
The angle of rotation of the axis in order to eliminate the ‘${\text{xy}}$’ term in the equation ${x^2} + 2\sqrt 3 xy - {y^2} = 2{a^2}$ is
A. \[\dfrac{\pi }{6}\]
B. $\dfrac{\pi }{4}$
C. $\dfrac{\pi }{3}$
D.$\dfrac{\pi }{2}$
Answer
591.9k+ views
Hint: If the coordinate axis is rotated at an angle of ‘$\theta $’ then the co-ordinate of a point is given by
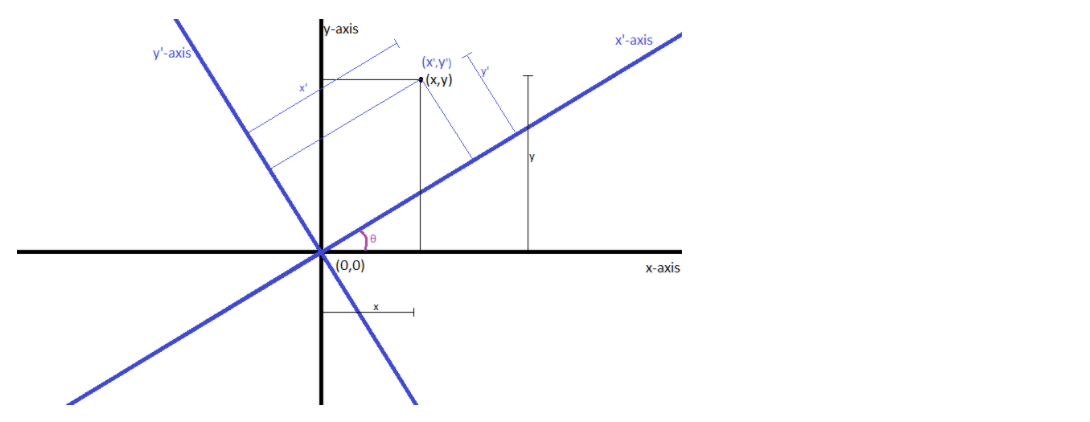
\[x = x'\cos \theta - y'\sin \theta \]
\[y = x'\sin \theta + y'\cos \theta \]
Using these we’ll find the equation of the curve with-respect-to new axis and then compare the coefficient of to $x'y'$ zero.
After that, we’ll have an equation on theta, and solving that equation for theta we’ll get our required answer.
Complete step by step answer:
If the co-ordinate axis is rotated through an angle‘$\theta $’ then the co-ordinate of any point with-respect-to the new axis is defined by
\[x' = x\cos \theta + y\sin \theta \]
\[y' = - x\sin \theta + y\cos \theta \]
Now solving for x and y, we get
\[x = x'\cos \theta - y'\sin \theta ..........(i)\]
\[y = x'\sin \theta + y'\cos \theta ...........(ii)\]
Where x’ and y’ are the new co-ordinate axis after rotation.
Now putting the value of x and y from equation (i) and (ii) in the given equation i.e. ${x^2} + 2\sqrt 3 xy - {y^2} = 2{a^2}$, we will get
\[{(x'\cos \theta - y'\sin \theta )^2} + 2\sqrt 3 (x'\cos \theta - y'\sin \theta )(x'\sin \theta + y'\cos \theta ) - {(x'\sin \theta + y'\cos \theta )^2} = 2{a^2}\]
On simplifying and using equation i.e. ${x^2} + 2\sqrt 3 xy - {y^2} = 2{a^2}$,\[ \Rightarrow {(x')^2}[{\cos ^2}\theta + 2\sqrt 3 \cos \theta \sin \theta - {\sin ^2}\theta ] + {(y')^2}[{\sin ^2}\theta - 2\sqrt {3\cos \theta \sin \theta } - {\cos ^2}\theta ] + x'y'[ - 2\cos \theta \sin \theta + 2\sqrt 3 {\cos ^2}\theta - 2\sqrt 3 {\sin ^2}\theta - 2\cos \theta \sin \theta ] = 2{a^2}\]
Now we have to find at what value of ${\text{\theta }}$ the coefficient of $x'y'$ will be eliminated i.e.,
\[i.e.[ - 2\cos \theta \sin \theta + 2\sqrt 3 {\cos ^2}\theta - 2\sqrt 3 {\sin ^2}\theta - 2\cos \theta \sin \theta ] = 0\]
\[ \Rightarrow 2\sqrt 3 ({\cos ^2}\theta - {\sin ^2}\theta ) - 4\cos \theta \sin \theta = 0\]
using double angle formula i.e. \[{\cos ^2}\theta - {\sin ^2}x = \cos (2\theta )\] and \[2\sin \theta \cos \theta = \sin (2\theta )\]
\[ \Rightarrow 2\sqrt 3 \cos (2\theta ) - 2\sin (2\theta ) = 0\]
Now, dividing the whole equation by 4
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}\cos (2\theta ) - \dfrac{1}{2}\sin (2\theta ) = 0.............(iii)\]
substituting the values of \[\sin \left( {\dfrac{\pi }{3}} \right) = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}\]and \[\cos \left( {\dfrac{\pi }{3}} \right) = \dfrac{1}{2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \sin \left( {\dfrac{\pi }{3}} \right)\cos (2\theta ) - \cos \left( {\dfrac{\pi }{3}} \right)\sin (2\theta ) = 0\]
