
The angle of reflection is the angle between ________ and ________.
Answer
579.9k+ views
Hint: The angle of reflection is a term more frequently used in optical physics. So, to answer this question we will be discussing the definition of angle of reflection in optical physics and how it is obtained. Along that, we will also be discussing the laws of reflection.
Complete step-by-step answer:
As shown in the figure, the angle of reflection is the angle between the normal and the reflected ray. The angle r, shown in the figure represents the angle of reflection.
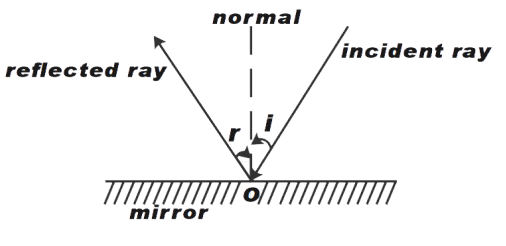
Reflection is a phenomenon that occurs when a ray of light strikes a shiny metal surface. A mirror is the most common way to explain the phenomenon of reflection. As shown in the diagram above, the ray of light strikes the horizontal mirror at point O. This ray of light is termed as incident ray. This ray of light is reflected back at some angle through a point O. This other ray is termed as the reflected ray. If we draw a vertical line from point O, perpendicular to the mirror, we get the normal. This normal divides the reflected ray and incident ray in two equal parts. It means that the angle made by the normal and reflected ray is equal to the angle made by normal and incident rays. This is also the first law of reflection. It states that angle of reflection and angle of incidence are equal i.e. (i= r). The second law of reflection states that the angle of reflection and angle of incidence lie in the same plane.
Therefore, the correct answer is, the angle of reflection, the angle between the normal and reflected ray.
Note: In this case, the mirror is a plane surface therefore the angle of reflection and incidence is the same. If the ray of light strikes the rough surface, these angles differ from each other. Such a reflection of light is called diffuse reflection.
Complete step-by-step answer:
As shown in the figure, the angle of reflection is the angle between the normal and the reflected ray. The angle r, shown in the figure represents the angle of reflection.

Reflection is a phenomenon that occurs when a ray of light strikes a shiny metal surface. A mirror is the most common way to explain the phenomenon of reflection. As shown in the diagram above, the ray of light strikes the horizontal mirror at point O. This ray of light is termed as incident ray. This ray of light is reflected back at some angle through a point O. This other ray is termed as the reflected ray. If we draw a vertical line from point O, perpendicular to the mirror, we get the normal. This normal divides the reflected ray and incident ray in two equal parts. It means that the angle made by the normal and reflected ray is equal to the angle made by normal and incident rays. This is also the first law of reflection. It states that angle of reflection and angle of incidence are equal i.e. (i= r). The second law of reflection states that the angle of reflection and angle of incidence lie in the same plane.
Therefore, the correct answer is, the angle of reflection, the angle between the normal and reflected ray.
Note: In this case, the mirror is a plane surface therefore the angle of reflection and incidence is the same. If the ray of light strikes the rough surface, these angles differ from each other. Such a reflection of light is called diffuse reflection.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




