
The angles of a quadrilateral are in AP and the greatest angle is the double of the least angle. Then find the least angle in radian.
\[
A.{\text{ }}\dfrac{\pi }{6} \\
B.{\text{ }}\dfrac{\pi }{4} \\
C.{\text{ }}\dfrac{\pi }{3} \\
D.{\text{ }}\dfrac{\pi }{5} \\
\]
Answer
611.7k+ views
Hint: Sum of all the angles of a quadrilateral is equal to \[2\pi \]. So, we have to form two equations, one with the given condition between greatest and the least angle and another with the condition that the sum of all the angles is equal to \[2\pi \]. On solving these equations, we will get the least angle.
Complete Step-by-step answer:
As we know that the sum of all the angles of a quadrilateral is equal to \[2\pi \].
And we are given that all the angles of the quadrilateral are in AP.
As we know that AP is the sequence in which the difference of each consecutive term is the same.
So, if the least angle of the quadrilateral ABCD is a.
Then according to the condition of AP, it's all other angles must be a + d, a + 2d, a + 3d. Where a and d are in radians.
So, a will be the least angle of the quadrilateral ABCD and a + 3d will be the greatest angle of the quadrilateral ABCD.
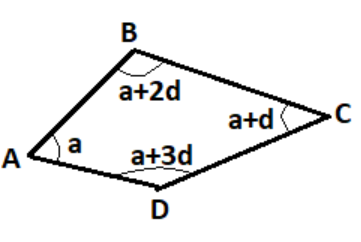
Now the sum of all the angles should be equal to \[2\pi \].
So, (a) + (a + d) + (a + 2d) + (a + 3d) = \[2\pi \]
4a + 6d = \[2\pi \]
Dividing both sides of the above equation by 2. We get,
2a + 3d = \[\pi \] (1)
Now as given in the question that the greatest angle is the double of the least angle.
So, a + 3d = 2a
Now subtracting both sides of the above equation by a. We get,
3d = a
Now putting the value of 3d in equation 1. We get,
2a + a = \[\pi \]
So, 3a = \[\pi \]
\[a = \dfrac{\pi }{3}\]
So, the least angle of the quadrilateral in radian will be \[\dfrac{\pi }{3}\].
Hence, the correct option will be C.
Note:- Whenever we come up with this type of problem, we assume the least angle as a and the other angles as (a + d), (a + 2d) and (a + 3d). Because all the angles of the quadrilateral are in AP and the difference of two consecutive terms (here angles) is equal. And then equate the sum of all angles of the quadrilateral with \[2\pi \] because the sum of all the angles of the quadrilateral is equal to \[2\pi \] . And then we equate twice of a with a + 3d because it is given in the question. Now after solving these two equations we will get the value of a which is the required least angle of the quadrilateral. This will be the easiest and efficient way to find the solution of the problem.
Complete Step-by-step answer:
As we know that the sum of all the angles of a quadrilateral is equal to \[2\pi \].
And we are given that all the angles of the quadrilateral are in AP.
As we know that AP is the sequence in which the difference of each consecutive term is the same.
So, if the least angle of the quadrilateral ABCD is a.
Then according to the condition of AP, it's all other angles must be a + d, a + 2d, a + 3d. Where a and d are in radians.
So, a will be the least angle of the quadrilateral ABCD and a + 3d will be the greatest angle of the quadrilateral ABCD.

Now the sum of all the angles should be equal to \[2\pi \].
So, (a) + (a + d) + (a + 2d) + (a + 3d) = \[2\pi \]
4a + 6d = \[2\pi \]
Dividing both sides of the above equation by 2. We get,
2a + 3d = \[\pi \] (1)
Now as given in the question that the greatest angle is the double of the least angle.
So, a + 3d = 2a
Now subtracting both sides of the above equation by a. We get,
3d = a
Now putting the value of 3d in equation 1. We get,
2a + a = \[\pi \]
So, 3a = \[\pi \]
\[a = \dfrac{\pi }{3}\]
So, the least angle of the quadrilateral in radian will be \[\dfrac{\pi }{3}\].
Hence, the correct option will be C.
Note:- Whenever we come up with this type of problem, we assume the least angle as a and the other angles as (a + d), (a + 2d) and (a + 3d). Because all the angles of the quadrilateral are in AP and the difference of two consecutive terms (here angles) is equal. And then equate the sum of all angles of the quadrilateral with \[2\pi \] because the sum of all the angles of the quadrilateral is equal to \[2\pi \] . And then we equate twice of a with a + 3d because it is given in the question. Now after solving these two equations we will get the value of a which is the required least angle of the quadrilateral. This will be the easiest and efficient way to find the solution of the problem.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Find the mode and median of the data 13 16 12 14 1-class-9-maths-CBSE

What were the main changes brought about by the Bolsheviks class 9 social science CBSE

What is the theme or message of the poem The road not class 9 english CBSE

What are the major achievements of the UNO class 9 social science CBSE

Explain the importance of pH in everyday life class 9 chemistry CBSE

Differentiate between parenchyma collenchyma and sclerenchyma class 9 biology CBSE