now on using \[\sin A\cos B - \cos A\sin B = \sin (A - B)\]
\[ \Rightarrow \sin \left( {\dfrac{\pi }{3} - 2\theta } \right) = 0 = \sin (0)\]
On comparing,
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{\pi }{3} - 2\theta = 0\]
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{\pi }{3} = 2\theta \]
dividing both sides by 2
\[\therefore \theta = \dfrac{\pi }{6}\]
Hence, the correct option is (A).
Note: After equation (iii) we can also it by converting the in form of cosine as given below
i.e. \[\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}\cos (2\theta ) - \dfrac{1}{2}\sin (2\theta ) = 0\]
on substituting the values of \[\cos \left( {\dfrac{\pi }{6}} \right) = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}\] and \[\sin \left( {\dfrac{\pi }{6}} \right) = \dfrac{1}{2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \cos \left( {\dfrac{\pi }{6}} \right)\cos (2\theta ) - \sin \left( {\dfrac{\pi }{6}} \right)\sin (2\theta ) = 0\]
on using \[\cos A\cos B - \sin A\sin B = \cos (A + B)\]
\[ \Rightarrow \cos \left( {\dfrac{\pi }{6} + 2\theta } \right) = 0 = \cos (\dfrac{\pi }{2})\]
On comparing
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{\pi }{2} - \dfrac{\pi }{6} = 2\theta \]
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{\pi }{6} + 2\theta = \dfrac{\pi }{2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow 2\theta = \dfrac{{3\pi - \pi }}{6}\]
\[ \Rightarrow 2\theta = \dfrac{{2\pi }}{6}\]
Dividing both sides with 2
\[\therefore \theta = \dfrac{\pi }{6}\]
Additional information: Some general formula of trigonometry that used in the above solution
1) \[{\cos ^2}\theta - {\sin ^2}\theta = \cos (2\theta )\]
2) $2\sin \theta \cos \theta = \sin (2\theta )$
3) $\sin A\cos B - \cos A\sin B = \sin (A - B)$
The general solution of the equation$\sin x = \sin y$ is given by
$x = n\pi + {( - 1)^n}y$, where n is a set of whole numbers.

\[x = x'\cos \theta - y'\sin \theta \]
\[y = x'\sin \theta + y'\cos \theta \]
Using these we’ll find the equation of the curve with-respect-to new axis and then compare the coefficient of to $x'y'$ zero.
After that, we’ll have an equation on theta, and solving that equation for theta we’ll get our required answer.
Complete step by step answer:
If the co-ordinate axis is rotated through an angle‘$\theta $’ then the co-ordinate of any point with-respect-to the new axis is defined by
\[x' = x\cos \theta + y\sin \theta \]
\[y' = - x\sin \theta + y\cos \theta \]
Now solving for x and y, we get
\[x = x'\cos \theta - y'\sin \theta ..........(i)\]
\[y = x'\sin \theta + y'\cos \theta ...........(ii)\]
Where x’ and y’ are the new co-ordinate axis after rotation.
