
The anomeric carbon in D-(+)-glucose is:
A. C-1 carbon
B. C-2 carbon
C. C-5 carbon
D. C-6 carbon
Answer
576.3k+ views
Hint: Think about the definition of the anomeric carbon and how the placement of the hydroxyl group around it enables it to form the $\alpha $- and $\beta $- anomers of and given sugar.
Complete step by step solution:
- We know that anomeric carbon is carbon whose stereochemistry determines the type of anomer that the compound is. It is used to refer to only the cyclized forms of sugars.
- In the open chain form of the sugar, the anomeric carbon is known to be the carbonyl carbon that is involved in the aldehydic or the ketonic group. After cyclization, the anomeric carbon is found near the oxygen atom in the pyranose or furanose ring.
- Here, we are concerned about the pyranose form of glucose. First let us look at the Fischer projection formula and how it undergoes cyclization.
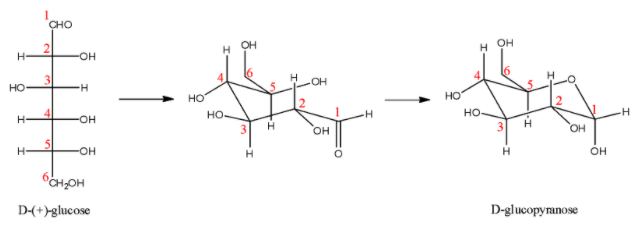
Here, we can see the carbon atom that is next to the oxygen atom in the pyranose ring, and we can determine that it is the same carbon that is present in the aldehydic group in the Fischer projection formula.
- The ring can close in two different ways: with the new OH group down or up in the conventional Haworth projection. This carbon atom which can assume either configuration is referred to as anomeric carbon and the two different cyclised forms as anomers of each other called $\alpha $- D – glucopyranose and $\beta $- D – glucopyranose. When the hydroxyl group on the C-1 atom is pointing downwards, it is called the $\alpha $- anomer and when it is pointing upwards, it is called the $\beta $- anomer. The structures are:
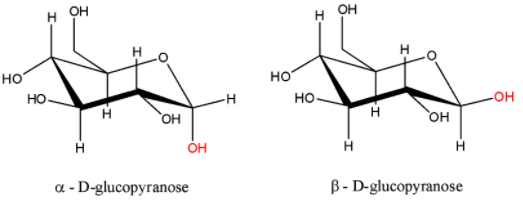
Therefore, from above we can easily conclude that option A is the correct option to the given question.
Note: An anomer is a special case of an epimer. An epimer is an isomer where the stereochemistry of a sugar is changed at one and only one chiral center. In anomers, that chiral centre happens to be the C-1 atom. D-glucose and D-galactose are epimers of each other.
Complete step by step solution:
- We know that anomeric carbon is carbon whose stereochemistry determines the type of anomer that the compound is. It is used to refer to only the cyclized forms of sugars.
- In the open chain form of the sugar, the anomeric carbon is known to be the carbonyl carbon that is involved in the aldehydic or the ketonic group. After cyclization, the anomeric carbon is found near the oxygen atom in the pyranose or furanose ring.
- Here, we are concerned about the pyranose form of glucose. First let us look at the Fischer projection formula and how it undergoes cyclization.

Here, we can see the carbon atom that is next to the oxygen atom in the pyranose ring, and we can determine that it is the same carbon that is present in the aldehydic group in the Fischer projection formula.
- The ring can close in two different ways: with the new OH group down or up in the conventional Haworth projection. This carbon atom which can assume either configuration is referred to as anomeric carbon and the two different cyclised forms as anomers of each other called $\alpha $- D – glucopyranose and $\beta $- D – glucopyranose. When the hydroxyl group on the C-1 atom is pointing downwards, it is called the $\alpha $- anomer and when it is pointing upwards, it is called the $\beta $- anomer. The structures are:

Therefore, from above we can easily conclude that option A is the correct option to the given question.
Note: An anomer is a special case of an epimer. An epimer is an isomer where the stereochemistry of a sugar is changed at one and only one chiral center. In anomers, that chiral centre happens to be the C-1 atom. D-glucose and D-galactose are epimers of each other.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




