
The angle of elevation of a jet plane from a point A on the ground is ${{60}^{\circ }}$. After a flight of 15 seconds, the angle of elevation changes to ${{30}^{\circ }}$. If the jet plane is flying at a constant height of $1500\sqrt{2}m$, find the speed of the jet plane.
Answer
616.5k+ views
Hint: Use the value of the tangent of angles to find the distance from point A to the base of the vertical line at which the aeroplane is flying. Calculate the distance between two points at which the plane is flying. Use the fact that speed is the ratio of distance covered to the time taken to calculate the speed of the jet plane.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We have data regarding the angle of elevation of a plane flying from a fixed point. We have to calculate the speed of the plane.
Let’s assume that the plane is viewed from point A on the ground. When the plane is at point B, the angle of elevation is ${{60}^{\circ }}$. When the plane is at point C, the angle of elevation is ${{30}^{\circ }}$, as shown in the figure.
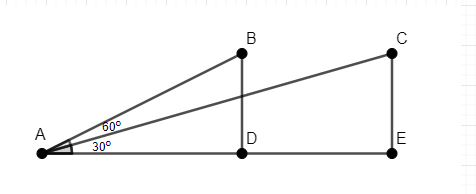
We know that the plane is flying at the height of $1500\sqrt{2}m$. Thus, we have $BD=CE=1500\sqrt{2}m$.
In $\Delta ABD$, we have $\angle BAD={{60}^{\circ }}$. Thus, we have $\tan \left( \angle BAD \right)=\tan \left( {{60}^{\circ }} \right)$. We know that tangent of any angle is the ratio of the length of perpendicular to the length of the base.
Thus, we have $\tan \left( \angle BAD \right)=\dfrac{BD}{AD}$.
So, we have $\tan \left( \angle BAD \right)=\tan \left( {{60}^{\circ }}
\right)=\sqrt{3}=\dfrac{BD}{AD}$.
Substituting $BD=1500\sqrt{3}m$ in the above equation, we have
$\sqrt{3}=\dfrac{1500\sqrt{3}}{AD}$.
Rearranging the terms, we have $AD=\dfrac{1500\sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{3}}=1500m$.
We will now consider $\Delta ACE$.
In $\Delta ACE$, we have $\angle CAE={{30}^{\circ }}$. Thus, we have $\tan \left( \angle CAE \right)=\tan \left( {{30}^{\circ }} \right)$. We know that tangent of any angle is the ratio of the length of perpendicular to the length of the base.
Thus, we have $\tan \left( \angle CAE \right)=\dfrac{CE}{AE}$.
So, we have $\tan \left( \angle CAE \right)=\tan \left( {{30}^{\circ }}
\right)=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}}=\dfrac{CE}{AE}$.
Substituting $CE=1500\sqrt{3}m$ in the above equation, we have
$\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}}=\dfrac{1500\sqrt{3}}{AE}$.
Rearranging the terms, we have $AE=1500\sqrt{3}\times \sqrt{3}=4500m$.
We will now calculate the horizontal distance between two planes, which is equal to the
difference between AE and AD.
Thus, the distance between the two planes is $=AE-AD=4500-1500=3000m$. The plane took
15 seconds to cover this distance.
We know that the speed of any object is the ratio of distance covered by the object to the
time taken to cover the distance.
Thus, the speed of the plane $=\dfrac{3000}{15}=200m/s$.
Hence, the speed of the plane is $200m/s$.
Note: We can’t solve this question without finding the distance between two points at which the plane is flying. Also, one must know that formula for calculating the speed of any object. Be careful about units while calculating the speed.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We have data regarding the angle of elevation of a plane flying from a fixed point. We have to calculate the speed of the plane.
Let’s assume that the plane is viewed from point A on the ground. When the plane is at point B, the angle of elevation is ${{60}^{\circ }}$. When the plane is at point C, the angle of elevation is ${{30}^{\circ }}$, as shown in the figure.

We know that the plane is flying at the height of $1500\sqrt{2}m$. Thus, we have $BD=CE=1500\sqrt{2}m$.
In $\Delta ABD$, we have $\angle BAD={{60}^{\circ }}$. Thus, we have $\tan \left( \angle BAD \right)=\tan \left( {{60}^{\circ }} \right)$. We know that tangent of any angle is the ratio of the length of perpendicular to the length of the base.
Thus, we have $\tan \left( \angle BAD \right)=\dfrac{BD}{AD}$.
So, we have $\tan \left( \angle BAD \right)=\tan \left( {{60}^{\circ }}
\right)=\sqrt{3}=\dfrac{BD}{AD}$.
Substituting $BD=1500\sqrt{3}m$ in the above equation, we have
$\sqrt{3}=\dfrac{1500\sqrt{3}}{AD}$.
Rearranging the terms, we have $AD=\dfrac{1500\sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{3}}=1500m$.
We will now consider $\Delta ACE$.
In $\Delta ACE$, we have $\angle CAE={{30}^{\circ }}$. Thus, we have $\tan \left( \angle CAE \right)=\tan \left( {{30}^{\circ }} \right)$. We know that tangent of any angle is the ratio of the length of perpendicular to the length of the base.
Thus, we have $\tan \left( \angle CAE \right)=\dfrac{CE}{AE}$.
So, we have $\tan \left( \angle CAE \right)=\tan \left( {{30}^{\circ }}
\right)=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}}=\dfrac{CE}{AE}$.
Substituting $CE=1500\sqrt{3}m$ in the above equation, we have
$\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}}=\dfrac{1500\sqrt{3}}{AE}$.
Rearranging the terms, we have $AE=1500\sqrt{3}\times \sqrt{3}=4500m$.
We will now calculate the horizontal distance between two planes, which is equal to the
difference between AE and AD.
Thus, the distance between the two planes is $=AE-AD=4500-1500=3000m$. The plane took
15 seconds to cover this distance.
We know that the speed of any object is the ratio of distance covered by the object to the
time taken to cover the distance.
Thus, the speed of the plane $=\dfrac{3000}{15}=200m/s$.
Hence, the speed of the plane is $200m/s$.
Note: We can’t solve this question without finding the distance between two points at which the plane is flying. Also, one must know that formula for calculating the speed of any object. Be careful about units while calculating the speed.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




