
The angle of intersection between the curves \[y=\left[ \left| \sin x \right|+\left| \cos x \right| \right]\] and ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}=10$ , where $x$ denote the greatest integer $\le x$ , is
A.${{\tan }^{-1}}3$
B. ${{\tan }^{-1}}(-3)$
C. ${{\tan }^{-1}}\sqrt{3}$
D. ${{\tan }^{-1}}\left( -\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}} \right)$
Answer
585.9k+ views
Hint: We need to find the angle of intersection between the curves \[y=\left[ \left| \sin x \right|+\left| \cos x \right| \right]\] and ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}=10$ . For this first find the range of \[y=\left[ \left| \sin x \right|+\left| \cos x \right| \right]\] . After that, we will be considering only the value of lower bound since $x$ denotes the greatest integer $\le x$ ,i.e. $y=1$ . After that, substitute that value in ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}=10$ . Find its slope by differentiating. Then get the next slope by differentiating $y=1$ . Now use the equation $\tan \theta =\left| \dfrac{{{m}_{2}}-{{m}_{1}}}{1+{{m}_{1}}{{m}_{2}}} \right|$ to get the value of the angle.
Complete step by step answer:
We need to find the angle of intersection between the curves \[y=\left[ \left| \sin x \right|+\left| \cos x \right| \right]\] and ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}=10$ .
Let us find the range of \[y=\left[ \left| \sin x \right|+\left| \cos x \right| \right]\] .
We know that the range of $\left| \sin x \right|$ is
$0\le \left| \sin x \right|\le 1$
And the range of $\left| \cos x \right|$ is
$0\le \left| \cos x \right|\le 1$
Therefore, range of \[y=\left[ \left| \sin x \right|+\left| \cos x \right| \right]\] can be found out as follows:
\[y=\sin x+\cos x\]where$x\in \left( 0,\dfrac{\pi }{2} \right)$ .
Now multiply and divide RHS by $\sqrt{2}$ . So the above equation becomes,
\[y=\sqrt{2}\left( \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\sin x+\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\cos x \right)...(i)\]
Now, $\sin \left( x+\dfrac{\pi }{4} \right)=\sin x\cos \dfrac{\pi }{4}+\cos x\sin \dfrac{\pi }{4}$
Solving, we get
$\sin \left( x+\dfrac{\pi }{4} \right)=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\sin x+\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\cos x$
Therefore equation $(i)$ can be written as
\[y=\sqrt{2}\sin \left( x+\dfrac{\pi }{4} \right)\]
We know that $\sin x$ ranges from $[-1,1]$ .
Therefore, $-1\le \sin \left( x+\dfrac{\pi }{4} \right)\le 1$
Multiplying by $\sqrt{2}$ we get
$-\sqrt{2}\le \sqrt{2}\sin \left( x+\dfrac{\pi }{4} \right)\le \sqrt{2}$
As $\left| \sin x \right|$ ranges from $0\le \left| \sin x \right|\le 1$ , comparing with the above one, we get
\[y=\left[ \left| \sin x \right|+\left| \cos x \right| \right]=[1,\sqrt{2}]\]
It is given that $x$ denote the greatest integer $\le x$ . So we will consider the value $y=1$ .
Given that ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}=10$ . Substituting the value of $y$ here, we get
${{x}^{2}}+1=10\Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}=9$
$x=\pm 3$
Therefore, the intersection points are $q(3,1)$ and $p(-3,1)$ .