Now putting the value of x and y from equation (i) and (ii) in the given equation i.e. ${x^2} + 2\sqrt 3 xy - {y^2} = 2{a^2}$, we will get
\[{(x'\cos \theta - y'\sin \theta )^2} + 2\sqrt 3 (x'\cos \theta - y'\sin \theta )(x'\sin \theta + y'\cos \theta ) - {(x'\sin \theta + y'\cos \theta )^2} = 2{a^2}\]
On simplifying and using equation i.e. ${x^2} + 2\sqrt 3 xy - {y^2} = 2{a^2}$,\[ \Rightarrow {(x')^2}[{\cos ^2}\theta + 2\sqrt 3 \cos \theta \sin \theta - {\sin ^2}\theta ] + {(y')^2}[{\sin ^2}\theta - 2\sqrt {3\cos \theta \sin \theta } - {\cos ^2}\theta ] + x'y'[ - 2\cos \theta \sin \theta + 2\sqrt 3 {\cos ^2}\theta - 2\sqrt 3 {\sin ^2}\theta - 2\cos \theta \sin \theta ] = 2{a^2}\]
Now we have to find at what value of ${\text{\theta }}$ the coefficient of $x'y'$ will be eliminated i.e.,
\[i.e.[ - 2\cos \theta \sin \theta + 2\sqrt 3 {\cos ^2}\theta - 2\sqrt 3 {\sin ^2}\theta - 2\cos \theta \sin \theta ] = 0\]
\[ \Rightarrow 2\sqrt 3 ({\cos ^2}\theta - {\sin ^2}\theta ) - 4\cos \theta \sin \theta = 0\]
using double angle formula i.e. \[{\cos ^2}\theta - {\sin ^2}x = \cos (2\theta )\] and \[2\sin \theta \cos \theta = \sin (2\theta )\]
\[ \Rightarrow 2\sqrt 3 \cos (2\theta ) - 2\sin (2\theta ) = 0\]
Now, dividing the whole equation by 4
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}\cos (2\theta ) - \dfrac{1}{2}\sin (2\theta ) = 0.............(iii)\]
substituting the values of \[\sin \left( {\dfrac{\pi }{3}} \right) = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}\]and \[\cos \left( {\dfrac{\pi }{3}} \right) = \dfrac{1}{2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \sin \left( {\dfrac{\pi }{3}} \right)\cos (2\theta ) - \cos \left( {\dfrac{\pi }{3}} \right)\sin (2\theta ) = 0\]
now on using \[\sin A\cos B - \cos A\sin B = \sin (A - B)\]
\[ \Rightarrow \sin \left( {\dfrac{\pi }{3} - 2\theta } \right) = 0 = \sin (0)\]
On comparing,
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{\pi }{3} - 2\theta = 0\]
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{\pi }{3} = 2\theta \]
dividing both sides by 2
\[\therefore \theta = \dfrac{\pi }{6}\]
Hence, the correct option is (A).
Note: After equation (iii) we can also it by converting the in form of cosine as given below
i.e. \[\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}\cos (2\theta ) - \dfrac{1}{2}\sin (2\theta ) = 0\]
on substituting the values of \[\cos \left( {\dfrac{\pi }{6}} \right) = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}\] and \[\sin \left( {\dfrac{\pi }{6}} \right) = \dfrac{1}{2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \cos \left( {\dfrac{\pi }{6}} \right)\cos (2\theta ) - \sin \left( {\dfrac{\pi }{6}} \right)\sin (2\theta ) = 0\]
on using \[\cos A\cos B - \sin A\sin B = \cos (A + B)\]
\[ \Rightarrow \cos \left( {\dfrac{\pi }{6} + 2\theta } \right) = 0 = \cos (\dfrac{\pi }{2})\]
On comparing
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{\pi }{2} - \dfrac{\pi }{6} = 2\theta \]
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{\pi }{6} + 2\theta = \dfrac{\pi }{2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow 2\theta = \dfrac{{3\pi - \pi }}{6}\]
\[ \Rightarrow 2\theta = \dfrac{{2\pi }}{6}\]
Dividing both sides with 2
\[\therefore \theta = \dfrac{\pi }{6}\]
Additional information: Some general formula of trigonometry that used in the above solution
1) \[{\cos ^2}\theta - {\sin ^2}\theta = \cos (2\theta )\]
2) $2\sin \theta \cos \theta = \sin (2\theta )$
3) $\sin A\cos B - \cos A\sin B = \sin (A - B)$
The general solution of the equation$\sin x = \sin y$ is given by
$x = n\pi + {( - 1)^n}y$, where n is a set of whole numbers.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Accountancy: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE

What is the full form of pH?





