
The area of a circle inscribed in an equilateral triangle is 154sq.cm. Find the perimeter of the triangle.
Answer
569.7k+ views
Hint: One should be aware of perimeter and area of circle and triangle. It involves some basic formulae for perimeter and area. And basically for triangles, Pythagora's theorem is also used.
Area of circle =$\text{ }\pi {{\text{r}}^{2}}$, Where r is the radius of circle and value of $\pi $ is $\dfrac{22}{7}$.
Equilateral triangle is the triangle which has all sides equal and each angle is of ${{60}^{\circ }}$ .
Pythagoras theorem is used in right-angled triangles.

According to this theorem,
${{\left( hypotenuse \right)}^{2}}={{\left( perpendicular \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( base \right)}^{2}}$
${{\left( AC \right)}^{2}}={{\left( AB \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( BC \right)}^{2}}$
Complete step-by-step answer:
Now, let’s solve the question.
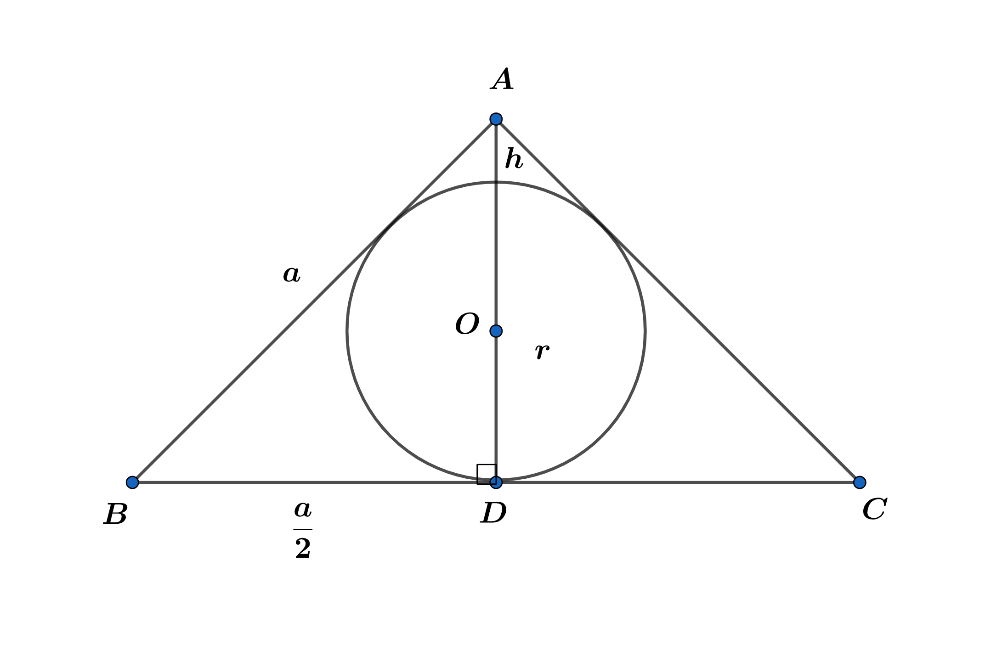
Let the radius of the circle be ‘r’ cm.
Then, area of circle =$\pi {{r}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow 154=\dfrac{22}{7}\times {{r}^{2}}$
Now, we need to find r.
$\Rightarrow {{r}^{2}}=154\times \dfrac{7}{22}$
After reducing,
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{r}^{2}}=49 \\
& \Rightarrow r=7cm \\
\end{align}$
As we know that ABC is an equilateral triangle, h is the altitude of $\Delta ABC$ and O is the centre of $\Delta ABC$, is the point of intersection of the angular bisectors. So we can say that these bisectors are also the altitude and medians whose point of intersection divides the medians in the ratio 2:1, hence:
$\therefore \angle $ADB = ${{90}^{\circ }}$ and OD = $\dfrac{1}{3}$ AD and OD is radius of circle.
Now, let each side of the triangle be ‘a’ cm and its height be ‘h’ cm.
Then, \[r=\dfrac{h}{3}\Rightarrow h=3r\]
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow h=3\times 7 \\
& \Rightarrow h=21cm \\
\end{align}\]
From figure we can observe that height is the perpendicular, if a is the side then $\dfrac{a}{\begin{align}
& 2 \\
& \\
\end{align}}$ is the base of the right angled triangle and ‘a’ i.e. side of the triangle will be considered as the hypotenuse of the triangle.
$\Rightarrow {{a}^{2}}={{h}^{2}}+{{\left( \dfrac{a}{2} \right)}^{2}}$
On further solving,
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{h}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}-{{\left( \dfrac{a}{2} \right)}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow h=\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}-{{\left( \dfrac{a}{2} \right)}^{2}}}=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}a}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{21\times 2}{\sqrt{3}}=a \\
& \Rightarrow a=\dfrac{42}{\sqrt{3}}\times \dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{3}} \\
& \Rightarrow 14\sqrt{3} \\
\end{align}$
Value of $\sqrt{3}$ is 1.73.
Perimeter of the equilateral triangle is $3\times 14\times 1.73$ = 72.66cm.
Note: Remember all the formulae before solving questions related to perimeter and area. At the end, solve the whole answer including root value. Do not leave the answer in under root. And always draw diagrams before solving such questions. The common mistake done by students is that they do not rationalise root value.
Area of circle =$\text{ }\pi {{\text{r}}^{2}}$, Where r is the radius of circle and value of $\pi $ is $\dfrac{22}{7}$.
Equilateral triangle is the triangle which has all sides equal and each angle is of ${{60}^{\circ }}$ .
Pythagoras theorem is used in right-angled triangles.