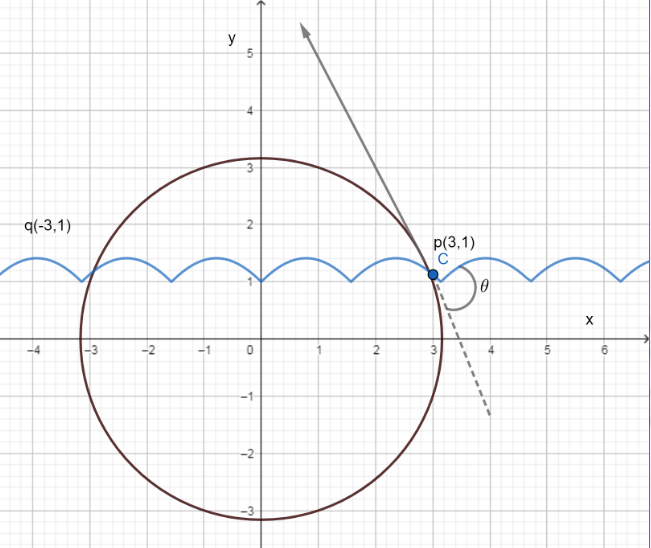
We need to find the slope of the tangent $(\pm 3,1)$ to ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}=10$ .
Now differentiate ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}=10$ with respect to $x$ . We will get
$2x+2y\dfrac{dy}{dx}=0$
$\Rightarrow x+y\dfrac{dy}{dx}=0$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{dy}{dx}=\dfrac{-x}{y}$
Now for the point $q(3,1)$ ,
${{\left. \dfrac{dy}{dx} \right|}_{p(3,1)}}=-3$
For the point $p(-3,1)$ ,
${{\left. \dfrac{dy}{dx} \right|}_{p(-3,1)}}=3$
Therefore, slope ${{m}_{1}}=\pm 3$ .
We have, $y=1$ .
Differentiating $y$ with respect to $x$ , we get
${{\left. \dfrac{dy}{dx} \right|}_{p}}=0$
That is, the slope ${{m}_{2}}={{\left. \dfrac{dy}{dx} \right|}_{p}}=0$ .
Now, to find the angle of intersection, we have
$\tan \theta =\left| \dfrac{{{m}_{2}}-{{m}_{1}}}{1+{{m}_{1}}{{m}_{2}}} \right|$
We will use in this case ${{m}_{2}}=-3$ as per the figure.
Substituting the value, we will get
$\tan \theta =\left| \dfrac{0-(-3)}{1+0\times -3} \right|=\left| 3 \right|=\pm 3$
Taking inverse of $\tan $ we will get the value of $\theta $ .
Therefore, $\theta ={{\tan }^{-1}}3$ and $\theta ={{\tan }^{-1}}(-3)$ .
Hence the correct options are A and B.
Note:
In this question, it is not necessary to write the steps to get the range of \[y=\left[ \left| \sin x \right|+\left| \cos x \right| \right]\] .
We know that when $\sin x$ increases $\cos x$ decreases. So the maximum value cannot be obtained.
We know that at $x=\dfrac{\pi }{4}$ both $\sin x$ and $\cos x$ will be the same, i.e, $\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}$ .
So \[y=\sin x+\cos x=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}+\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}=\sqrt{2}\] .
Therefore, the maximum value of \[y=\left[ \left| \sin x \right|+\left| \cos x \right| \right]=\sqrt{2}\] .
To find the minimum value, we know that minimum value of $\sin x=0$ and that of $\cos x=1$ .
Now \[y=\left[ \left| \sin x \right|+\left| \cos x \right| \right]=0+1=1\] .
Thus the range of \[y=\left[ \left| \sin x \right|+\left| \cos x \right| \right]=[1,\sqrt{2}]\] .
Complete step by step answer:
We need to find the angle of intersection between the curves \[y=\left[ \left| \sin x \right|+\left| \cos x \right| \right]\] and ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}=10$ .
Let us find the range of \[y=\left[ \left| \sin x \right|+\left| \cos x \right| \right]\] .
We know that the range of $\left| \sin x \right|$ is
$0\le \left| \sin x \right|\le 1$
And the range of $\left| \cos x \right|$ is
$0\le \left| \cos x \right|\le 1$
Therefore, range of \[y=\left[ \left| \sin x \right|+\left| \cos x \right| \right]\] can be found out as follows:
\[y=\sin x+\cos x\]where$x\in \left( 0,\dfrac{\pi }{2} \right)$ .
