
The angle of elevation of the top of a tower from two points distant s and t from its foot are complementary. Prove that the height of the tower is \[\sqrt{st}\].
Answer
607.2k+ views
Hint: They gave distance from foot and asked the height of tower. So, you can just apply the properties of trigonometry by using a tangent of angles and find the relation between the height and the distance from the foot of the tower. By using the relation and the condition of complementary angles try to eliminate angle and find height in terms of distances.
Complete step-by-step answer:
If there is triangle ABC, right angled at B then:
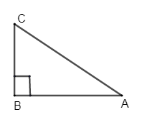
\[\tan \left( BAC \right)=\dfrac{BC}{AB}\], \[\tan \left( BCA \right)=\dfrac{AB}{BC}\]
Given that the 2 points from where we measure all at a distance of s, r from the foot of the tower. Let the points be A, B and the foot of tower be C and top of the tower be C and top of the tower be D as shown in the figure.
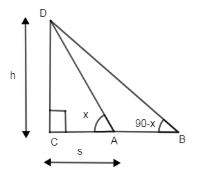
The angles are x, 90 – x; as it is given they are complementary.
The CA is given to be S and CB is given to be t.
The height of the tower is assumed by us as h.
By basic knowledge of trigonometry, we can see 2 right angled triangles in the figure triangle ACD, triangle BCD.
By finding tangents of angles x, 90 – x; we get the following:
\[\begin{align}
& \tan x=\dfrac{CD}{AC}=\dfrac{h}{s}-(1) \\
& \tan \left( 90-x \right)=\dfrac{CD}{BC}=\dfrac{h}{t}-(2) \\
\end{align}\]
By basic knowledge of trigonometric, we know that \[\tan x\] is:
\[\tan \left( 90-x \right)=\cot x\]
By substituting this in equation (2) in L.H.S, we get:
\[\cot x=\dfrac{h}{t}-(3)\]
By multiplying the equation (1) and equation (3), we get:
\[\tan x.\cot x=\dfrac{h}{s}.\dfrac{h}{t}-(4)\]
By basic knowledge of trigonometry, we know that this true:
\[\tan x.\cot x=1\]
By substituting in equation (4), it gets converted to:
\[{{h}^{2}}=st\]
By applying square root on both sides of equation we get:
\[h=\sqrt{st}\]
Hence, we proved the expression asked in question.
Note: Whenever you get questions of angle of elevation, the first idea is to apply tan or sin to get a relation between distances given. Be careful while taking and as they are the crucial points we use in this question. Don’t confuse anytime, tan of angle in the right angled triangle is always opposite side divided by adjacent. Don’t take it reverse.
Complete step-by-step answer:
If there is triangle ABC, right angled at B then:

\[\tan \left( BAC \right)=\dfrac{BC}{AB}\], \[\tan \left( BCA \right)=\dfrac{AB}{BC}\]
Given that the 2 points from where we measure all at a distance of s, r from the foot of the tower. Let the points be A, B and the foot of tower be C and top of the tower be C and top of the tower be D as shown in the figure.

The angles are x, 90 – x; as it is given they are complementary.
The CA is given to be S and CB is given to be t.
The height of the tower is assumed by us as h.
By basic knowledge of trigonometry, we can see 2 right angled triangles in the figure triangle ACD, triangle BCD.
By finding tangents of angles x, 90 – x; we get the following:
\[\begin{align}
& \tan x=\dfrac{CD}{AC}=\dfrac{h}{s}-(1) \\
& \tan \left( 90-x \right)=\dfrac{CD}{BC}=\dfrac{h}{t}-(2) \\
\end{align}\]
By basic knowledge of trigonometric, we know that \[\tan x\] is:
\[\tan \left( 90-x \right)=\cot x\]
By substituting this in equation (2) in L.H.S, we get:
\[\cot x=\dfrac{h}{t}-(3)\]
By multiplying the equation (1) and equation (3), we get:
\[\tan x.\cot x=\dfrac{h}{s}.\dfrac{h}{t}-(4)\]
By basic knowledge of trigonometry, we know that this true:
\[\tan x.\cot x=1\]
By substituting in equation (4), it gets converted to:
\[{{h}^{2}}=st\]
By applying square root on both sides of equation we get:
\[h=\sqrt{st}\]
Hence, we proved the expression asked in question.
Note: Whenever you get questions of angle of elevation, the first idea is to apply tan or sin to get a relation between distances given. Be careful while taking and as they are the crucial points we use in this question. Don’t confuse anytime, tan of angle in the right angled triangle is always opposite side divided by adjacent. Don’t take it reverse.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE





