
The area in the bounded by the hyperbola $9{{x}^{2}}-{{y}^{2}}=36$ and the lines $x=2,x=4$ is \[\]
A. $6\sqrt{3}$\[\]
B. $\log \left( \sqrt{3}+2 \right)$\[\]
C. $12\sqrt{3}-\log \left( 2+\sqrt{3} \right)$\[\]
D. None of these\[\]
Answer
584.1k+ views
Hint: We draw the plot of the given hyperbola $9{{x}^{2}}-{{y}^{2}}=36$ and the two lines $x=2,x=4$. We find the required region and the limits for the definite integral to find the area. We write the given equation $9{{x}^{2}}-{{y}^{2}}=36$ in explicit form for the first quadrant and integrate within the obtained limits .\[\]
Complete step by step answer:
We know that the area $A$ enclosed by two curves $f\left( x \right),g\left( x \right)$ with two points of intersection is determined using definite integral with limits ${{x}_{1}},{{x}_{2}}$ obtained from investigation as
\[A=\int_{{{x}_{1}}}^{{{x}_{2}}}{\left( f\left( x \right)-g\left( x \right) \right)}\]
We also know the standard indefinite integral of the implicit function $\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}-{{y}^{2}}}$ as
\[\int{\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}-{{y}^{2}}}dx=\dfrac{x}{2}}\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}-{{y}^{2}}}-\log \left( x+\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}-{{y}^{2}}} \right)+c\]
Where $c$ is any real constant of integration.
We know that the standard equation of hyperbola with vertices $\left( -a,0 \right),\left( a,0 \right)$ is
\[\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}-\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1\]
We convert the given equation into the standard from and obtain the value of $a$. We have,
\[\begin{align}
& 9{{x}^{2}}-{{y}^{2}}=36 \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{4}-\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{36}=1 \\
\end{align}\]
We compare the obtained equation in the stand form and get${{a}^{2}}=4\Rightarrow a=\pm 2$. So the vertices of the hyperbola are $\left( -2,0 \right),\left( 2,0 \right)$ out of which only $\left( 2,0 \right)$ lies in the first quadrant. We pot the hyperbola and draw the line $x=2$ and observe that it passes through the vertex$\left( 2,0 \right)$. We draw the line $x=4$ and find the region enclosed by the hyperbola and the lines.\[\]
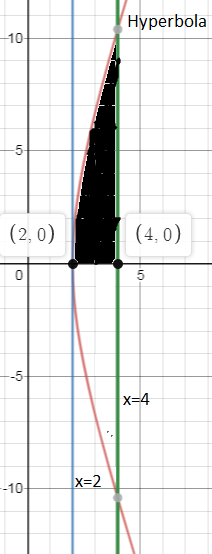
So we see that the shaded region is the required as asked in the question which is enclosed by the two lines a, the hyperbola and lies in the first quadrant. We see that the hyperbola decides the beginning of the region at the left at $x=2$ to be ended at the point $x=4$. So the limit of definite integral will be 2 to 4. Now we shall write the equation of hyperbola in explicit functional form
\[\begin{align}
& 9{{x}^{2}}-{{y}^{2}}=36 \\
& \Rightarrow y=\pm 3\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}-4} \\
\end{align}\]
We only take the positive sign for the first quadrant and find the required area $A$ in square units as ,
\[\begin{align}
& A=\int_{2}^{4}{3\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}-4}} \\
& =3\left[ \dfrac{x}{2}\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}-4}-\log \left( x+\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}-4} \right) \right]_{2}^{4} \\
& =3\left[ \left( 2\cdot 2\sqrt{3}-\log \left( 4+2\sqrt{3} \right) \right)-\left( 0-\log 2 \right) \right] \\
& =3\left[ 4\sqrt{3}-\log \left( \dfrac{4+2\sqrt{3}}{2} \right) \right] \\
& =12\sqrt{3}-\log \left( 2+\sqrt{3} \right) \\
\end{align}\]
So the correct option is C.\[\]
Note:
We have rejected the area under $x-$axis as it was asked for the area in the first quadrant. We have to add the area under $x-$axis to find the total area which is enclosed by the curves which is in this case is equal because of the hyperbola is symmetrical about $x-$axis. So total area enclosed is $24\sqrt{3}-2\log \left( 2+\sqrt{3} \right)$.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that the area $A$ enclosed by two curves $f\left( x \right),g\left( x \right)$ with two points of intersection is determined using definite integral with limits ${{x}_{1}},{{x}_{2}}$ obtained from investigation as
\[A=\int_{{{x}_{1}}}^{{{x}_{2}}}{\left( f\left( x \right)-g\left( x \right) \right)}\]
We also know the standard indefinite integral of the implicit function $\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}-{{y}^{2}}}$ as
\[\int{\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}-{{y}^{2}}}dx=\dfrac{x}{2}}\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}-{{y}^{2}}}-\log \left( x+\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}-{{y}^{2}}} \right)+c\]
Where $c$ is any real constant of integration.
We know that the standard equation of hyperbola with vertices $\left( -a,0 \right),\left( a,0 \right)$ is
\[\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}-\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1\]
We convert the given equation into the standard from and obtain the value of $a$. We have,
\[\begin{align}
& 9{{x}^{2}}-{{y}^{2}}=36 \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{4}-\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{36}=1 \\
\end{align}\]
We compare the obtained equation in the stand form and get${{a}^{2}}=4\Rightarrow a=\pm 2$. So the vertices of the hyperbola are $\left( -2,0 \right),\left( 2,0 \right)$ out of which only $\left( 2,0 \right)$ lies in the first quadrant. We pot the hyperbola and draw the line $x=2$ and observe that it passes through the vertex$\left( 2,0 \right)$. We draw the line $x=4$ and find the region enclosed by the hyperbola and the lines.\[\]

So we see that the shaded region is the required as asked in the question which is enclosed by the two lines a, the hyperbola and lies in the first quadrant. We see that the hyperbola decides the beginning of the region at the left at $x=2$ to be ended at the point $x=4$. So the limit of definite integral will be 2 to 4. Now we shall write the equation of hyperbola in explicit functional form
\[\begin{align}
& 9{{x}^{2}}-{{y}^{2}}=36 \\
& \Rightarrow y=\pm 3\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}-4} \\
\end{align}\]
We only take the positive sign for the first quadrant and find the required area $A$ in square units as ,
\[\begin{align}
& A=\int_{2}^{4}{3\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}-4}} \\
& =3\left[ \dfrac{x}{2}\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}-4}-\log \left( x+\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}-4} \right) \right]_{2}^{4} \\
& =3\left[ \left( 2\cdot 2\sqrt{3}-\log \left( 4+2\sqrt{3} \right) \right)-\left( 0-\log 2 \right) \right] \\
& =3\left[ 4\sqrt{3}-\log \left( \dfrac{4+2\sqrt{3}}{2} \right) \right] \\
& =12\sqrt{3}-\log \left( 2+\sqrt{3} \right) \\
\end{align}\]
So the correct option is C.\[\]
Note:
We have rejected the area under $x-$axis as it was asked for the area in the first quadrant. We have to add the area under $x-$axis to find the total area which is enclosed by the curves which is in this case is equal because of the hyperbola is symmetrical about $x-$axis. So total area enclosed is $24\sqrt{3}-2\log \left( 2+\sqrt{3} \right)$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