Now multiply and divide RHS by $\sqrt{2}$ . So the above equation becomes,
\[y=\sqrt{2}\left( \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\sin x+\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\cos x \right)...(i)\]
Now, $\sin \left( x+\dfrac{\pi }{4} \right)=\sin x\cos \dfrac{\pi }{4}+\cos x\sin \dfrac{\pi }{4}$
Solving, we get
$\sin \left( x+\dfrac{\pi }{4} \right)=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\sin x+\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\cos x$
Therefore equation $(i)$ can be written as
\[y=\sqrt{2}\sin \left( x+\dfrac{\pi }{4} \right)\]
We know that $\sin x$ ranges from $[-1,1]$ .
Therefore, $-1\le \sin \left( x+\dfrac{\pi }{4} \right)\le 1$
Multiplying by $\sqrt{2}$ we get
$-\sqrt{2}\le \sqrt{2}\sin \left( x+\dfrac{\pi }{4} \right)\le \sqrt{2}$
As $\left| \sin x \right|$ ranges from $0\le \left| \sin x \right|\le 1$ , comparing with the above one, we get
\[y=\left[ \left| \sin x \right|+\left| \cos x \right| \right]=[1,\sqrt{2}]\]
It is given that $x$ denote the greatest integer $\le x$ . So we will consider the value $y=1$ .
Given that ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}=10$ . Substituting the value of $y$ here, we get
${{x}^{2}}+1=10\Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}=9$
$x=\pm 3$
Therefore, the intersection points are $q(3,1)$ and $p(-3,1)$ .

We need to find the slope of the tangent $(\pm 3,1)$ to ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}=10$ .
Now differentiate ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}=10$ with respect to $x$ . We will get
$2x+2y\dfrac{dy}{dx}=0$
$\Rightarrow x+y\dfrac{dy}{dx}=0$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{dy}{dx}=\dfrac{-x}{y}$
Now for the point $q(3,1)$ ,
${{\left. \dfrac{dy}{dx} \right|}_{p(3,1)}}=-3$
For the point $p(-3,1)$ ,
${{\left. \dfrac{dy}{dx} \right|}_{p(-3,1)}}=3$
Therefore, slope ${{m}_{1}}=\pm 3$ .
We have, $y=1$ .
Differentiating $y$ with respect to $x$ , we get
${{\left. \dfrac{dy}{dx} \right|}_{p}}=0$
That is, the slope ${{m}_{2}}={{\left. \dfrac{dy}{dx} \right|}_{p}}=0$ .
Now, to find the angle of intersection, we have
$\tan \theta =\left| \dfrac{{{m}_{2}}-{{m}_{1}}}{1+{{m}_{1}}{{m}_{2}}} \right|$
We will use in this case ${{m}_{2}}=-3$ as per the figure.
Substituting the value, we will get
$\tan \theta =\left| \dfrac{0-(-3)}{1+0\times -3} \right|=\left| 3 \right|=\pm 3$
Taking inverse of $\tan $ we will get the value of $\theta $ .
Therefore, $\theta ={{\tan }^{-1}}3$ and $\theta ={{\tan }^{-1}}(-3)$ .
Hence the correct options are A and B.
Note:
In this question, it is not necessary to write the steps to get the range of \[y=\left[ \left| \sin x \right|+\left| \cos x \right| \right]\] .
We know that when $\sin x$ increases $\cos x$ decreases. So the maximum value cannot be obtained.
We know that at $x=\dfrac{\pi }{4}$ both $\sin x$ and $\cos x$ will be the same, i.e, $\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}$ .
So \[y=\sin x+\cos x=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}+\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}=\sqrt{2}\] .
Therefore, the maximum value of \[y=\left[ \left| \sin x \right|+\left| \cos x \right| \right]=\sqrt{2}\] .
To find the minimum value, we know that minimum value of $\sin x=0$ and that of $\cos x=1$ .
Now \[y=\left[ \left| \sin x \right|+\left| \cos x \right| \right]=0+1=1\] .
Thus the range of \[y=\left[ \left| \sin x \right|+\left| \cos x \right| \right]=[1,\sqrt{2}]\] .
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




