
The angle of elevation of the top of a $24{\text{ m}}$ high pillar from the window of a building $6{\text{ m}}$ above the ground and the angle of depression of its base are complementary angles. The distance of building from pillar is:
(A) $2\sqrt 3 {\text{ m}}$
(B) $8\sqrt 3 {\text{ m}}$
(C) $12\sqrt 3 {\text{ m}}$
(D) $6\sqrt 3 {\text{ m}}$
Answer
588k+ views
Hint: Analyse the situation with a diagram. Consider two different triangles for angle of elevation and angle of depression and compare the results obtained from both of them. Use formula $\tan \theta = \dfrac{{{\text{Perpendicular}}}}{{{\text{Base}}}}$
Complete step-by-step answer:
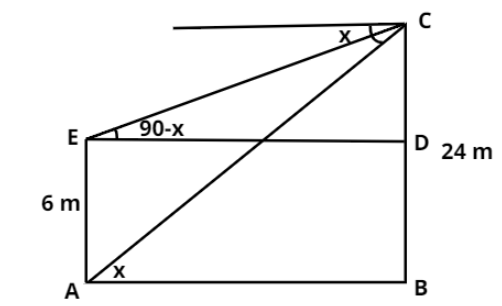
Consider the above diagram. AE is representing the building while E is the position of window. BC is a pillar.
According to the question, the angle of elevation from the window and angle of depression of the base of the building are complementary angles i.e. their sum is ${90^ \circ }$. So if $\angle CAB = x$ then $\angle CED = 90 - x$.
Let the length AB, which is the distance of the building from pillar, to be $h$, $AB = h$.
Now, in triangle ABC:
$
\Rightarrow \tan x = \dfrac{{BC}}{{AB}} \\
\Rightarrow \tan x = \dfrac{{24}}{h}{\text{ }}.....{\text{(1)}} \\
$
Again in triangle DCE,
$ \Rightarrow \tan \left( {90 - x} \right) = \dfrac{{CD}}{{DE}}$
From the figure, we have:
$ \Rightarrow DE = AB = h$
$ \Rightarrow CD = CB - DB$ and $DB = EA = 6{\text{ m}}$ whereas $CB = 24{\text{ m}}$.
Thus, $CD = 24 - 6 = 18{\text{ m}}$
Putting these values in above expression, we’ll get:
$ \Rightarrow \tan \left( {90 - x} \right) = \dfrac{{18}}{h}$
We know that $\tan \left( {90 - x} \right) = \cot x$. So we have:
$ \Rightarrow \cot x = \dfrac{{18}}{h}{\text{ }}.....{\text{(2)}}$
Now multiplying equation (1) and (2) we’ll get:
$ \Rightarrow \tan x\cot x = \dfrac{{24}}{h} \times \dfrac{{18}}{h}$
We know that $\tan x\cot x = 1$. Using this, we’ll get:
$
\Rightarrow 1 = \dfrac{{6 \times 4 \times 6 \times 3}}{{{h^2}}} \\
\Rightarrow {h^2} = {6^2} \times {2^2} \times 3 \\
$
Taking square root both sides, we have:
$
\Rightarrow h = 6 \times 2\sqrt 3 \\
\Rightarrow h = 12\sqrt 3 \\
$
Thus the distance of the building from the pillar is \[12\sqrt 3 \].
(C) is the correct option.
Note: The formula of $\tan \theta $ is used in a triangle whenever a relation between two non-hypotenuse sides of the triangle is required. Other trigonometric ratios can also be used if hypotenuse is to be determined or a relation between hypotenuse and any other side is to be compared.
Complete step-by-step answer:

Consider the above diagram. AE is representing the building while E is the position of window. BC is a pillar.
According to the question, the angle of elevation from the window and angle of depression of the base of the building are complementary angles i.e. their sum is ${90^ \circ }$. So if $\angle CAB = x$ then $\angle CED = 90 - x$.
Let the length AB, which is the distance of the building from pillar, to be $h$, $AB = h$.
Now, in triangle ABC:
$
\Rightarrow \tan x = \dfrac{{BC}}{{AB}} \\
\Rightarrow \tan x = \dfrac{{24}}{h}{\text{ }}.....{\text{(1)}} \\
$
Again in triangle DCE,
$ \Rightarrow \tan \left( {90 - x} \right) = \dfrac{{CD}}{{DE}}$
From the figure, we have:
$ \Rightarrow DE = AB = h$
$ \Rightarrow CD = CB - DB$ and $DB = EA = 6{\text{ m}}$ whereas $CB = 24{\text{ m}}$.
Thus, $CD = 24 - 6 = 18{\text{ m}}$
Putting these values in above expression, we’ll get:
$ \Rightarrow \tan \left( {90 - x} \right) = \dfrac{{18}}{h}$
We know that $\tan \left( {90 - x} \right) = \cot x$. So we have:
$ \Rightarrow \cot x = \dfrac{{18}}{h}{\text{ }}.....{\text{(2)}}$
Now multiplying equation (1) and (2) we’ll get:
$ \Rightarrow \tan x\cot x = \dfrac{{24}}{h} \times \dfrac{{18}}{h}$
We know that $\tan x\cot x = 1$. Using this, we’ll get:
$
\Rightarrow 1 = \dfrac{{6 \times 4 \times 6 \times 3}}{{{h^2}}} \\
\Rightarrow {h^2} = {6^2} \times {2^2} \times 3 \\
$
Taking square root both sides, we have:
$
\Rightarrow h = 6 \times 2\sqrt 3 \\
\Rightarrow h = 12\sqrt 3 \\
$
Thus the distance of the building from the pillar is \[12\sqrt 3 \].
(C) is the correct option.
Note: The formula of $\tan \theta $ is used in a triangle whenever a relation between two non-hypotenuse sides of the triangle is required. Other trigonometric ratios can also be used if hypotenuse is to be determined or a relation between hypotenuse and any other side is to be compared.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




