
The angle of refraction in glass is ${30^0}$ when a ray of light passing through air is incident on a plane glass surface at ${60^0}$. The same ray incident at the same angle on a liquid surface is refracted through ${45^0}$. What is the angle of refraction when this ray passing through the liquid is incident on the glass surface at ${45^0}$
Answer
573.9k+ views
Hint: Velocity of light will be different in different media. If velocity of light is higher in one medium and lesser in another medium then the first one is called a rarer medium and the second one is called denser medium. There is a law called snell’s law which relates the refractive indices of the media.
Formula used:
${\mu _i}\sin i = {\mu _r}\sin r$
Complete step by step answer:
Velocity is nothing but the rate of change of displacement i.e the ratio of displacement to the time taken. So the time taken will be displacement upon the velocity.
Velocity of light in any medium of refractive index(n) will be
$v = \dfrac{c}{n}$ where ‘c’ is the velocity of light in the free space and ‘n’ is the refractive index of the medium.
For air, the refractive index will be one. For glass, the refractive index will be greater than one. Hence when light enters from air to glass, its velocity decreases. In order to maintain the same time displacement also must decrease. That means the path travelled in the air by the light must decrease. This will be possible if the light bends towards the normal. Hence the incident angle and the refracted angle will be different. They are related with refractive indices and given by snell’s law.
${\mu _i}\sin i = {\mu _r}\sin r$
Where ${\mu _i}$ is the refractive index of incident medium and ${\mu _r}$ is the refractive index of refracted medium. $i$ is the incident angle and $r$ is the refracted angle.
The air refractive index is one.
For air to slab refraction shown below we apply snell's law to get a glass refractive index.
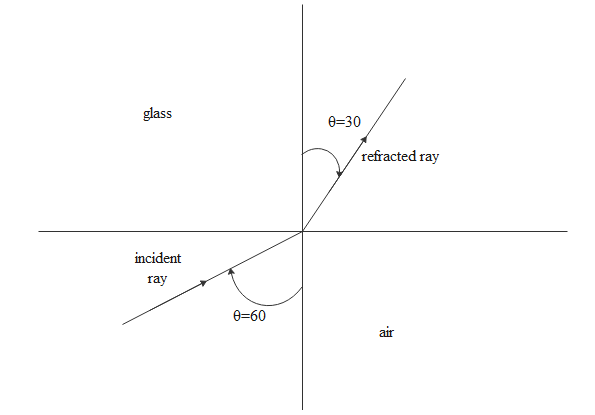
${\mu _i}\sin i = {\mu _r}\sin r$
$\eqalign{
& \Rightarrow 1\sin 60 = {\mu _g}\sin 30 \cr
& \Rightarrow {\mu _g} = \dfrac{{\sin 60}}{{\sin 30}} \cr
& \Rightarrow {\mu _g} = \sqrt 3 \cr} $
For air liquid interaction shown below we have
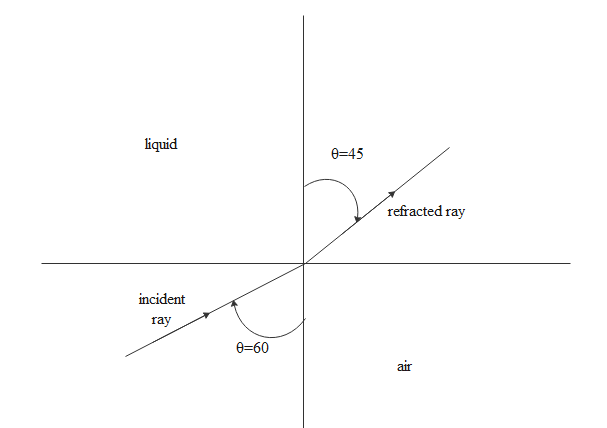
${\mu _i}\sin i = {\mu _r}\sin r$
$\eqalign{
& \Rightarrow 1\sin 60 = {\mu _l}\sin 45 \cr
& \Rightarrow {\mu _l} = \dfrac{{\sin 60}}{{\sin 45}} \cr
& \therefore {\mu _l} = \dfrac{{\sqrt 6 }}{2} \cr} $
For liquid glass interaction we have
${\mu _i}\sin i = {\mu _r}\sin r$
$\eqalign{
& \Rightarrow {\mu _l}\sin 45 = {\mu _g}\sin r \cr
& \Rightarrow \sin r = \dfrac{{{\mu _l}\sin 45}}{{{\mu _g}}} \cr
& \Rightarrow \sin r = \dfrac{{\dfrac{{\sqrt 6 }}{2}\sin 45}}{{\sqrt 3 }} \cr
& \Rightarrow \sin r = \dfrac{1}{2} \cr
& \therefore r = {30^0} \cr} $
Hence angle of refraction at glass surface will be 30 degrees.
Note:
Actually when there is a change in the velocity when light enters the different medium, there will be change in the length travelled too, because let us assume the light entered the rarer medium, then the velocity of light increases and the light will bend away from the normal so that the distance travelled also increases so that the time will be constant. One more thing to be remembered is that the refractive index of any medium can’t be less than one.
Formula used:
${\mu _i}\sin i = {\mu _r}\sin r$
Complete step by step answer:
Velocity is nothing but the rate of change of displacement i.e the ratio of displacement to the time taken. So the time taken will be displacement upon the velocity.
Velocity of light in any medium of refractive index(n) will be
$v = \dfrac{c}{n}$ where ‘c’ is the velocity of light in the free space and ‘n’ is the refractive index of the medium.
For air, the refractive index will be one. For glass, the refractive index will be greater than one. Hence when light enters from air to glass, its velocity decreases. In order to maintain the same time displacement also must decrease. That means the path travelled in the air by the light must decrease. This will be possible if the light bends towards the normal. Hence the incident angle and the refracted angle will be different. They are related with refractive indices and given by snell’s law.
${\mu _i}\sin i = {\mu _r}\sin r$
Where ${\mu _i}$ is the refractive index of incident medium and ${\mu _r}$ is the refractive index of refracted medium. $i$ is the incident angle and $r$ is the refracted angle.
The air refractive index is one.
For air to slab refraction shown below we apply snell's law to get a glass refractive index.

${\mu _i}\sin i = {\mu _r}\sin r$
$\eqalign{
& \Rightarrow 1\sin 60 = {\mu _g}\sin 30 \cr
& \Rightarrow {\mu _g} = \dfrac{{\sin 60}}{{\sin 30}} \cr
& \Rightarrow {\mu _g} = \sqrt 3 \cr} $
For air liquid interaction shown below we have

${\mu _i}\sin i = {\mu _r}\sin r$
$\eqalign{
& \Rightarrow 1\sin 60 = {\mu _l}\sin 45 \cr
& \Rightarrow {\mu _l} = \dfrac{{\sin 60}}{{\sin 45}} \cr
& \therefore {\mu _l} = \dfrac{{\sqrt 6 }}{2} \cr} $
For liquid glass interaction we have
${\mu _i}\sin i = {\mu _r}\sin r$
$\eqalign{
& \Rightarrow {\mu _l}\sin 45 = {\mu _g}\sin r \cr
& \Rightarrow \sin r = \dfrac{{{\mu _l}\sin 45}}{{{\mu _g}}} \cr
& \Rightarrow \sin r = \dfrac{{\dfrac{{\sqrt 6 }}{2}\sin 45}}{{\sqrt 3 }} \cr
& \Rightarrow \sin r = \dfrac{1}{2} \cr
& \therefore r = {30^0} \cr} $
Hence angle of refraction at glass surface will be 30 degrees.
Note:
Actually when there is a change in the velocity when light enters the different medium, there will be change in the length travelled too, because let us assume the light entered the rarer medium, then the velocity of light increases and the light will bend away from the normal so that the distance travelled also increases so that the time will be constant. One more thing to be remembered is that the refractive index of any medium can’t be less than one.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




