
The angle bisectors BD and CE of a triangle ABC are divided by the incentre $I$ in the ratios 3:2 and 2:1 respectively. Then what is the ratio in which $I$ divides the angle bisector through A?
A. 3:1
B. 11:4
C. 6:5
D. 7:4
Answer
613.5k+ views
Hint- First, we will make the figure of a triangle and fill in the details given to us by the question. We will then find out the ratio of each side of the triangle and then solve further to find out the different values and the ratio of $I$.
Complete step-by-step answer:
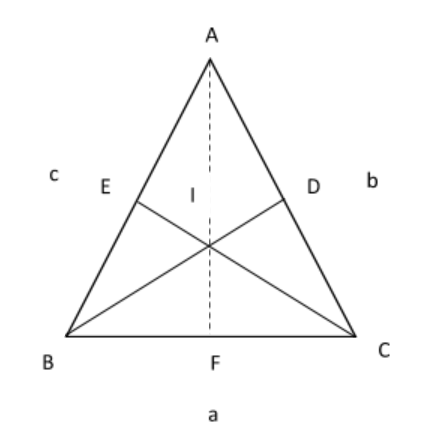
Let the ratio in which dividing AF be $\dfrac{{b + c}}{a}$ (we have to find out)
Let the ratio in which diving BD be $\dfrac{{a + c}}{b}$
Let the ratio in which diving CE be $\dfrac{{a + b}}{c}$
It is given to us in the question that-
$ \to \dfrac{{a + c}}{b} = \dfrac{3}{2}$
$ \to \dfrac{{a + b}}{c} = \dfrac{2}{1}$
Naming the above equations 1 and 2 respectively-
$ \to \dfrac{{a + c}}{b} = \dfrac{3}{2}$ (equation 1)
$ \to \dfrac{{a + b}}{c} = \dfrac{2}{1}$ (equation 2)
Solving equation 1 first by cross multiplication-
$ \to \dfrac{{a + c}}{b} = \dfrac{3}{2}$
$
\to 2a + 2c = 3b \\
\\
\to 2a = 3b - 2c \\
\\
\to 2c = 3b - 2a \\
$
Let this be equation 3-
$ \to 2c = 3b - 2a$ (equation 3)
Now, solving equation 2 by cross multiplication-
$
\to \dfrac{{a + b}}{c} = \dfrac{2}{1} \\
\\
\to a + b = 2c \\
$
Putting the value of 2c from equation 3 into the above equation-
$
\to a + b = 3b - 2a \\
\\
\to 3a = 2b \\
\\
\Rightarrow b = \dfrac{3}{2}a \\
$
Putting the value of b into equation 3, we get-
$
\to 2c = \dfrac{3}{2}a \times 3 - 2a \\
\\
\to 2c = \dfrac{{9a}}{2} - 2a \\
\\
\to 2c = \dfrac{{5a}}{2} \\
\\
\Rightarrow c = \dfrac{{5a}}{4} \\
$
Now, finding out the ratio in which $I$ divides the angle bisector through A-
$ \to \dfrac{{b + c}}{a}$ (as said earlier)
Putting the values of b and c into the above equation-
$
\to \dfrac{{\dfrac{3}{2}a + \dfrac{5}{4}a}}{a} \\
\\
\to \dfrac{3}{2} + \dfrac{5}{4} \\
\\
\to \dfrac{{6 + 5}}{4} \\
\\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{11}}{4} \\
$
Thus, the ratio is 11:4.
Note: Making a figure in the equation is necessary for better understanding. Do remember that the ratio can always be found out in the way $\dfrac{{a + b}}{c}$, where the numerator is the sum of the opposite two sides and the denominator is the third side where the perpendicular bisector lies.
Complete step-by-step answer:

Let the ratio in which dividing AF be $\dfrac{{b + c}}{a}$ (we have to find out)
Let the ratio in which diving BD be $\dfrac{{a + c}}{b}$
Let the ratio in which diving CE be $\dfrac{{a + b}}{c}$
It is given to us in the question that-
$ \to \dfrac{{a + c}}{b} = \dfrac{3}{2}$
$ \to \dfrac{{a + b}}{c} = \dfrac{2}{1}$
Naming the above equations 1 and 2 respectively-
$ \to \dfrac{{a + c}}{b} = \dfrac{3}{2}$ (equation 1)
$ \to \dfrac{{a + b}}{c} = \dfrac{2}{1}$ (equation 2)
Solving equation 1 first by cross multiplication-
$ \to \dfrac{{a + c}}{b} = \dfrac{3}{2}$
$
\to 2a + 2c = 3b \\
\\
\to 2a = 3b - 2c \\
\\
\to 2c = 3b - 2a \\
$
Let this be equation 3-
$ \to 2c = 3b - 2a$ (equation 3)
Now, solving equation 2 by cross multiplication-
$
\to \dfrac{{a + b}}{c} = \dfrac{2}{1} \\
\\
\to a + b = 2c \\
$
Putting the value of 2c from equation 3 into the above equation-
$
\to a + b = 3b - 2a \\
\\
\to 3a = 2b \\
\\
\Rightarrow b = \dfrac{3}{2}a \\
$
Putting the value of b into equation 3, we get-
$
\to 2c = \dfrac{3}{2}a \times 3 - 2a \\
\\
\to 2c = \dfrac{{9a}}{2} - 2a \\
\\
\to 2c = \dfrac{{5a}}{2} \\
\\
\Rightarrow c = \dfrac{{5a}}{4} \\
$
Now, finding out the ratio in which $I$ divides the angle bisector through A-
$ \to \dfrac{{b + c}}{a}$ (as said earlier)
Putting the values of b and c into the above equation-
$
\to \dfrac{{\dfrac{3}{2}a + \dfrac{5}{4}a}}{a} \\
\\
\to \dfrac{3}{2} + \dfrac{5}{4} \\
\\
\to \dfrac{{6 + 5}}{4} \\
\\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{11}}{4} \\
$
Thus, the ratio is 11:4.
Note: Making a figure in the equation is necessary for better understanding. Do remember that the ratio can always be found out in the way $\dfrac{{a + b}}{c}$, where the numerator is the sum of the opposite two sides and the denominator is the third side where the perpendicular bisector lies.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