According to this theorem,
${{\left( hypotenuse \right)}^{2}}={{\left( perpendicular \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( base \right)}^{2}}$
${{\left( AC \right)}^{2}}={{\left( AB \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( BC \right)}^{2}}$
Complete step-by-step answer:
Now, let’s solve the question.

Let the radius of the circle be ‘r’ cm.
Then, area of circle =$\pi {{r}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow 154=\dfrac{22}{7}\times {{r}^{2}}$
Now, we need to find r.
$\Rightarrow {{r}^{2}}=154\times \dfrac{7}{22}$
After reducing,
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{r}^{2}}=49 \\
& \Rightarrow r=7cm \\
\end{align}$
As we know that ABC is an equilateral triangle, h is the altitude of $\Delta ABC$ and O is the centre of $\Delta ABC$, is the point of intersection of the angular bisectors. So we can say that these bisectors are also the altitude and medians whose point of intersection divides the medians in the ratio 2:1, hence:
$\therefore \angle $ADB = ${{90}^{\circ }}$ and OD = $\dfrac{1}{3}$ AD and OD is radius of circle.
Now, let each side of the triangle be ‘a’ cm and its height be ‘h’ cm.
Then, \[r=\dfrac{h}{3}\Rightarrow h=3r\]
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow h=3\times 7 \\
& \Rightarrow h=21cm \\
\end{align}\]
From figure we can observe that height is the perpendicular, if a is the side then $\dfrac{a}{\begin{align}
& 2 \\
& \\
\end{align}}$ is the base of the right angled triangle and ‘a’ i.e. side of the triangle will be considered as the hypotenuse of the triangle.
$\Rightarrow {{a}^{2}}={{h}^{2}}+{{\left( \dfrac{a}{2} \right)}^{2}}$
On further solving,
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{h}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}-{{\left( \dfrac{a}{2} \right)}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow h=\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}-{{\left( \dfrac{a}{2} \right)}^{2}}}=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}a}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{21\times 2}{\sqrt{3}}=a \\
& \Rightarrow a=\dfrac{42}{\sqrt{3}}\times \dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{3}} \\
& \Rightarrow 14\sqrt{3} \\
\end{align}$
Value of $\sqrt{3}$ is 1.73.
Perimeter of the equilateral triangle is $3\times 14\times 1.73$ = 72.66cm.
Note: Remember all the formulae before solving questions related to perimeter and area. At the end, solve the whole answer including root value. Do not leave the answer in under root. And always draw diagrams before solving such questions. The common mistake done by students is that they do not rationalise root value.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 10 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
A boat goes 24 km upstream and 28 km downstream in class 10 maths CBSE

State and explain Ohms law class 10 physics CBSE

Write a letter to the editor of a newspaper explaining class 10 english CBSE

Distinguish between soap and detergent class 10 chemistry CBSE

a Why did Mendel choose pea plants for his experiments class 10 biology CBSE

What is a "free hit" awarded for in limited-overs cricket?




