this equation we will get the value of side of triangle i.e. a
\[{{\rm{a}}^2}{\rm{ = 49}}\sqrt {\rm{3}} \times \dfrac{4}{{\sqrt 3 }}{\rm{ = 49}} \times {\rm{4 = 196}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {\rm{a = }}\sqrt {196} {\rm{ = 14 cm}}\]
Therefore, \[{\rm{14 cm}}\] is the length of the side of the triangle.
It is given that the radius of the circles drawn is equal to the half the length of the side of the triangle.
Radius of the circle, \[{\rm{r = }}\dfrac{{\rm{a}}}{{\rm{2}}}{\rm{ = }}\dfrac{{{\rm{14}}}}{{\rm{2}}}{\rm{ = 7 cm}}\]
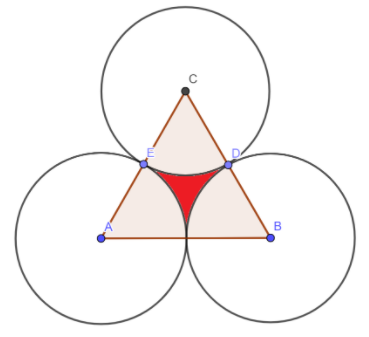
Now we have to find the value of the area of sectors present inside the triangle.
There are three sectors present in the triangle. We will find the area of one sector and then multiply it with three to get the total area of the sectors.
Area of one sector \[{\rm{ = }}\dfrac{{\rm{\theta }}}{{{\rm{360}}}}{\rm{ \times \pi }}{{\rm{r}}^{\rm{2}}}{\rm{ = }}\dfrac{{{\rm{60}}}}{{{\rm{360}}}}{\rm{ \times 3}}{\rm{.14 \times }}{{\rm{7}}^{\rm{2}}}{\rm{ = }}\dfrac{{\rm{1}}}{{\rm{6}}}{\rm{ \times 154 = }}\dfrac{{{\rm{77}}}}{{\rm{3}}}{\rm{c}}{{\rm{m}}^{\rm{2}}}\]
Total area of the sectors present inside the triangle \[{\rm{ = 3 \times area of each sector = 3}} \times \dfrac{{{\rm{77}}}}{{\rm{3}}} = 77{\rm{c}}{{\rm{m}}^{\rm{2}}}\]
Then by subtracting the area of total sectors from the total area of the equilateral triangle, we will get the area of the triangle not included in the circles.
Area of the triangle not included in the circles \[{\rm{ = 49}}\sqrt {\rm{3}} {\rm{ - 77 = (49 \times 1}}{\rm{.732) - 77 = 84}}{\rm{.86 - 77 = 7}}{\rm{.86 c}}{{\rm{m}}^{\rm{2}}}\]
Hence, area of the triangle not included in the circles i.e. red colored shaded region shown in the figure is \[{\rm{7}}{\rm{.86 c}}{{\rm{m}}^{\rm{2}}}\]
Note:
Geometry is the branch of mathematics that deals with points, lines and shapes.
There are some basic definitions which we need to know:
A triangle is a polygon with three edges/sides and three vertices. Side is one of the straight line segments which is used to construct/draw a polygon.
When two or more lines cross each other in a plane, they are called intersecting lines and the point where these lines intersect is called a Point of Intersection or vertices.
Here, we have to find the area of the triangle not included in the circles. Firstly we will find the side of the equilateral triangle by equating the equation of area of the equilateral triangle with its given value. Then we will find the area of each sector and then multiplying it with three as the triangle has three vertices at which the sectors are formed. Then by subtracting the area of total sectors from the total area of the equilateral triangle, we will get the area of the triangle not included in the circles.
Complete step by step solution:
It is given that area of the equilateral triangle is \[{\rm{49}}\sqrt {\rm{3}} {\rm{c}}{{\rm{m}}^{\rm{2}}}\].
We know that all the sides of an equilateral triangle is equal and all the three angle is equal to\[{60^{\circ}}\]
Let, \[{\rm{a cm}}\] be the side of the equilateral triangle
Area of the equilateral triangle \[{\rm{ = }}\dfrac{{\sqrt {\rm{3}} {{\rm{a}}^{\rm{2}}}}}{{\rm{4}}}{\rm{ = 49}}\sqrt {\rm{3}} \]
So, by solving this equation we will get the value of side of triangle i.e. a
\[{{\rm{a}}^2}{\rm{ = 49}}\sqrt {\rm{3}} \times \dfrac{4}{{\sqrt 3 }}{\rm{ = 49}} \times {\rm{4 = 196}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {\rm{a = }}\sqrt {196} {\rm{ = 14 cm}}\]
Therefore, \[{\rm{14 cm}}\] is the length of the side of the triangle.
It is given that the radius of the circles drawn is equal to the half the length of the side of the triangle.
Radius of the circle, \[{\rm{r = }}\dfrac{{\rm{a}}}{{\rm{2}}}{\rm{ = }}\dfrac{{{\rm{14}}}}{{\rm{2}}}{\rm{ = 7 cm}}\]

Now we have to find the value of the area of sectors present inside the triangle.
There are three sectors present in the triangle. We will find the area of one sector and then multiply it with three to get the total area of the sectors.
Area of one sector \[{\rm{ = }}\dfrac{{\rm{\theta }}}{{{\rm{360}}}}{\rm{ \times \pi }}{{\rm{r}}^{\rm{2}}}{\rm{ = }}\dfrac{{{\rm{60}}}}{{{\rm{360}}}}{\rm{ \times 3}}{\rm{.14 \times }}{{\rm{7}}^{\rm{2}}}{\rm{ = }}\dfrac{{\rm{1}}}{{\rm{6}}}{\rm{ \times 154 = }}\dfrac{{{\rm{77}}}}{{\rm{3}}}{\rm{c}}{{\rm{m}}^{\rm{2}}}\]
Total area of the sectors present inside the triangle \[{\rm{ = 3 \times area of each sector = 3}} \times \dfrac{{{\rm{77}}}}{{\rm{3}}} = 77{\rm{c}}{{\rm{m}}^{\rm{2}}}\]
Then by subtracting the area of total sectors from the total area of the equilateral triangle, we will get the area of the triangle not included in the circles.
Area of the triangle not included in the circles \[{\rm{ = 49}}\sqrt {\rm{3}} {\rm{ - 77 = (49 \times 1}}{\rm{.732) - 77 = 84}}{\rm{.86 - 77 = 7}}{\rm{.86 c}}{{\rm{m}}^{\rm{2}}}\]
Hence, area of the triangle not included in the circles i.e. red colored shaded region shown in the figure is \[{\rm{7}}{\rm{.86 c}}{{\rm{m}}^{\rm{2}}}\]
Note:
Geometry is the branch of mathematics that deals with points, lines and shapes.
There are some basic definitions which we need to know:
A triangle is a polygon with three edges/sides and three vertices. Side is one of the straight line segments which is used to construct/draw a polygon.
When two or more lines cross each other in a plane, they are called intersecting lines and the point where these lines intersect is called a Point of Intersection or vertices.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




