
The angle which the normal ray makes with the mirror is equal to:
A). $30^\circ $
B). $45^\circ $
C). $90^\circ $
D). $180^\circ $
Answer
587.1k+ views
Hint: In this question we will use the law of reflection. There are three laws of reflection that state that
i). The incident ray, the reflected ray, and the normal at the point of incidence are all in the same plane.
ii). The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
iii). The reflected ray the incident ray is on the opposite sides of the normal.
Complete step-by-step solution:
A ray of light strikes a mirror in the plane and a ray of light reflects from the mirror. Reflection involves a change of direction of the light ray, and the Angle of Incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. The standard line is to the mirror rim, which gives the mirror an angle of 90 degrees. For all directions, this line is used as a reference point. The angle of incidence is the angle that makes the incident ray with the normal and the angle of reflected angle that makes the reflected ray with the normal. The diagram is as follows:
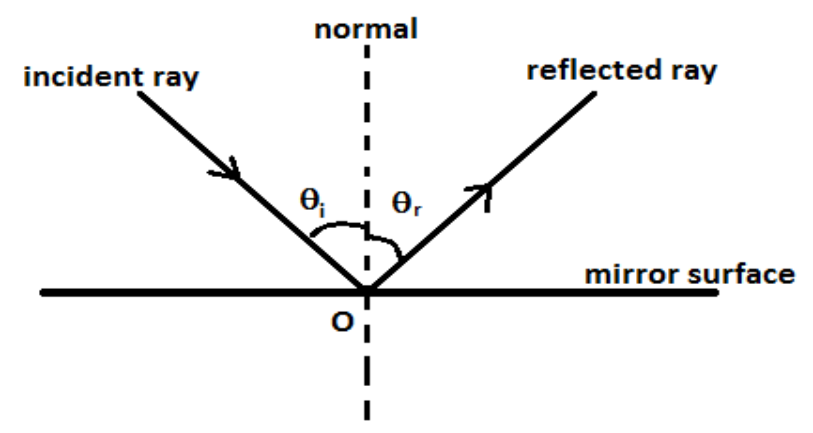
Where ${\theta _i} = $angle of incidence
And, ${\theta _r} = $angle of reflection.
The perpendicular drawn to the surface of the mirror at the point of incidence is known as a normal ray. So, the angle made by the ray with the mirror is equal to $90^\circ $. So, when a ray of light will strike the mirror surface at the $90^\circ $ then the ray of light will get reflected back from the same path as that of the incident ray. Hence the normal is perpendicular to the mirror surface as shown in the figure.
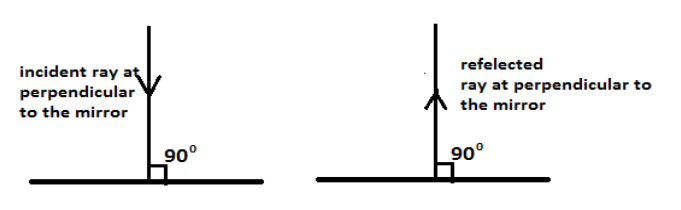
Hence option (C) is the correct answer.
Note: We should know some important terms when solving these questions and they are- the point on the mirror of the plane where reflection takes place is the point of incidence, the plane in which the incident rays, the reflected rays and the normal lines, and the plane of reflection are perpendicular to the mirror. The image formed by a plane mirror is always a virtual image (behind the mirror), the same size as that of the object. The image distance and the object distance are equal in the plane mirror and the image formed by the plane mirror is laterally inverted which means the left of the object will appear as the right of the image and vice-versa.
i). The incident ray, the reflected ray, and the normal at the point of incidence are all in the same plane.
ii). The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
iii). The reflected ray the incident ray is on the opposite sides of the normal.
Complete step-by-step solution:
A ray of light strikes a mirror in the plane and a ray of light reflects from the mirror. Reflection involves a change of direction of the light ray, and the Angle of Incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. The standard line is to the mirror rim, which gives the mirror an angle of 90 degrees. For all directions, this line is used as a reference point. The angle of incidence is the angle that makes the incident ray with the normal and the angle of reflected angle that makes the reflected ray with the normal. The diagram is as follows:

Where ${\theta _i} = $angle of incidence
And, ${\theta _r} = $angle of reflection.
The perpendicular drawn to the surface of the mirror at the point of incidence is known as a normal ray. So, the angle made by the ray with the mirror is equal to $90^\circ $. So, when a ray of light will strike the mirror surface at the $90^\circ $ then the ray of light will get reflected back from the same path as that of the incident ray. Hence the normal is perpendicular to the mirror surface as shown in the figure.

Hence option (C) is the correct answer.
Note: We should know some important terms when solving these questions and they are- the point on the mirror of the plane where reflection takes place is the point of incidence, the plane in which the incident rays, the reflected rays and the normal lines, and the plane of reflection are perpendicular to the mirror. The image formed by a plane mirror is always a virtual image (behind the mirror), the same size as that of the object. The image distance and the object distance are equal in the plane mirror and the image formed by the plane mirror is laterally inverted which means the left of the object will appear as the right of the image and vice-versa.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




