
The altitudes BN and CM of $\Delta ABC$meet at H. Prove that
A) $CN.HM = BM.HN$
B) $\dfrac{{HC}}{{HB}} = \sqrt {\dfrac{{CN.HN}}{{BM.HM}}} $
C) $\Delta MHN \sim \Delta BHC$
Answer
576.3k+ views
Hint: According to given in the question that the altitudes BN and CM of $\Delta ABC$ meet at H so first of all we have to draw the figure for the given triangle which is as below:
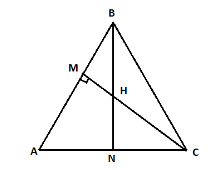
First of all we have to prove (1) $CN.HM = BM.HN$ so, as given in the question BN is perpendicular to AC and CM is perpendicular to AB and in triangle BHM and triangle CHN as we know $\angle M = \angle N$ which is equal to ${90^\circ}$. Hence, with the help of triangle BHM and triangle CHN we can prove that $CN.HM = BM.HN$
Now, to prove (2) $\dfrac{{HC}}{{HB}} = \sqrt {\dfrac{{CN.HN}}{{BM.HM}}} $ as we obtained from the above triangle BHM and triangle CHN which is $CN.HM = BM.HN$ we have to apply components to prove the $\dfrac{{HC}}{{HB}} = \sqrt {\dfrac{{CN.HN}}{{BM.HM}}} $
Now, to prove (3) $\Delta MHN \sim \Delta BHC$ we have to apply or check all the congruent properties for the triangle MHN and BHC.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Step 1: First of all we have to prove (a) $CN.HM = BM.HN$ so we have to consider the diagram as given below:
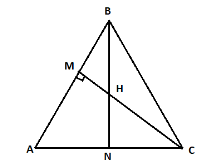
So, in triangle BHM and triangle CHN,
$BN \bot AC$ and $CM \bot AB$
Hence, in triangle BHM and triangle CHN,
$ \Rightarrow \angle M = \angle N = {90^\circ}$
And as we know that $\angle BHM$ and $\angle CHN$are velocity opposite angles hence,
$\angle BHM$= $\angle CHN$
Therefore we can say that $\Delta BHM \sim \Delta CHN$ with the help of same centre (A-A)
Hence,
$CN.HM = BM.HN$
Step 2: Now, we have to prove (b) $\dfrac{{HC}}{{HB}} = \sqrt {\dfrac{{CN.HN}}{{BM.HM}}} $as we obtained from that step 1 that,
$\dfrac{{BM}}{{CN}} = \dfrac{{HM}}{{HN}}...............(1)$
So, $CN.HM = BM.HN$
Hence,
$\dfrac{{BM}}{{HM}} = \dfrac{{CN}}{{NH}}$
Now, we have to apply the components rule as mentioned in the solution hint.
$\dfrac{{BM + HM}}{{HM}} = \dfrac{{CN + NH}}{{NH}}$
But as we know that from the diagram $GH = BM + HM$ and $CH = CN + NH$
Hence,
$\dfrac{{BH}}{{CH}} = \dfrac{{MH}}{{NH}}...............(2)$
Now,
$\dfrac{{CH}}{{BH}} = \dfrac{{NH}}{{MH}}$
Hence,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{CH}}{{BH}} = \sqrt {\dfrac{{NH}}{{MH}} \times \dfrac{{NH}}{{MH}}} $
Now, from the equation we can obtain,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{CH}}{{BH}} = \sqrt {\dfrac{{NH.CN}}{{MN.BM}}} $
Step 3: Now, we have to prove, (3) $\Delta MHN \sim \Delta BHC$ we have to apply the properties of congruent triangle MHN and triangle BHC.
As we know that $\angle MHN$ and $\angle BHC$ are vertically opposite angles.
And,
$\dfrac{{BH}}{{CH}} = \dfrac{{MH}}{{NH}}$ which is obtained from the equation (2).
