
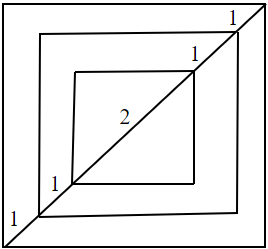
The adjoining figure shows a set of concentric squares. If the diagonal of the innermost square is 2 units and if the distance between the corresponding corners of any two successive squares is 1 unit, find the difference between the areas of the eighth and seventh squares, counting from the innermost square.
(A) $10\sqrt 2 $ sq.units.
(B) 30 sq.units.
(C) $35\sqrt 2 $ sq.units.
(D) 20 sq.units.

Answer
568.8k+ views
Hint: From the figure, we can observe that the length of the diagonal of the innermost square is 2 units and the lengths of the diagonals of subsequent squares are increasing by 2 units. Thus the lengths of the diagonals are 2 units, 4 units, 6 units and so on. Use this pattern to find the diagonal lengths of seventh and eighth squares and hence find the sides of these squares. Use formula \[A = {\text{sid}}{{\text{e}}^2}\] for squares to find their areas and hence their difference.
Complete step-by-step solution:
According to the question, we have been given a set of concentric squares with the innermost square having 2 units as its diagonal length.
Now, from the figure, we can observe that the length of the diagonal of the innermost square is 2 units and the lengths of the diagonals of subsequent squares are increasing by 2 units. Thus the lengths of the diagonals are 2 units, 4 units, 6 units and so on.
From this, we can say that the length of the diagonal of ${n^{{\text{th}}}}$ square is $2n$ units. Thus starting from the innermost square, the lengths of the diagonals of seventh and eighth squares are 14 units and 16 units respectively.
We know that the length of a side of a square can be obtained using formula:
$ \Rightarrow {\text{side}} = \dfrac{{{\text{Diagonal}}}}{{\sqrt 2 }}$
If ${a_7}$ and ${a_8}$ are the side-lengths of these squares, then we have:
$ \Rightarrow {a_7} = \dfrac{{14}}{{\sqrt 2 }}{\text{ and }}a = \dfrac{{16}}{{\sqrt 2 }}$
Also the area of a square is obtained using formula \[A = {\text{sid}}{{\text{e}}^2}\]. So, if ${A_7}$ and ${A_8}$ are the areas of these squares, then we have:
$ \Rightarrow {A_7} = {\left( {\dfrac{{14}}{{\sqrt 2 }}} \right)^2}{\text{uni}}{{\text{t}}^2}{\text{ and }}{A_8} = {\left( {\dfrac{{16}}{{\sqrt 2 }}} \right)^2}{\text{uni}}{{\text{t}}^2}$
The difference between the areas of these squares is given as:
$
\Rightarrow {A_8} - {A_7} = {\left( {\dfrac{{16}}{{\sqrt 2 }}} \right)^2} - {\left( {\dfrac{{14}}{{\sqrt 2 }}} \right)^2} \\
\Rightarrow {A_8} - {A_7} = \dfrac{{256}}{2} - \dfrac{{196}}{2} \\
\Rightarrow {A_8} - {A_7} = \dfrac{{60}}{2} \\
\Rightarrow {A_8} - {A_7} = 30{\text{ uni}}{{\text{t}}^2}
$
Hence the difference between the areas of eighth and seventh squares is 30 sq.units.
(B) is the correct option.
Note: We can also observe that the lengths of the diagonals of the squares are in arithmetic progression because the successive term is increasing by 2 units. So the first term of this A.P. is 2 and the common difference is also 2.
$ \Rightarrow a = 2{\text{ and }}d = 2$
Thus the general term can be found by using ${T_n} = a + \left( {n - 1} \right)d$. Putting values, we’ll get:
$
\Rightarrow {T_n} = 2 + \left( {n - 1} \right) \times 2 = 2 + 2n - 2 \\
\Rightarrow {T_n} = 2n
$
This is exactly what we have used in the above solution.
Complete step-by-step solution:
According to the question, we have been given a set of concentric squares with the innermost square having 2 units as its diagonal length.
Now, from the figure, we can observe that the length of the diagonal of the innermost square is 2 units and the lengths of the diagonals of subsequent squares are increasing by 2 units. Thus the lengths of the diagonals are 2 units, 4 units, 6 units and so on.
From this, we can say that the length of the diagonal of ${n^{{\text{th}}}}$ square is $2n$ units. Thus starting from the innermost square, the lengths of the diagonals of seventh and eighth squares are 14 units and 16 units respectively.
We know that the length of a side of a square can be obtained using formula:
$ \Rightarrow {\text{side}} = \dfrac{{{\text{Diagonal}}}}{{\sqrt 2 }}$
If ${a_7}$ and ${a_8}$ are the side-lengths of these squares, then we have:
$ \Rightarrow {a_7} = \dfrac{{14}}{{\sqrt 2 }}{\text{ and }}a = \dfrac{{16}}{{\sqrt 2 }}$
Also the area of a square is obtained using formula \[A = {\text{sid}}{{\text{e}}^2}\]. So, if ${A_7}$ and ${A_8}$ are the areas of these squares, then we have:
$ \Rightarrow {A_7} = {\left( {\dfrac{{14}}{{\sqrt 2 }}} \right)^2}{\text{uni}}{{\text{t}}^2}{\text{ and }}{A_8} = {\left( {\dfrac{{16}}{{\sqrt 2 }}} \right)^2}{\text{uni}}{{\text{t}}^2}$
The difference between the areas of these squares is given as:
$
\Rightarrow {A_8} - {A_7} = {\left( {\dfrac{{16}}{{\sqrt 2 }}} \right)^2} - {\left( {\dfrac{{14}}{{\sqrt 2 }}} \right)^2} \\
\Rightarrow {A_8} - {A_7} = \dfrac{{256}}{2} - \dfrac{{196}}{2} \\
\Rightarrow {A_8} - {A_7} = \dfrac{{60}}{2} \\
\Rightarrow {A_8} - {A_7} = 30{\text{ uni}}{{\text{t}}^2}
$
Hence the difference between the areas of eighth and seventh squares is 30 sq.units.
(B) is the correct option.
Note: We can also observe that the lengths of the diagonals of the squares are in arithmetic progression because the successive term is increasing by 2 units. So the first term of this A.P. is 2 and the common difference is also 2.
$ \Rightarrow a = 2{\text{ and }}d = 2$
Thus the general term can be found by using ${T_n} = a + \left( {n - 1} \right)d$. Putting values, we’ll get:
$
\Rightarrow {T_n} = 2 + \left( {n - 1} \right) \times 2 = 2 + 2n - 2 \\
\Rightarrow {T_n} = 2n
$
This is exactly what we have used in the above solution.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




