
The angle of elevation of tower of height h standing inside a triangular field at each corner is $60{}^\circ $ . If the length of the sides of the field are 30 m, 50 m and 70 m, then find the value of ${{h}^{2}}+h+1$ .
Answer
513k+ views
Hint: Firstly, draw the figure with the given conditions. Then, find the value of the triangular field using Heron’s formula which is given by $\Delta =\sqrt{s\left( s-a \right)\left( s-b \right)\left( s-c \right)}$ , where s is the semi-perimeter of the triangle which is given by $s=\dfrac{a+b+c}{2}$ and a, b and c are the sides of the triangle. Then find the circumradius, R using the formula $R=\dfrac{abc}{4\Delta }$ . Using the definition of $\tan \theta $ , that is, $\tan \theta =\dfrac{\text{Opposite side}}{\text{Adjacent side}}$ , the value of h can be found. Substitute this value of h in ${{h}^{2}}+h+1$ and simplify.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us illustrate the given situation. From the below figure, we can see that the triangular field is ABC on which a tower PQ of length h m is standing. $\angle PBQ=\angle PCQ=60{}^\circ $
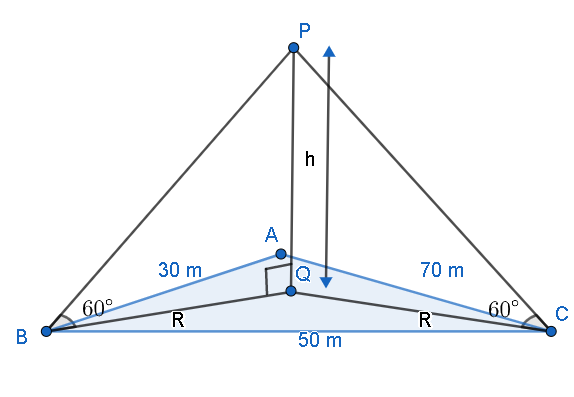
Let us consider $AB=30\text{m},BC=50\text{m and }AC=70\text{m}$ .
We have to find the value of h so that the value of ${{h}^{2}}+h+1$ can be found. Let us find the area of triangle ABC using Heron’s formula.
We know that according to Heron’s formula, the area of a triangle of sides a, b and c is given by
$\Delta =\sqrt{s\left( s-a \right)\left( s-b \right)\left( s-c \right)}$
where s is the semi-perimeter of the triangle which is given by
$s=\dfrac{a+b+c}{2}$
Let us substitute $a=30m,b=50m\text{ and }c=70m$ in the above formulas.
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow s=\dfrac{30+50+70}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow s=\dfrac{150}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow s=75\text{ m} \\
\end{align}$
Now, let us find the area of triangle ABC.
$\begin{align}
& \Delta =\sqrt{75\left( 75-30 \right)\left( 75-50 \right)\left( 75-70 \right)} \\
& \Delta =\sqrt{75\times 45\times 25\times 5} \\
& \Delta =\sqrt{421875} \\
& \Delta =375\sqrt{3}\text{ }{{\text{m}}^{2}} \\
\end{align}$
Let R be the circumradius of the triangle which is given by the formula
$R=\dfrac{abc}{4\Delta }$
where a, b and c are the sides of a triangle and $\Delta $ is the its area.
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow R=\dfrac{30\times 50\times 70}{4\times 375\sqrt{3}} \\
& \Rightarrow R=\dfrac{70}{\sqrt{3}}\text{ m} \\
\end{align}\]
From the figure, we can see that triangle PBQ is a right-angled triangle. Therefore,
$\begin{align}
& \tan \theta =\dfrac{\text{Opposite side}}{\text{Adjacent side}} \\
& \Rightarrow \tan 60{}^\circ =\dfrac{h}{R} \\
& \Rightarrow \sqrt{3}=\dfrac{h}{\dfrac{70}{\sqrt{3}}} \\
& \Rightarrow h=70\text{ m} \\
\end{align}$
Now, let us find ${{h}^{2}}+h+1$ .
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{h}^{2}}+h+1={{70}^{2}}+70+1 \\
& \Rightarrow {{h}^{2}}+h+1=4900+71 \\
& \Rightarrow {{h}^{2}}+h+1=4971 \\
\end{align}$
Hence, the value of ${{h}^{2}}+h+1$ is 4971.
Note: Students must be able to draw the figure with the given conditions carefully. They have a chance of making a mistake by writing the Heron’s formula as $\Delta =\sqrt{s\left( s+a \right)\left( s+b \right)\left( s+c \right)}$ . Students have a chance of making a mistake by considering $\angle PBC$ as $60{}^\circ $ .
Complete step by step answer:
Let us illustrate the given situation. From the below figure, we can see that the triangular field is ABC on which a tower PQ of length h m is standing. $\angle PBQ=\angle PCQ=60{}^\circ $

Let us consider $AB=30\text{m},BC=50\text{m and }AC=70\text{m}$ .
We have to find the value of h so that the value of ${{h}^{2}}+h+1$ can be found. Let us find the area of triangle ABC using Heron’s formula.
We know that according to Heron’s formula, the area of a triangle of sides a, b and c is given by
$\Delta =\sqrt{s\left( s-a \right)\left( s-b \right)\left( s-c \right)}$
where s is the semi-perimeter of the triangle which is given by
$s=\dfrac{a+b+c}{2}$
Let us substitute $a=30m,b=50m\text{ and }c=70m$ in the above formulas.
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow s=\dfrac{30+50+70}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow s=\dfrac{150}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow s=75\text{ m} \\
\end{align}$
Now, let us find the area of triangle ABC.
$\begin{align}
& \Delta =\sqrt{75\left( 75-30 \right)\left( 75-50 \right)\left( 75-70 \right)} \\
& \Delta =\sqrt{75\times 45\times 25\times 5} \\
& \Delta =\sqrt{421875} \\
& \Delta =375\sqrt{3}\text{ }{{\text{m}}^{2}} \\
\end{align}$
Let R be the circumradius of the triangle which is given by the formula
$R=\dfrac{abc}{4\Delta }$
where a, b and c are the sides of a triangle and $\Delta $ is the its area.
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow R=\dfrac{30\times 50\times 70}{4\times 375\sqrt{3}} \\
& \Rightarrow R=\dfrac{70}{\sqrt{3}}\text{ m} \\
\end{align}\]
From the figure, we can see that triangle PBQ is a right-angled triangle. Therefore,
$\begin{align}
& \tan \theta =\dfrac{\text{Opposite side}}{\text{Adjacent side}} \\
& \Rightarrow \tan 60{}^\circ =\dfrac{h}{R} \\
& \Rightarrow \sqrt{3}=\dfrac{h}{\dfrac{70}{\sqrt{3}}} \\
& \Rightarrow h=70\text{ m} \\
\end{align}$
Now, let us find ${{h}^{2}}+h+1$ .
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{h}^{2}}+h+1={{70}^{2}}+70+1 \\
& \Rightarrow {{h}^{2}}+h+1=4900+71 \\
& \Rightarrow {{h}^{2}}+h+1=4971 \\
\end{align}$
Hence, the value of ${{h}^{2}}+h+1$ is 4971.
Note: Students must be able to draw the figure with the given conditions carefully. They have a chance of making a mistake by writing the Heron’s formula as $\Delta =\sqrt{s\left( s+a \right)\left( s+b \right)\left( s+c \right)}$ . Students have a chance of making a mistake by considering $\angle PBC$ as $60{}^\circ $ .
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