Hence with the side-angle-side rule we have proved that $\Delta MHN \sim \Delta BHC$
Final solution: Hence, we have proved that (1)$CN.HM = BM.HN$ (2) $\dfrac{{HC}}{{HB}} = \sqrt {\dfrac{{CN.HN}}{{BM.HM}}} $
And (3)$\Delta MHN \sim \Delta BHC$
Note: Vertically opposite angles are the angles opposite to each other when two lines cross and in this situation they share the same vertex.
Two triangles are congruent if their corresponding sides are equal in length, and their corresponding angles are equal in measure.

First of all we have to prove (1) $CN.HM = BM.HN$ so, as given in the question BN is perpendicular to AC and CM is perpendicular to AB and in triangle BHM and triangle CHN as we know $\angle M = \angle N$ which is equal to ${90^\circ}$. Hence, with the help of triangle BHM and triangle CHN we can prove that $CN.HM = BM.HN$
Now, to prove (2) $\dfrac{{HC}}{{HB}} = \sqrt {\dfrac{{CN.HN}}{{BM.HM}}} $ as we obtained from the above triangle BHM and triangle CHN which is $CN.HM = BM.HN$ we have to apply components to prove the $\dfrac{{HC}}{{HB}} = \sqrt {\dfrac{{CN.HN}}{{BM.HM}}} $
Now, to prove (3) $\Delta MHN \sim \Delta BHC$ we have to apply or check all the congruent properties for the triangle MHN and BHC.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Step 1: First of all we have to prove (a) $CN.HM = BM.HN$ so we have to consider the diagram as given below:

So, in triangle BHM and triangle CHN,
$BN \bot AC$ and $CM \bot AB$
Hence, in triangle BHM and triangle CHN,
$ \Rightarrow \angle M = \angle N = {90^\circ}$
And as we know that $\angle BHM$ and $\angle CHN$are velocity opposite angles hence,
$\angle BHM$= $\angle CHN$
Therefore we can say that $\Delta BHM \sim \Delta CHN$ with the help of same centre (A-A)
Hence,
$CN.HM = BM.HN$
Step 2: Now, we have to prove (b) $\dfrac{{HC}}{{HB}} = \sqrt {\dfrac{{CN.HN}}{{BM.HM}}} $as we obtained from that step 1 that,
$\dfrac{{BM}}{{CN}} = \dfrac{{HM}}{{HN}}...............(1)$
So, $CN.HM = BM.HN$
Hence,
$\dfrac{{BM}}{{HM}} = \dfrac{{CN}}{{NH}}$
Now, we have to apply the components rule as mentioned in the solution hint.
$\dfrac{{BM + HM}}{{HM}} = \dfrac{{CN + NH}}{{NH}}$
But as we know that from the diagram $GH = BM + HM$ and $CH = CN + NH$
Hence,
$\dfrac{{BH}}{{CH}} = \dfrac{{MH}}{{NH}}...............(2)$
Now,
$\dfrac{{CH}}{{BH}} = \dfrac{{NH}}{{MH}}$
Hence,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{CH}}{{BH}} = \sqrt {\dfrac{{NH}}{{MH}} \times \dfrac{{NH}}{{MH}}} $
Now, from the equation we can obtain,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{CH}}{{BH}} = \sqrt {\dfrac{{NH.CN}}{{MN.BM}}} $
Step 3: Now, we have to prove, (3) $\Delta MHN \sim \Delta BHC$ we have to apply the properties of congruent triangle MHN and triangle BHC.
As we know that $\angle MHN$ and $\angle BHC$ are vertically opposite angles.
And,
$\dfrac{{BH}}{{CH}} = \dfrac{{MH}}{{NH}}$ which is obtained from the equation (2).
Hence with the side-angle-side rule we have proved that $\Delta MHN \sim \Delta BHC$
Final solution: Hence, we have proved that (1)$CN.HM = BM.HN$ (2) $\dfrac{{HC}}{{HB}} = \sqrt {\dfrac{{CN.HN}}{{BM.HM}}} $
And (3)$\Delta MHN \sim \Delta BHC$
Note: Vertically opposite angles are the angles opposite to each other when two lines cross and in this situation they share the same vertex.
Two triangles are congruent if their corresponding sides are equal in length, and their corresponding angles are equal in measure.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




